| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592219 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•There was no report to investigate the photocatalytic activities of CoFe2O4/g-C3N4.•The CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composites are magnetic and stable.•Combination of CoFe2O4 and g-C3N4 could enhance the activity of activating H2O2.•The possible photocatalytic mechanism was discussed in detail.
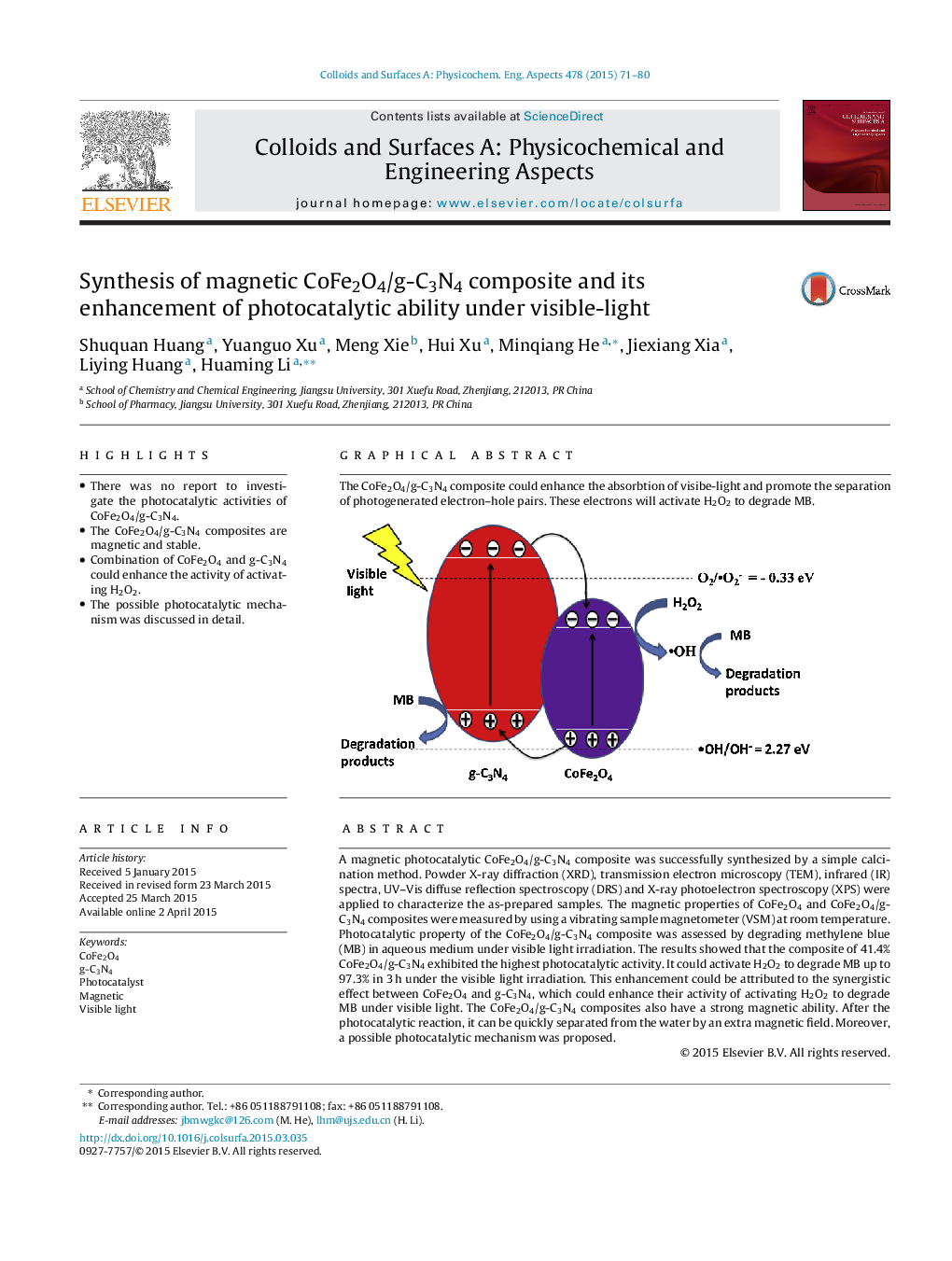
A magnetic photocatalytic CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composite was successfully synthesized by a simple calcination method. Powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), infrared (IR) spectra, UV–Vis diffuse reflection spectroscopy (DRS) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) were applied to characterize the as-prepared samples. The magnetic properties of CoFe2O4 and CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composites were measured by using a vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature. Photocatalytic property of the CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composite was assessed by degrading methylene blue (MB) in aqueous medium under visible light irradiation. The results showed that the composite of 41.4% CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity. It could activate H2O2 to degrade MB up to 97.3% in 3 h under the visible light irradiation. This enhancement could be attributed to the synergistic effect between CoFe2O4 and g-C3N4, which could enhance their activity of activating H2O2 to degrade MB under visible light. The CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composites also have a strong magnetic ability. After the photocatalytic reaction, it can be quickly separated from the water by an extra magnetic field. Moreover, a possible photocatalytic mechanism was proposed.
Graphical abstractThe CoFe2O4/g-C3N4 composite could enhance the absorbtion of visibe-light and promote the separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs. These electrons will activate H2O2 to degrade MB.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide