| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591810 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
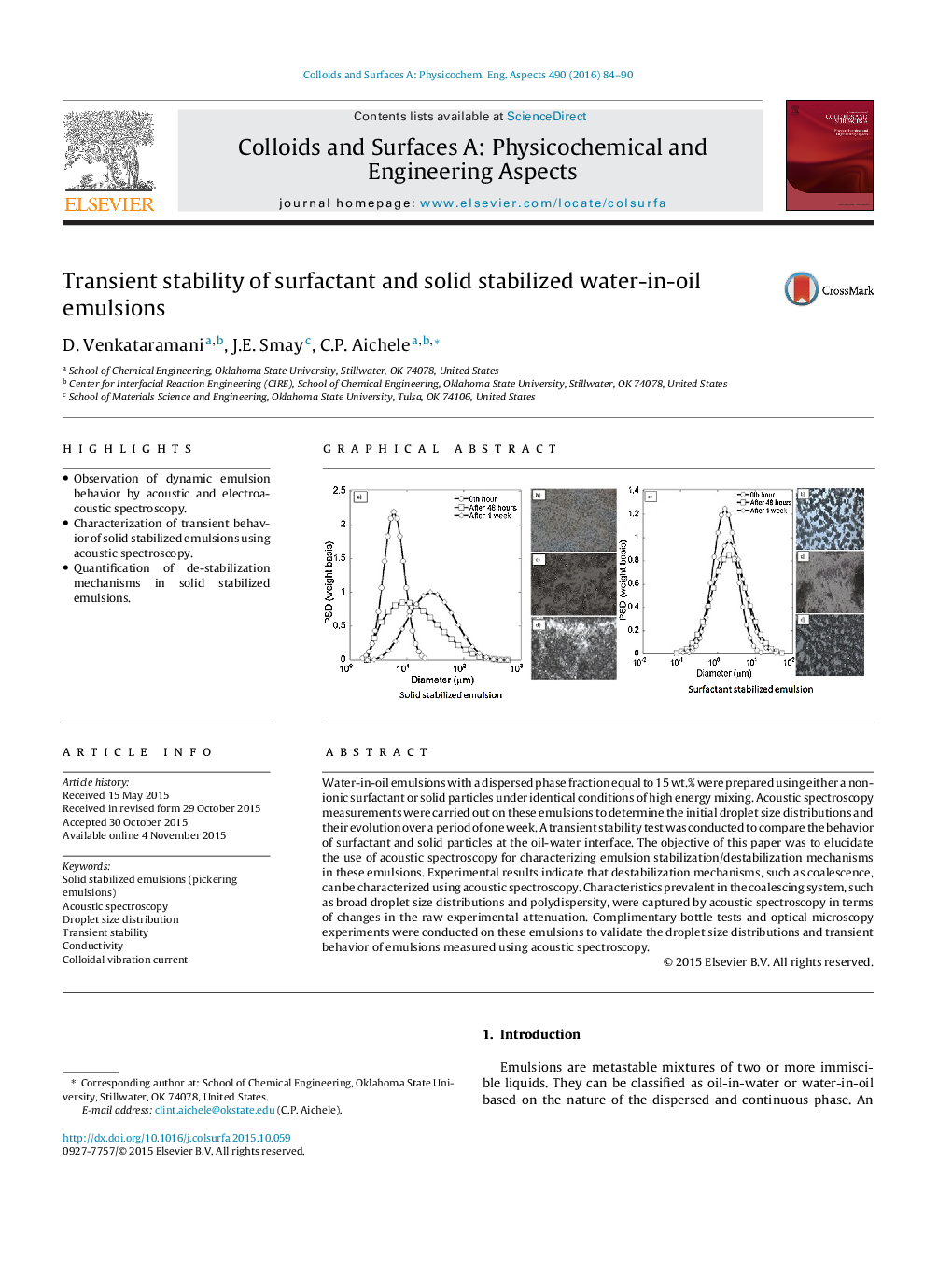
•Observation of dynamic emulsion behavior by acoustic and electroacoustic spectroscopy.•Characterization of transient behavior of solid stabilized emulsions using acoustic spectroscopy.•Quantification of de-stabilization mechanisms in solid stabilized emulsions.
Water-in-oil emulsions with a dispersed phase fraction equal to 15 wt.% were prepared using either a non-ionic surfactant or solid particles under identical conditions of high energy mixing. Acoustic spectroscopy measurements were carried out on these emulsions to determine the initial droplet size distributions and their evolution over a period of one week. A transient stability test was conducted to compare the behavior of surfactant and solid particles at the oil-water interface. The objective of this paper was to elucidate the use of acoustic spectroscopy for characterizing emulsion stabilization/destabilization mechanisms in these emulsions. Experimental results indicate that destabilization mechanisms, such as coalescence, can be characterized using acoustic spectroscopy. Characteristics prevalent in the coalescing system, such as broad droplet size distributions and polydispersity, were captured by acoustic spectroscopy in terms of changes in the raw experimental attenuation. Complimentary bottle tests and optical microscopy experiments were conducted on these emulsions to validate the droplet size distributions and transient behavior of emulsions measured using acoustic spectroscopy.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide