| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592057 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 7 Pages |
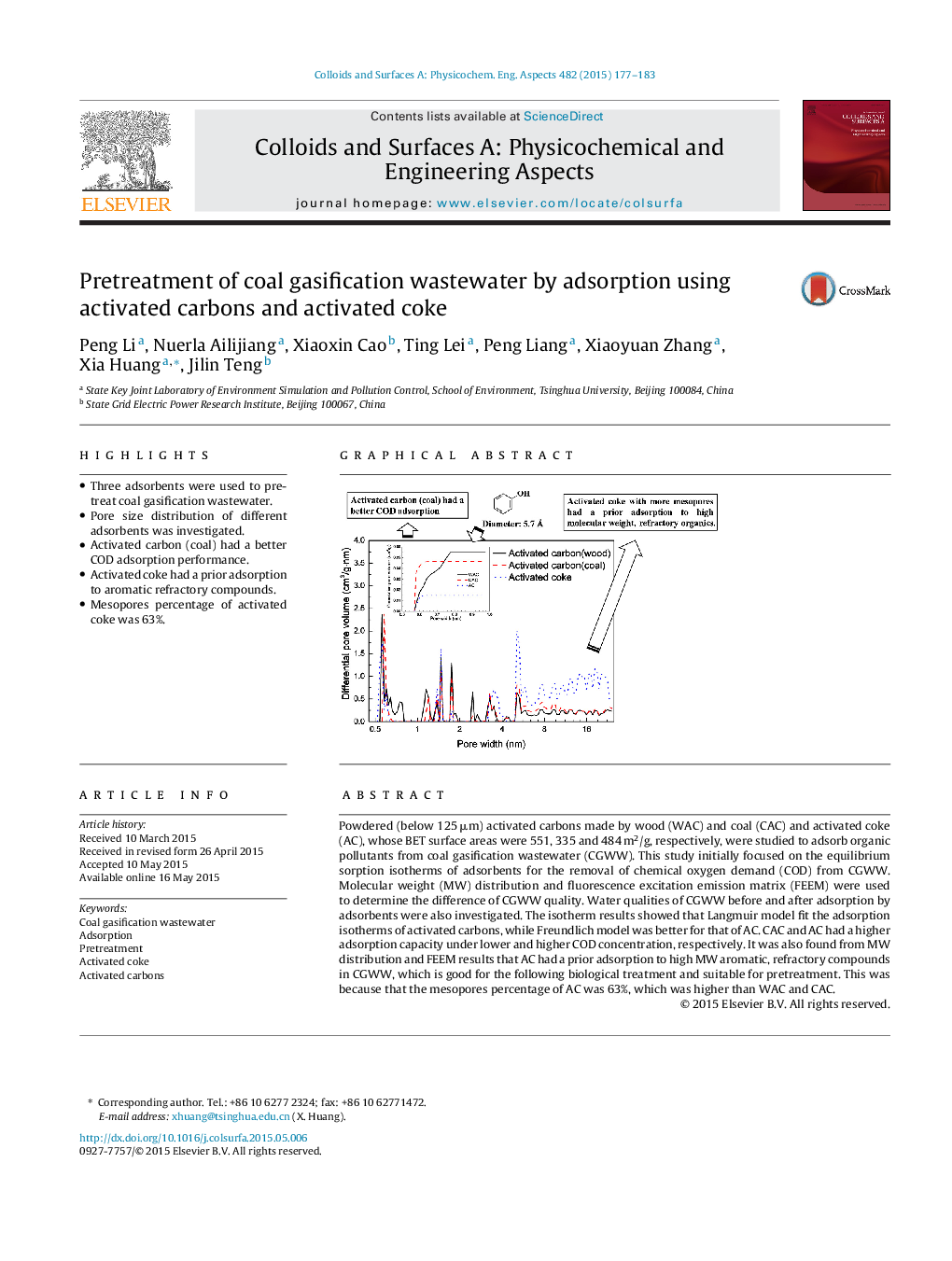
•Three adsorbents were used to pretreat coal gasification wastewater.•Pore size distribution of different adsorbents was investigated.•Activated carbon (coal) had a better COD adsorption performance.•Activated coke had a prior adsorption to aromatic refractory compounds.•Mesopores percentage of activated coke was 63%.
Powdered (below 125 μm) activated carbons made by wood (WAC) and coal (CAC) and activated coke (AC), whose BET surface areas were 551, 335 and 484 m2/g, respectively, were studied to adsorb organic pollutants from coal gasification wastewater (CGWW). This study initially focused on the equilibrium sorption isotherms of adsorbents for the removal of chemical oxygen demand (COD) from CGWW. Molecular weight (MW) distribution and fluorescence excitation emission matrix (FEEM) were used to determine the difference of CGWW quality. Water qualities of CGWW before and after adsorption by adsorbents were also investigated. The isotherm results showed that Langmuir model fit the adsorption isotherms of activated carbons, while Freundlich model was better for that of AC. CAC and AC had a higher adsorption capacity under lower and higher COD concentration, respectively. It was also found from MW distribution and FEEM results that AC had a prior adsorption to high MW aromatic, refractory compounds in CGWW, which is good for the following biological treatment and suitable for pretreatment. This was because that the mesopores percentage of AC was 63%, which was higher than WAC and CAC.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide