| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591664 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•Continuous flow microreactor based synthesis of Pd nanoparticles.•At optimum reaction conditions 5 nm Pd particles were obtained.•The electrochemical surface area (ECSA) of Pd nanoparticles was 2.6 cm2/mg.•Pd nanoparticles size decreases with an increase in concentration of precursor and reducing agent.•The average size of Pd nanoparticles increases with increase in flow rate.
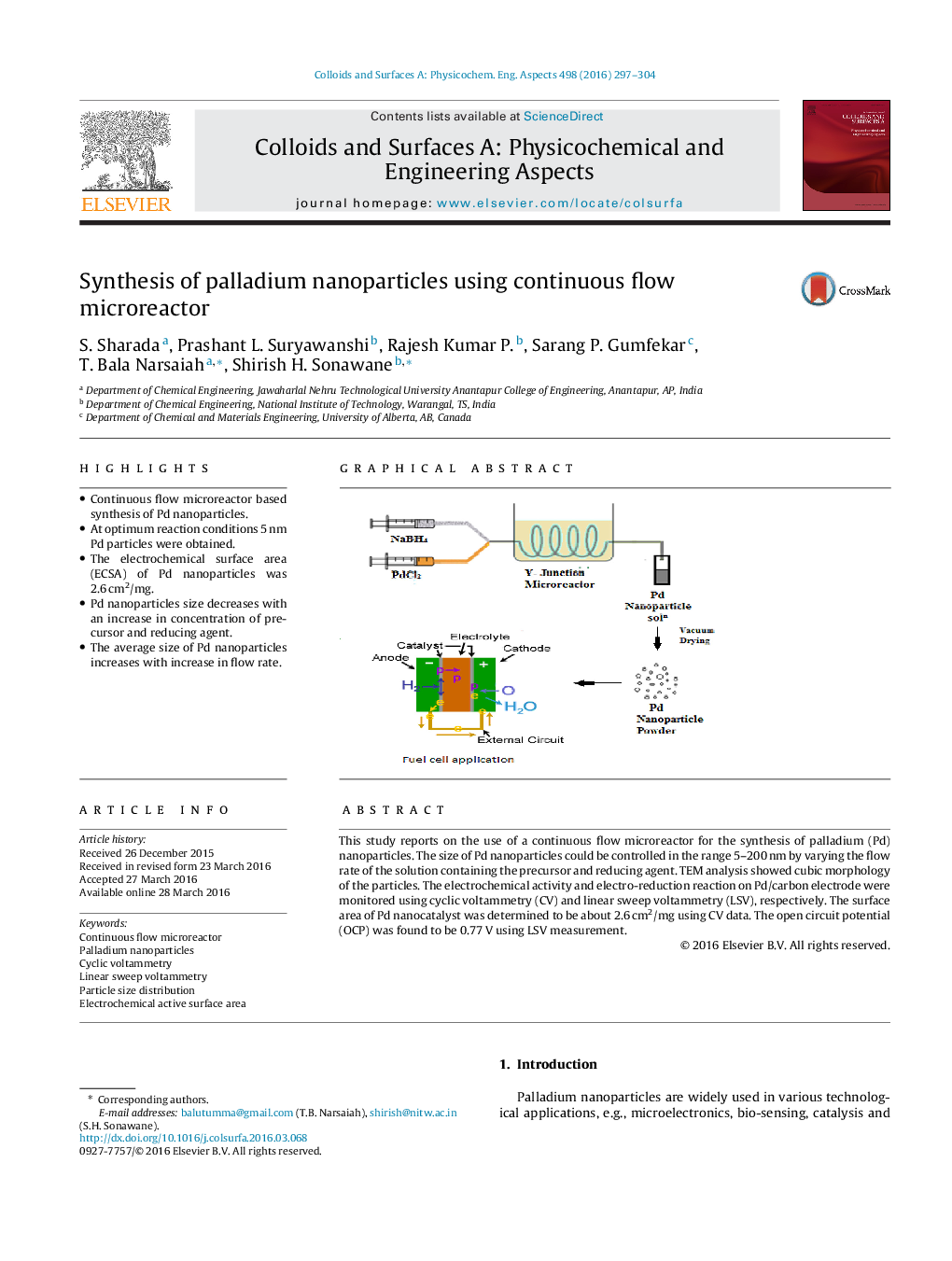
This study reports on the use of a continuous flow microreactor for the synthesis of palladium (Pd) nanoparticles. The size of Pd nanoparticles could be controlled in the range 5–200 nm by varying the flow rate of the solution containing the precursor and reducing agent. TEM analysis showed cubic morphology of the particles. The electrochemical activity and electro-reduction reaction on Pd/carbon electrode were monitored using cyclic voltammetry (CV) and linear sweep voltammetry (LSV), respectively. The surface area of Pd nanocatalyst was determined to be about 2.6 cm2/mg using CV data. The open circuit potential (OCP) was found to be 0.77 V using LSV measurement.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide