| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591834 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•Frequency-dependent dynamic moduli were monitored during aging.•Time—aging time—temperature superposition observed.•Non-equilibrium relaxation time spectra of aging clay suspension.•Rheological inverse from gel to glass as clay concentration increases.
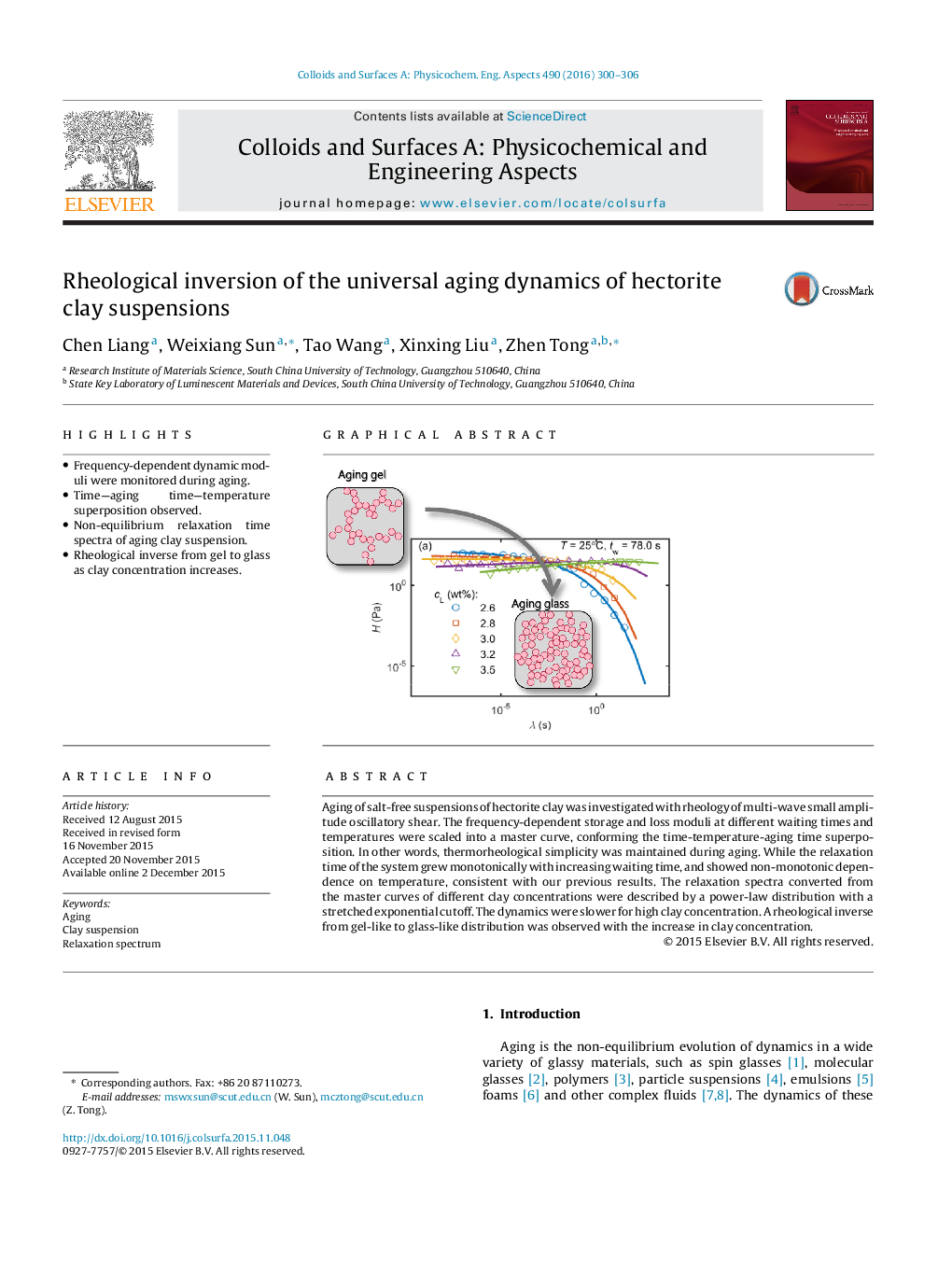
Aging of salt-free suspensions of hectorite clay was investigated with rheology of multi-wave small amplitude oscillatory shear. The frequency-dependent storage and loss moduli at different waiting times and temperatures were scaled into a master curve, conforming the time-temperature-aging time superposition. In other words, thermorheological simplicity was maintained during aging. While the relaxation time of the system grew monotonically with increasing waiting time, and showed non-monotonic dependence on temperature, consistent with our previous results. The relaxation spectra converted from the master curves of different clay concentrations were described by a power-law distribution with a stretched exponential cutoff. The dynamics were slower for high clay concentration. A rheological inverse from gel-like to glass-like distribution was observed with the increase in clay concentration.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide