| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592266 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 11 Pages |
•The aim was to sytnhesized novel copolymer hydrogels based on two acidic monomers.•These hydrogels were investigated as sorbents for cationic dyes removal.•Sorption capability is significantly improved compared to pure component hydrogels.•Synthesized copolymer hydrogels adsorbed better dyes in binary systems.
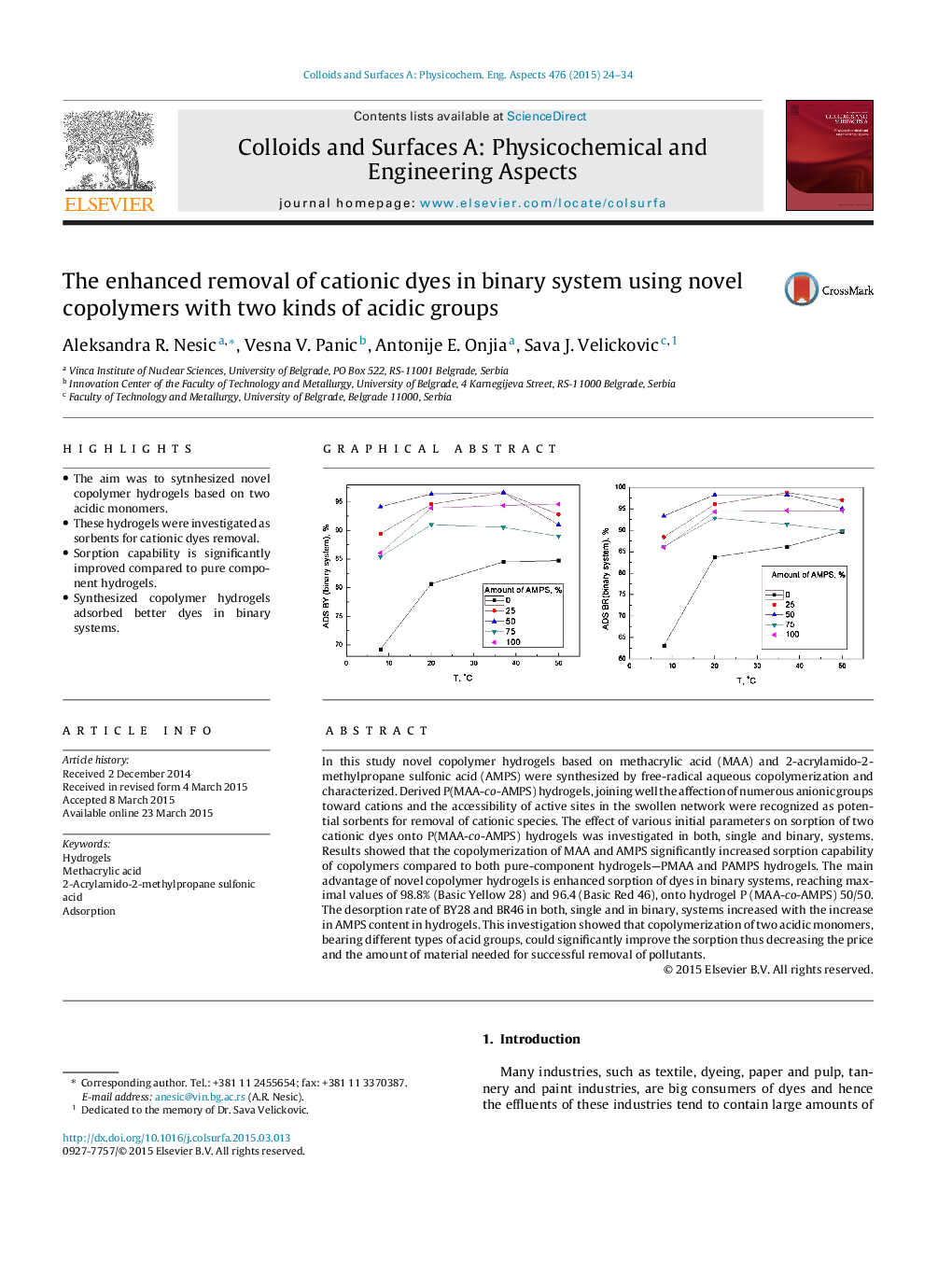
In this study novel copolymer hydrogels based on methacrylic acid (MAA) and 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (AMPS) were synthesized by free-radical aqueous copolymerization and characterized. Derived P(MAA-co-AMPS) hydrogels, joining well the affection of numerous anionic groups toward cations and the accessibility of active sites in the swollen network were recognized as potential sorbents for removal of cationic species. The effect of various initial parameters on sorption of two cationic dyes onto P(MAA-co-AMPS) hydrogels was investigated in both, single and binary, systems. Results showed that the copolymerization of MAA and AMPS significantly increased sorption capability of copolymers compared to both pure-component hydrogels—PMAA and PAMPS hydrogels. The main advantage of novel copolymer hydrogels is enhanced sorption of dyes in binary systems, reaching maximal values of 98.8% (Basic Yellow 28) and 96.4 (Basic Red 46), onto hydrogel P (MAA-co-AMPS) 50/50. The desorption rate of BY28 and BR46 in both, single and in binary, systems increased with the increase in AMPS content in hydrogels. This investigation showed that copolymerization of two acidic monomers, bearing different types of acid groups, could significantly improve the sorption thus decreasing the price and the amount of material needed for successful removal of pollutants.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide