| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591825 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
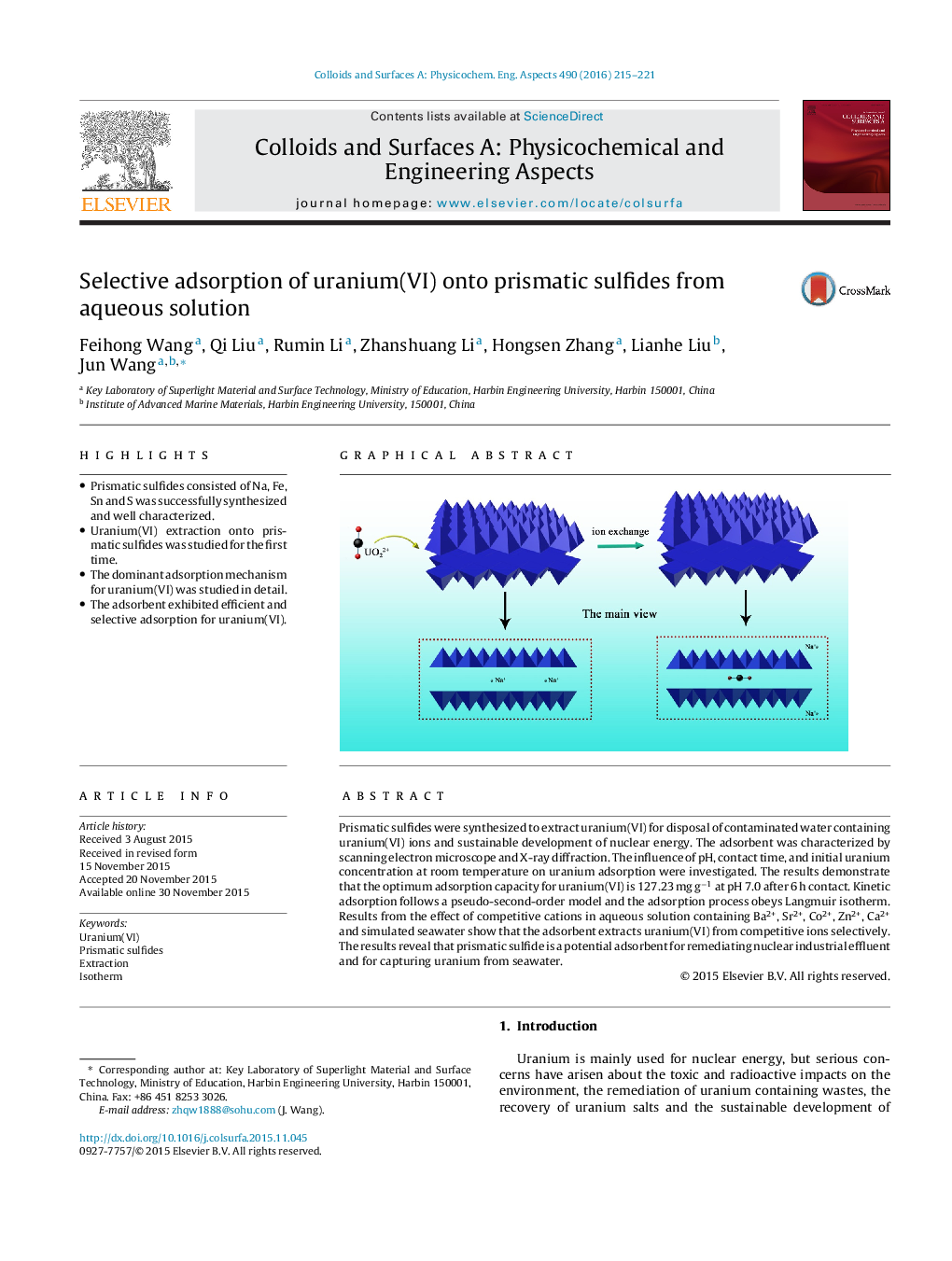
•Prismatic sulfides consisted of Na, Fe, Sn and S was successfully synthesized and well characterized.•Uranium(VI) extraction onto prismatic sulfides was studied for the first time.•The dominant adsorption mechanism for uranium(VI) was studied in detail.•The adsorbent exhibited efficient and selective adsorption for uranium(VI).
Prismatic sulfides were synthesized to extract uranium(VI) for disposal of contaminated water containing uranium(VI) ions and sustainable development of nuclear energy. The adsorbent was characterized by scanning electron microscope and X-ray diffraction. The influence of pH, contact time, and initial uranium concentration at room temperature on uranium adsorption were investigated. The results demonstrate that the optimum adsorption capacity for uranium(VI) is 127.23 mg g−1 at pH 7.0 after 6 h contact. Kinetic adsorption follows a pseudo-second-order model and the adsorption process obeys Langmuir isotherm. Results from the effect of competitive cations in aqueous solution containing Ba2+, Sr2+, Co2+, Zn2+, Ca2+ and simulated seawater show that the adsorbent extracts uranium(VI) from competitive ions selectively. The results reveal that prismatic sulfide is a potential adsorbent for remediating nuclear industrial effluent and for capturing uranium from seawater.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide