| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592429 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 6 Pages |
•Mesoporous TiO2/SBA-15 nanocomposites were synthesized using hydrothermal method.•In-situ method was used to encapsulate TiO2 nanoparticles in channels of SBA-15.•TiO2 nanoparticles were found in crystalline anatase form in SBA-15 matrix.•Effect of TiO2 concentration on the framework shrinkage of SBA-15 was studied.
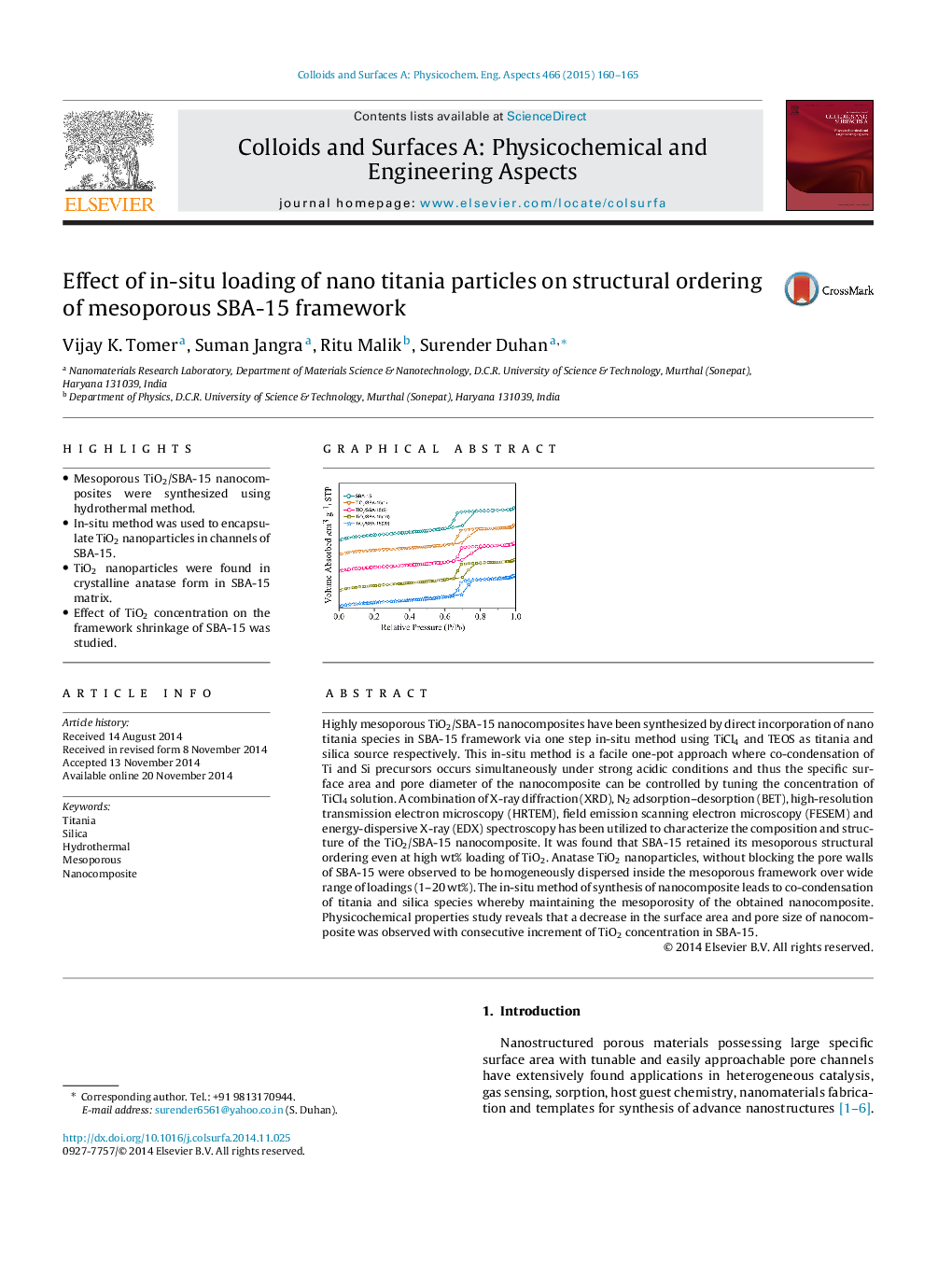
Highly mesoporous TiO2/SBA-15 nanocomposites have been synthesized by direct incorporation of nano titania species in SBA-15 framework via one step in-situ method using TiCl4 and TEOS as titania and silica source respectively. This in-situ method is a facile one-pot approach where co-condensation of Ti and Si precursors occurs simultaneously under strong acidic conditions and thus the specific surface area and pore diameter of the nanocomposite can be controlled by tuning the concentration of TiCl4 solution. A combination of X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption–desorption (BET), high-resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy has been utilized to characterize the composition and structure of the TiO2/SBA-15 nanocomposite. It was found that SBA-15 retained its mesoporous structural ordering even at high wt% loading of TiO2. Anatase TiO2 nanoparticles, without blocking the pore walls of SBA-15 were observed to be homogeneously dispersed inside the mesoporous framework over wide range of loadings (1–20 wt%). The in-situ method of synthesis of nanocomposite leads to co-condensation of titania and silica species whereby maintaining the mesoporosity of the obtained nanocomposite. Physicochemical properties study reveals that a decrease in the surface area and pore size of nanocomposite was observed with consecutive increment of TiO2 concentration in SBA-15.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide