| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 591908 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2016 | 16 Pages |
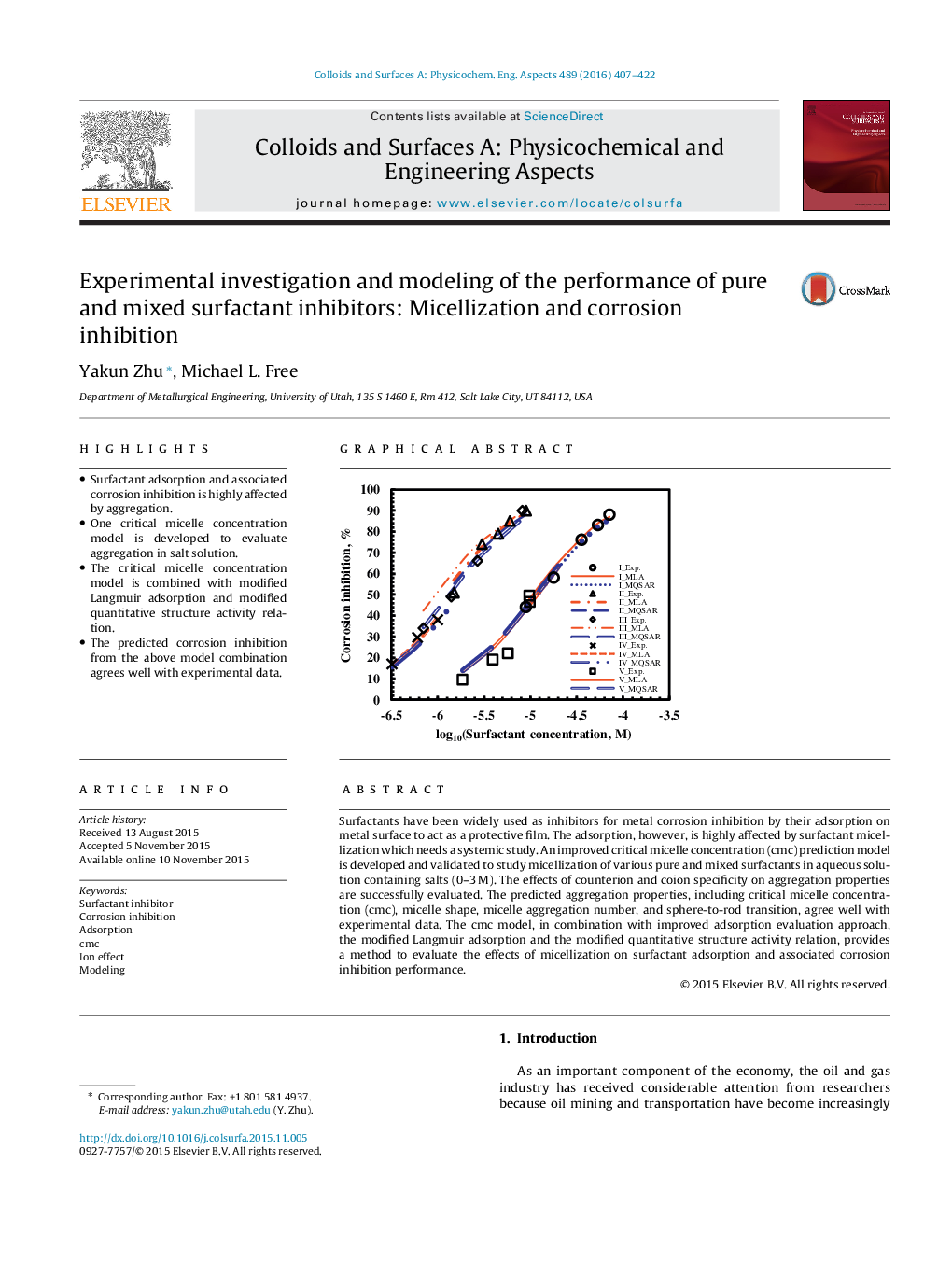
•Surfactant adsorption and associated corrosion inhibition is highly affected by aggregation.•One critical micelle concentration model is developed to evaluate aggregation in salt solution.•The critical micelle concentration model is combined with modified Langmuir adsorption and modified quantitative structure activity relation.•The predicted corrosion inhibition from the above model combination agrees well with experimental data.
Surfactants have been widely used as inhibitors for metal corrosion inhibition by their adsorption on metal surface to act as a protective film. The adsorption, however, is highly affected by surfactant micellization which needs a systemic study. An improved critical micelle concentration (cmc) prediction model is developed and validated to study micellization of various pure and mixed surfactants in aqueous solution containing salts (0–3 M). The effects of counterion and coion specificity on aggregation properties are successfully evaluated. The predicted aggregation properties, including critical micelle concentration (cmc), micelle shape, micelle aggregation number, and sphere-to-rod transition, agree well with experimental data. The cmc model, in combination with improved adsorption evaluation approach, the modified Langmuir adsorption and the modified quantitative structure activity relation, provides a method to evaluate the effects of micellization on surfactant adsorption and associated corrosion inhibition performance.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide