| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592061 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 9 Pages |
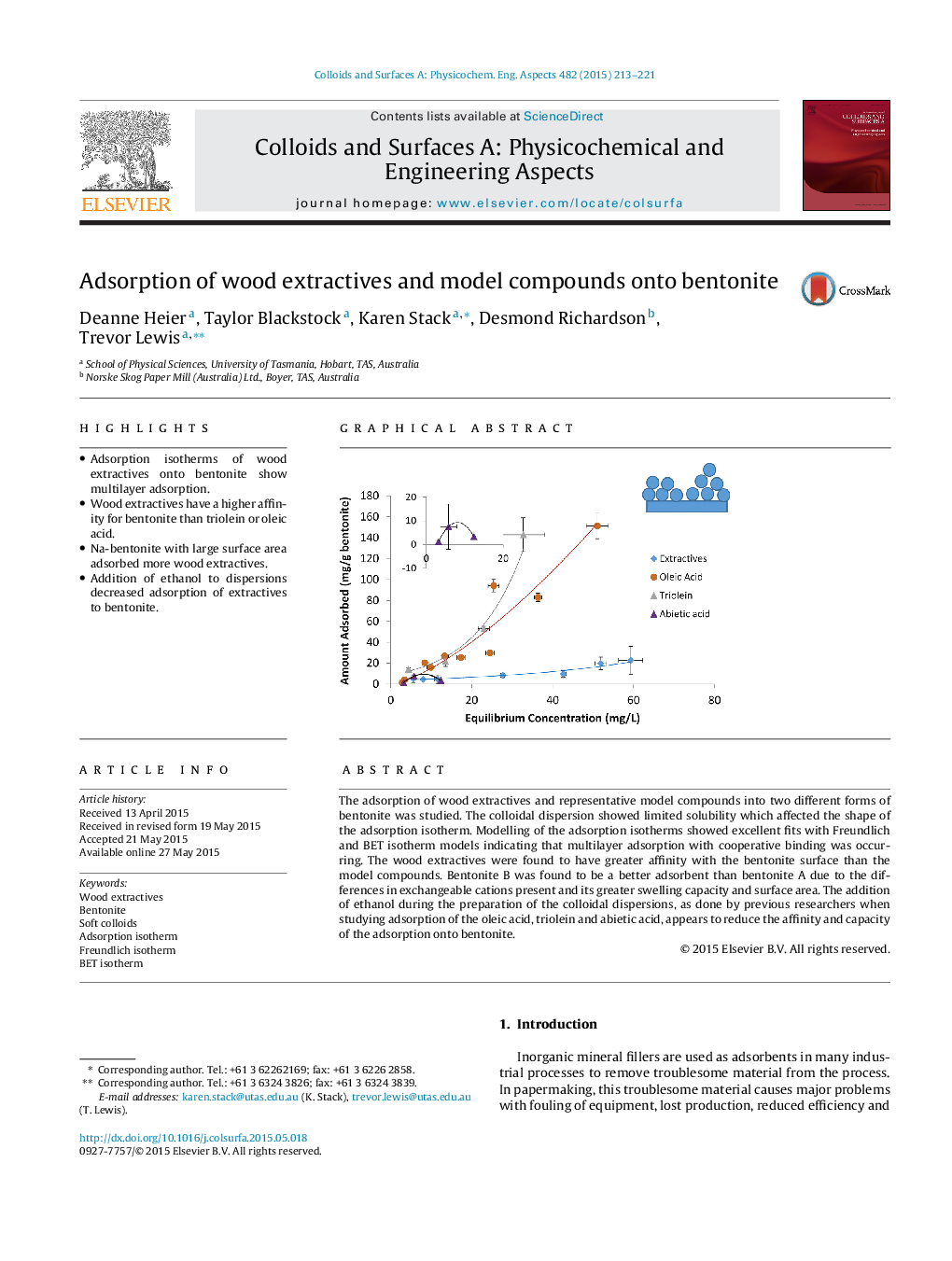
•Adsorption isotherms of wood extractives onto bentonite show multilayer adsorption.•Wood extractives have a higher affinity for bentonite than triolein or oleic acid.•Na-bentonite with large surface area adsorbed more wood extractives.•Addition of ethanol to dispersions decreased adsorption of extractives to bentonite.
The adsorption of wood extractives and representative model compounds into two different forms of bentonite was studied. The colloidal dispersion showed limited solubility which affected the shape of the adsorption isotherm. Modelling of the adsorption isotherms showed excellent fits with Freundlich and BET isotherm models indicating that multilayer adsorption with cooperative binding was occurring. The wood extractives were found to have greater affinity with the bentonite surface than the model compounds. Bentonite B was found to be a better adsorbent than bentonite A due to the differences in exchangeable cations present and its greater swelling capacity and surface area. The addition of ethanol during the preparation of the colloidal dispersions, as done by previous researchers when studying adsorption of the oleic acid, triolein and abietic acid, appears to reduce the affinity and capacity of the adsorption onto bentonite.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide