| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592442 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2015 | 7 Pages |
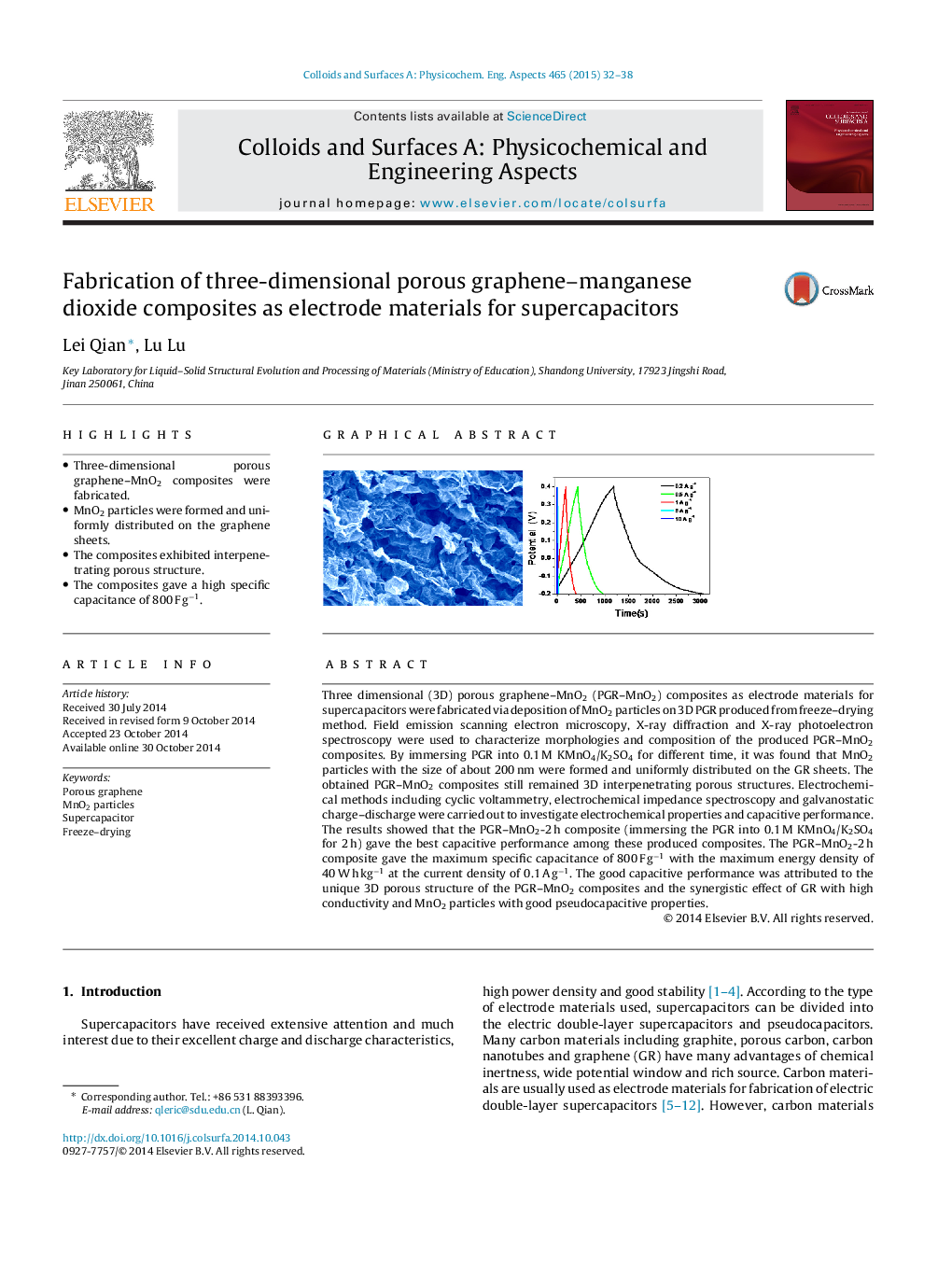
•Three-dimensional porous graphene–MnO2 composites were fabricated.•MnO2 particles were formed and uniformly distributed on the graphene sheets.•The composites exhibited interpenetrating porous structure.•The composites gave a high specific capacitance of 800 F g−1.
Three dimensional (3D) porous graphene–MnO2 (PGR–MnO2) composites as electrode materials for supercapacitors were fabricated via deposition of MnO2 particles on 3D PGR produced from freeze–drying method. Field emission scanning electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy were used to characterize morphologies and composition of the produced PGR–MnO2 composites. By immersing PGR into 0.1 M KMnO4/K2SO4 for different time, it was found that MnO2 particles with the size of about 200 nm were formed and uniformly distributed on the GR sheets. The obtained PGR–MnO2 composites still remained 3D interpenetrating porous structures. Electrochemical methods including cyclic voltammetry, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and galvanostatic charge–discharge were carried out to investigate electrochemical properties and capacitive performance. The results showed that the PGR–MnO2-2 h composite (immersing the PGR into 0.1 M KMnO4/K2SO4 for 2 h) gave the best capacitive performance among these produced composites. The PGR–MnO2-2 h composite gave the maximum specific capacitance of 800 F g−1 with the maximum energy density of 40 W h kg−1 at the current density of 0.1 A g−1. The good capacitive performance was attributed to the unique 3D porous structure of the PGR–MnO2 composites and the synergistic effect of GR with high conductivity and MnO2 particles with good pseudocapacitive properties.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide