| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592253 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 10 Pages |
•A novel conversion process for the utilization of EMR was first proposed.•Effect of Si/Al ratio on the EMRZ synthesis was investigated.•EMRZ showed good adsorption properties for removal of Mn2+ and Ni2+ ions.•The adsorption mechanism and kinetics were systematically studied.•Ion exchange was responsible for metal ions removal.
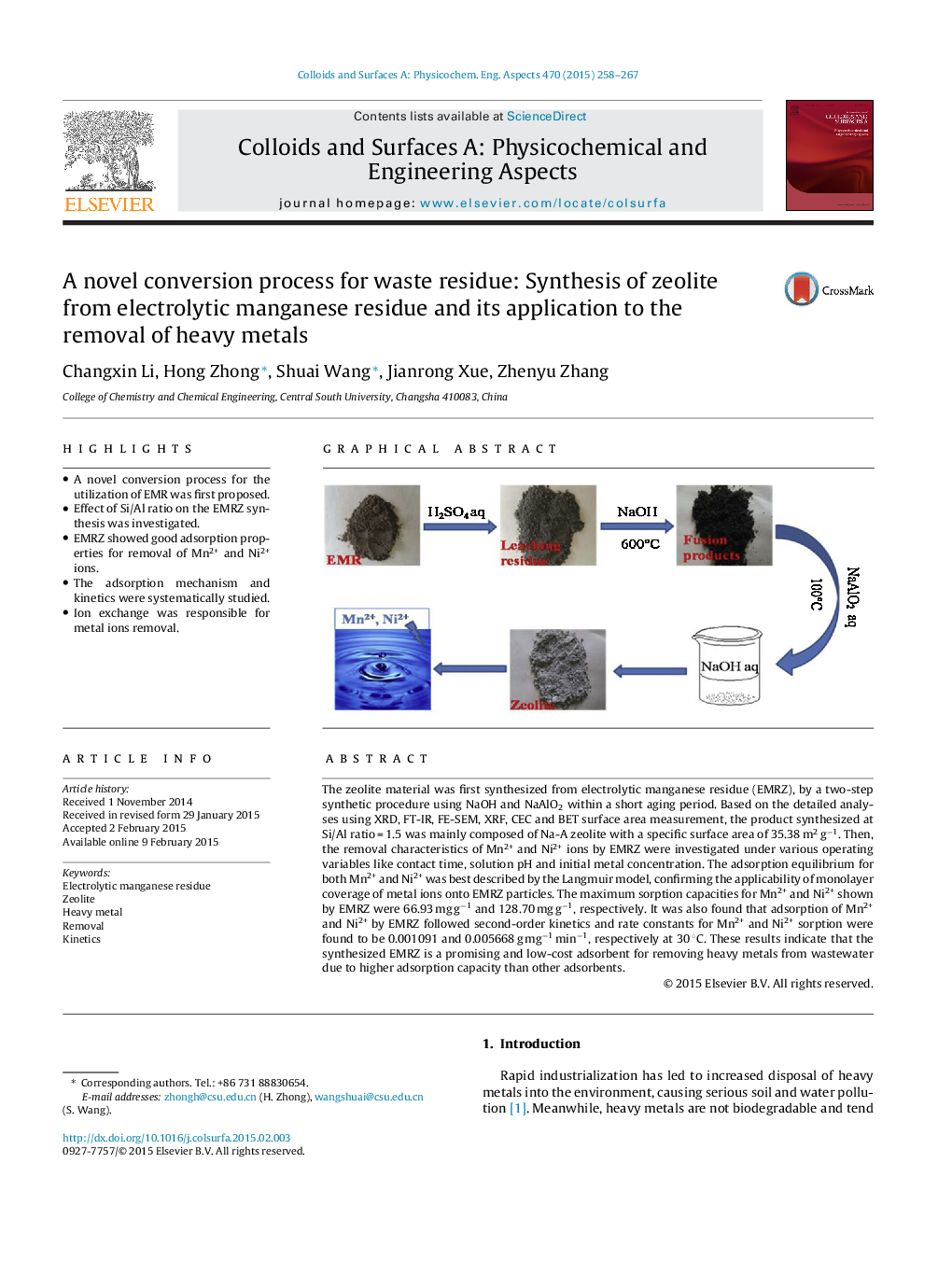
The zeolite material was first synthesized from electrolytic manganese residue (EMRZ), by a two-step synthetic procedure using NaOH and NaAlO2 within a short aging period. Based on the detailed analyses using XRD, FT-IR, FE-SEM, XRF, CEC and BET surface area measurement, the product synthesized at Si/Al ratio = 1.5 was mainly composed of Na-A zeolite with a specific surface area of 35.38 m2 g−1. Then, the removal characteristics of Mn2+ and Ni2+ ions by EMRZ were investigated under various operating variables like contact time, solution pH and initial metal concentration. The adsorption equilibrium for both Mn2+ and Ni2+ was best described by the Langmuir model, confirming the applicability of monolayer coverage of metal ions onto EMRZ particles. The maximum sorption capacities for Mn2+ and Ni2+ shown by EMRZ were 66.93 mg g−1 and 128.70 mg g−1, respectively. It was also found that adsorption of Mn2+ and Ni2+ by EMRZ followed second-order kinetics and rate constants for Mn2+ and Ni2+ sorption were found to be 0.001091 and 0.005668 g mg−1 min−1, respectively at 30 °C. These results indicate that the synthesized EMRZ is a promising and low-cost adsorbent for removing heavy metals from wastewater due to higher adsorption capacity than other adsorbents.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide