| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591620 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 6 Pages |
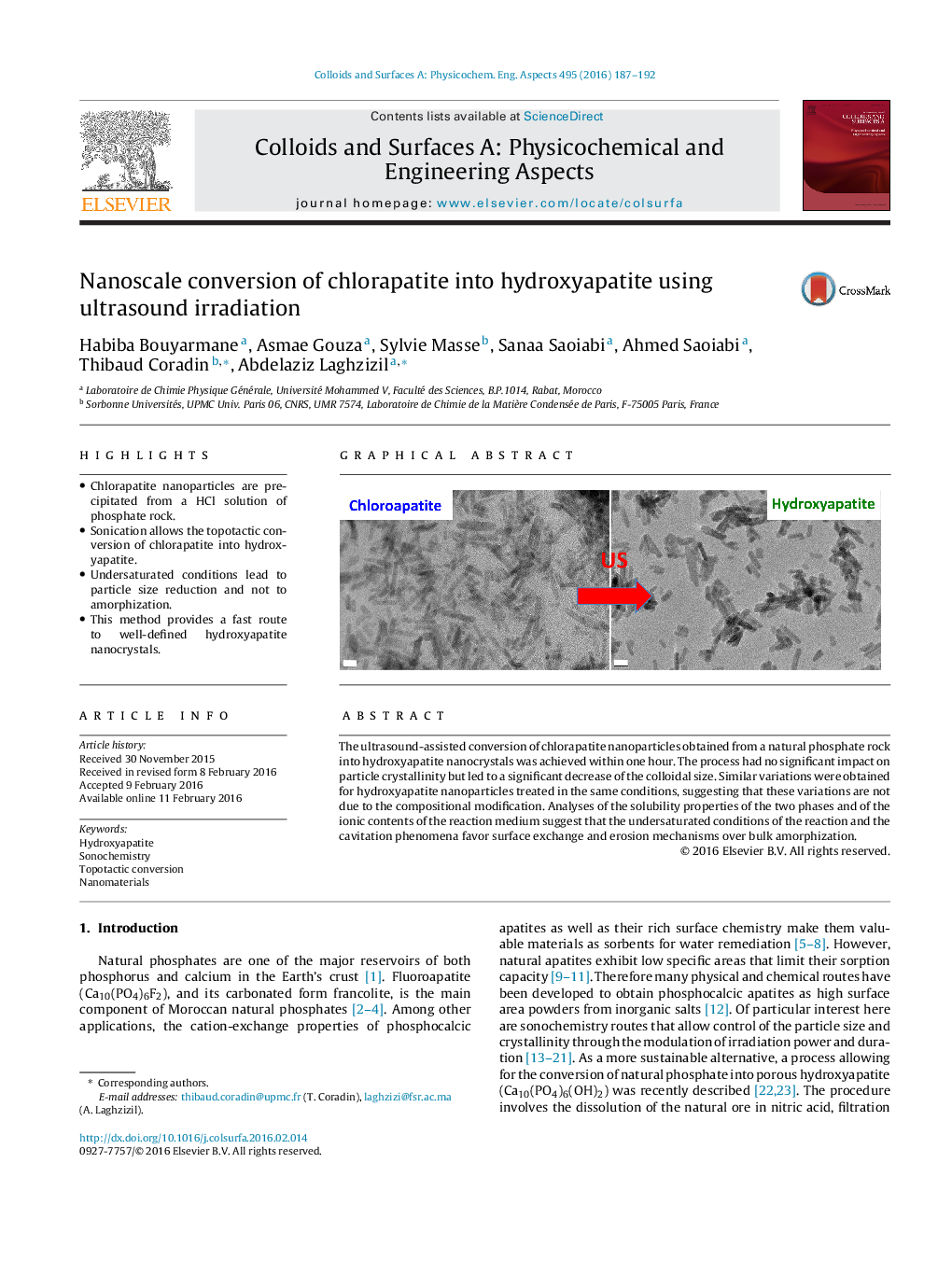
•Chlorapatite nanoparticles are precipitated from a HCl solution of phosphate rock.•Sonication allows the topotactic conversion of chlorapatite into hydroxyapatite.•Undersaturated conditions lead to particle size reduction and not to amorphization.•This method provides a fast route to well-defined hydroxyapatite nanocrystals.
The ultrasound-assisted conversion of chlorapatite nanoparticles obtained from a natural phosphate rock into hydroxyapatite nanocrystals was achieved within one hour. The process had no significant impact on particle crystallinity but led to a significant decrease of the colloidal size. Similar variations were obtained for hydroxyapatite nanoparticles treated in the same conditions, suggesting that these variations are not due to the compositional modification. Analyses of the solubility properties of the two phases and of the ionic contents of the reaction medium suggest that the undersaturated conditions of the reaction and the cavitation phenomena favor surface exchange and erosion mechanisms over bulk amorphization.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide