| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591760 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Nonionic PVA adsorption mechanism on MgxOy–SiO2 and ZnxOy–SiO2 was examined.•Spectrophotometry, microelectrophoresis and potentiometric titration were applied.•MgxOy (ZnxOy) content in mixed oxide structure affects adsorption properties of solid.•PVA shows the greater adsorption on MgxOy–SiO2 surface.•Polymer adsorption does not influence the solid surface charge density.
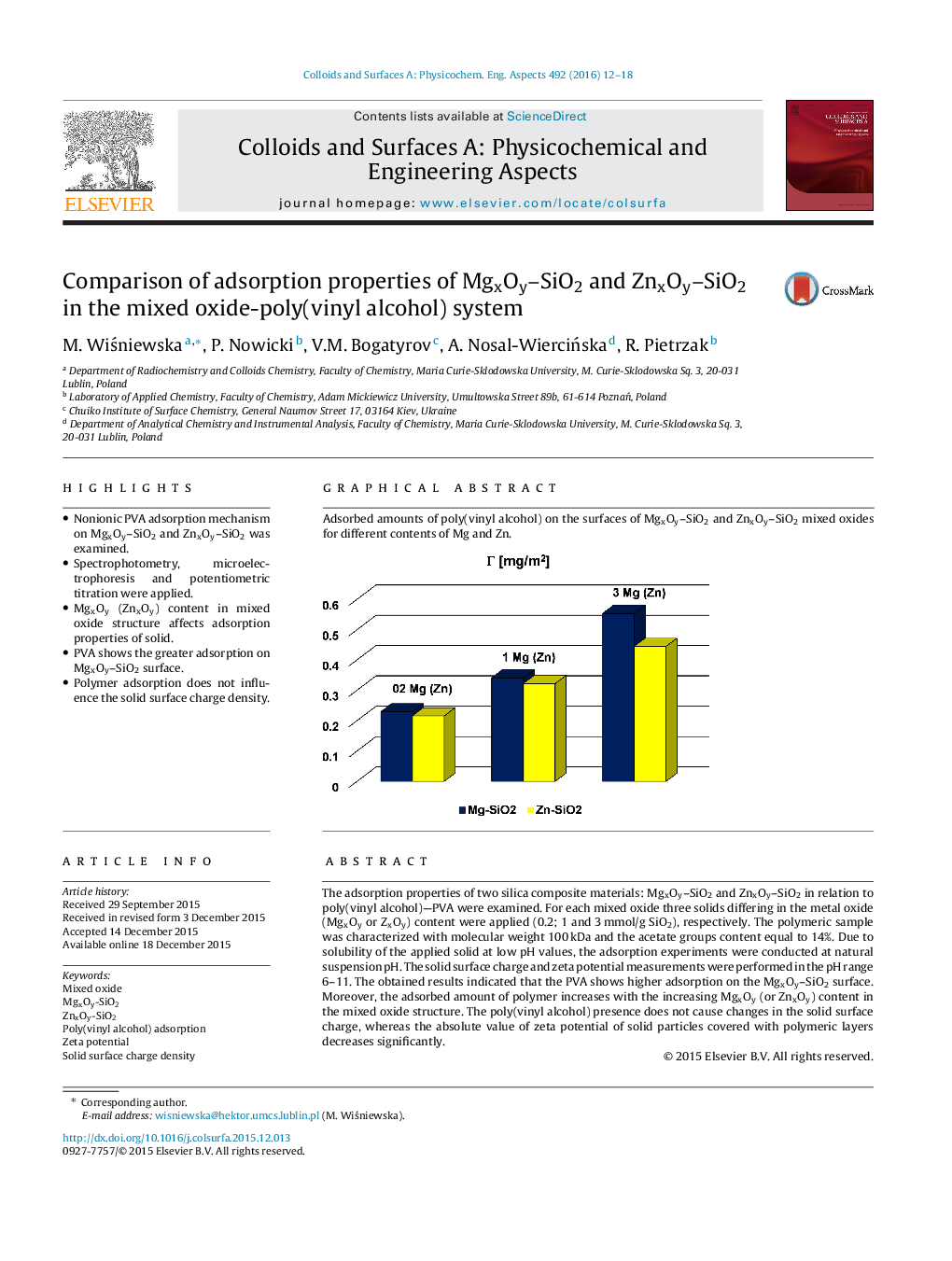
The adsorption properties of two silica composite materials: MgxOy–SiO2 and ZnxOy–SiO2 in relation to poly(vinyl alcohol)—PVA were examined. For each mixed oxide three solids differing in the metal oxide (MgxOy or ZxOy) content were applied (0.2; 1 and 3 mmol/g SiO2), respectively. The polymeric sample was characterized with molecular weight 100 kDa and the acetate groups content equal to 14%. Due to solubility of the applied solid at low pH values, the adsorption experiments were conducted at natural suspension pH. The solid surface charge and zeta potential measurements were performed in the pH range 6–11. The obtained results indicated that the PVA shows higher adsorption on the MgxOy–SiO2 surface. Moreover, the adsorbed amount of polymer increases with the increasing MgxOy (or ZnxOy) content in the mixed oxide structure. The poly(vinyl alcohol) presence does not cause changes in the solid surface charge, whereas the absolute value of zeta potential of solid particles covered with polymeric layers decreases significantly.
Graphical abstractAdsorbed amounts of poly(vinyl alcohol) on the surfaces of MgxOy–SiO2 and ZnxOy–SiO2 mixed oxides for different contents of Mg and Zn.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide