| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591798 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 8 Pages |
•We numerically investigated the demulsification phenomena of oil-in-water emulsions.•We used the coupled level set and volume-of-fluid (CLSVOF) method.•Coalescence of droplets captured on the membrane surface provides large droplets.•Oil droplets blocking the membrane pore is forced away by the permeating flow.
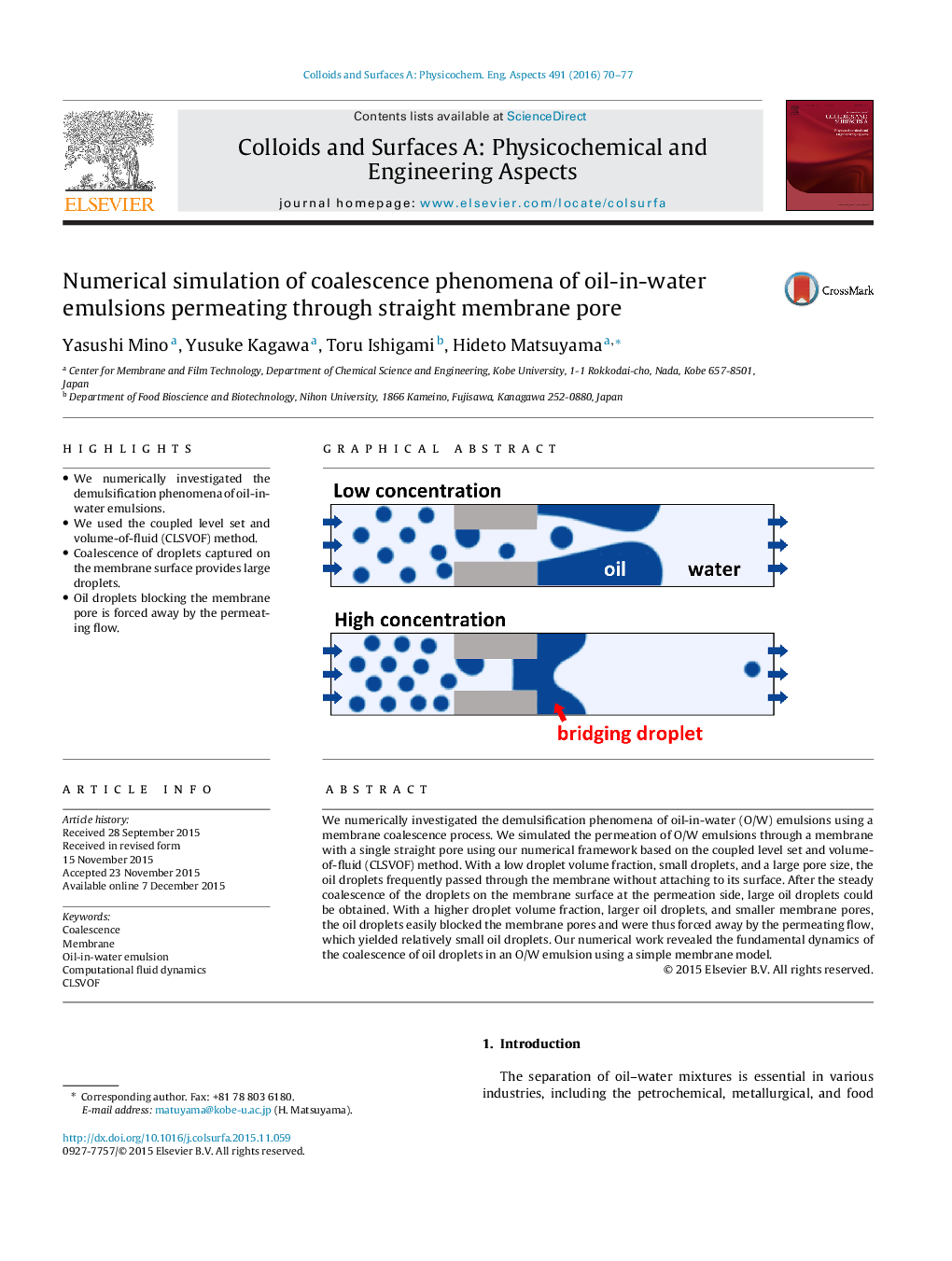
We numerically investigated the demulsification phenomena of oil-in-water (O/W) emulsions using a membrane coalescence process. We simulated the permeation of O/W emulsions through a membrane with a single straight pore using our numerical framework based on the coupled level set and volume-of-fluid (CLSVOF) method. With a low droplet volume fraction, small droplets, and a large pore size, the oil droplets frequently passed through the membrane without attaching to its surface. After the steady coalescence of the droplets on the membrane surface at the permeation side, large oil droplets could be obtained. With a higher droplet volume fraction, larger oil droplets, and smaller membrane pores, the oil droplets easily blocked the membrane pores and were thus forced away by the permeating flow, which yielded relatively small oil droplets. Our numerical work revealed the fundamental dynamics of the coalescence of oil droplets in an O/W emulsion using a simple membrane model.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide