| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592189 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 10 Pages |
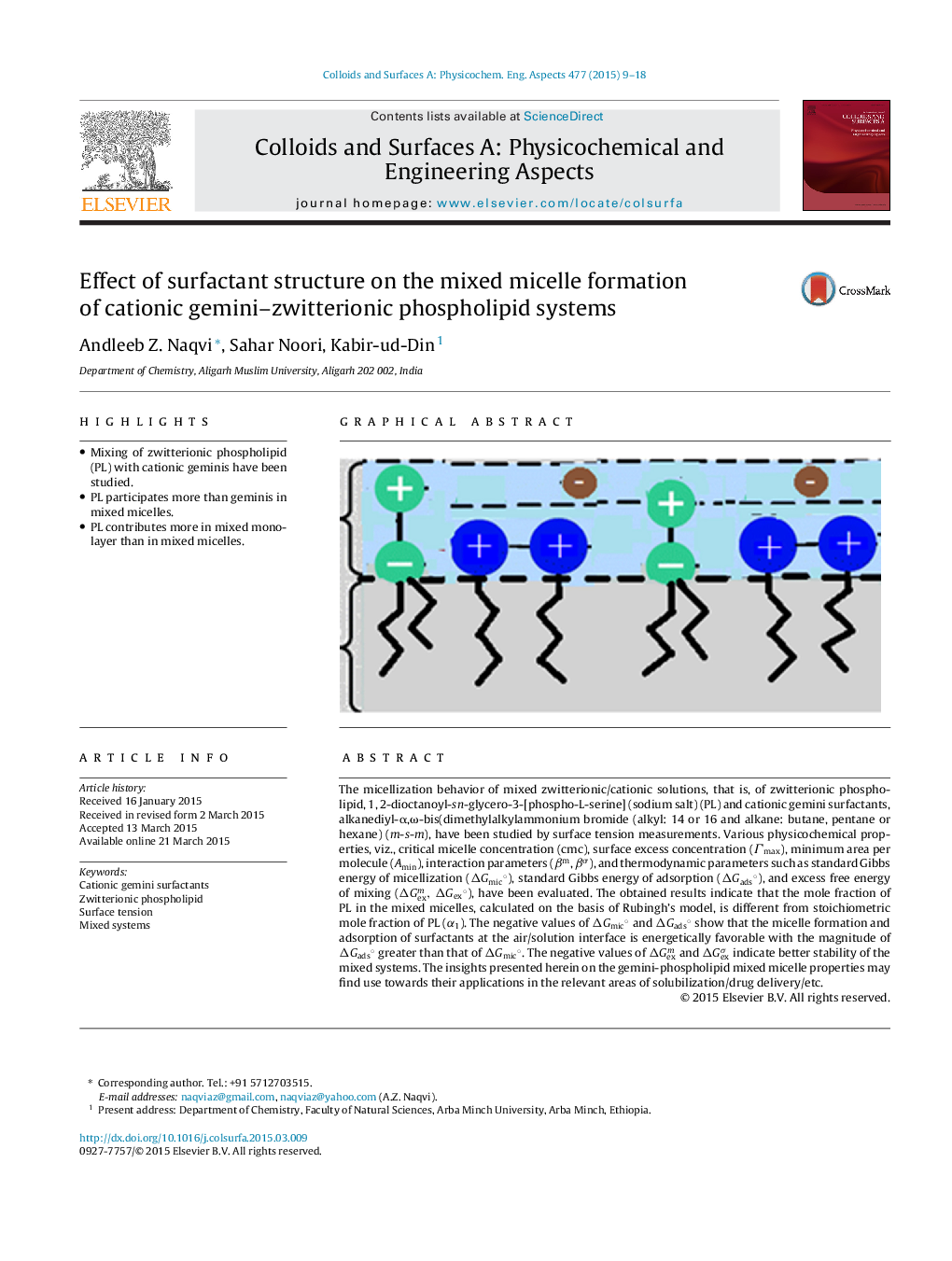
•Mixing of zwitterionic phospholipid (PL) with cationic geminis have been studied.•PL participates more than geminis in mixed micelles.•PL contributes more in mixed monolayer than in mixed micelles.
The micellization behavior of mixed zwitterionic/cationic solutions, that is, of zwitterionic phospholipid, 1, 2-dioctanoyl-sn-glycero-3-[phospho-L-serine] (sodium salt) (PL) and cationic gemini surfactants, alkanediyl-α,ω-bis(dimethylalkylammonium bromide (alkyl: 14 or 16 and alkane: butane, pentane or hexane) (m-s-m), have been studied by surface tension measurements. Various physicochemical properties, viz., critical micelle concentration (cmc), surface excess concentration (Γmax), minimum area per molecule (Amin), interaction parameters (βm, βσ), and thermodynamic parameters such as standard Gibbs energy of micellization (ΔGmic°ΔGmic°), standard Gibbs energy of adsorption (ΔGads°ΔGads°), and excess free energy of mixing (ΔGexm, ΔGex°), have been evaluated. The obtained results indicate that the mole fraction of PL in the mixed micelles, calculated on the basis of Rubingh's model, is different from stoichiometric mole fraction of PL (α1). The negative values of ΔGmic°ΔGmic° and ΔGads°ΔGads° show that the micelle formation and adsorption of surfactants at the air/solution interface is energetically favorable with the magnitude of ΔGads°ΔGads° greater than that of ΔGmic°ΔGmic°. The negative values of ΔGexm and ΔGexσ indicate better stability of the mixed systems. The insights presented herein on the gemini-phospholipid mixed micelle properties may find use towards their applications in the relevant areas of solubilization/drug delivery/etc.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide