| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592349 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 7 Pages |
•Rate of flocculation in the mixing flow by charge neutralization was analyzed.•Highest rate was observed at the lowest ionic strength.•The scenario from non-equilibrium adsorption to patch wise attraction was confirmed.
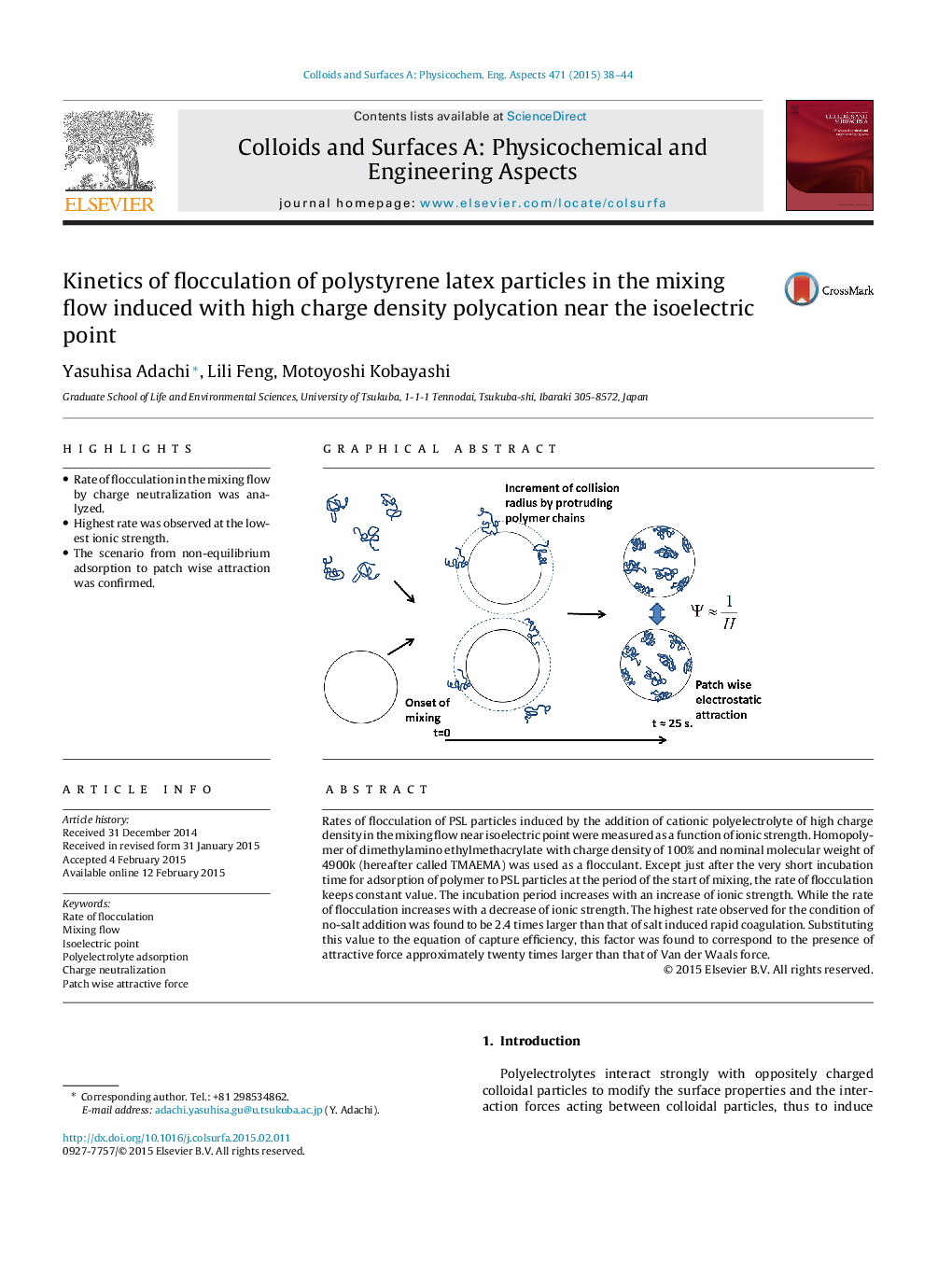
Rates of flocculation of PSL particles induced by the addition of cationic polyelectrolyte of high charge density in the mixing flow near isoelectric point were measured as a function of ionic strength. Homopolymer of dimethylamino ethylmethacrylate with charge density of 100% and nominal molecular weight of 4900k (hereafter called TMAEMA) was used as a flocculant. Except just after the very short incubation time for adsorption of polymer to PSL particles at the period of the start of mixing, the rate of flocculation keeps constant value. The incubation period increases with an increase of ionic strength. While the rate of flocculation increases with a decrease of ionic strength. The highest rate observed for the condition of no-salt addition was found to be 2.4 times larger than that of salt induced rapid coagulation. Substituting this value to the equation of capture efficiency, this factor was found to correspond to the presence of attractive force approximately twenty times larger than that of Van der Waals force.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide