| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592606 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2014 | 6 Pages |
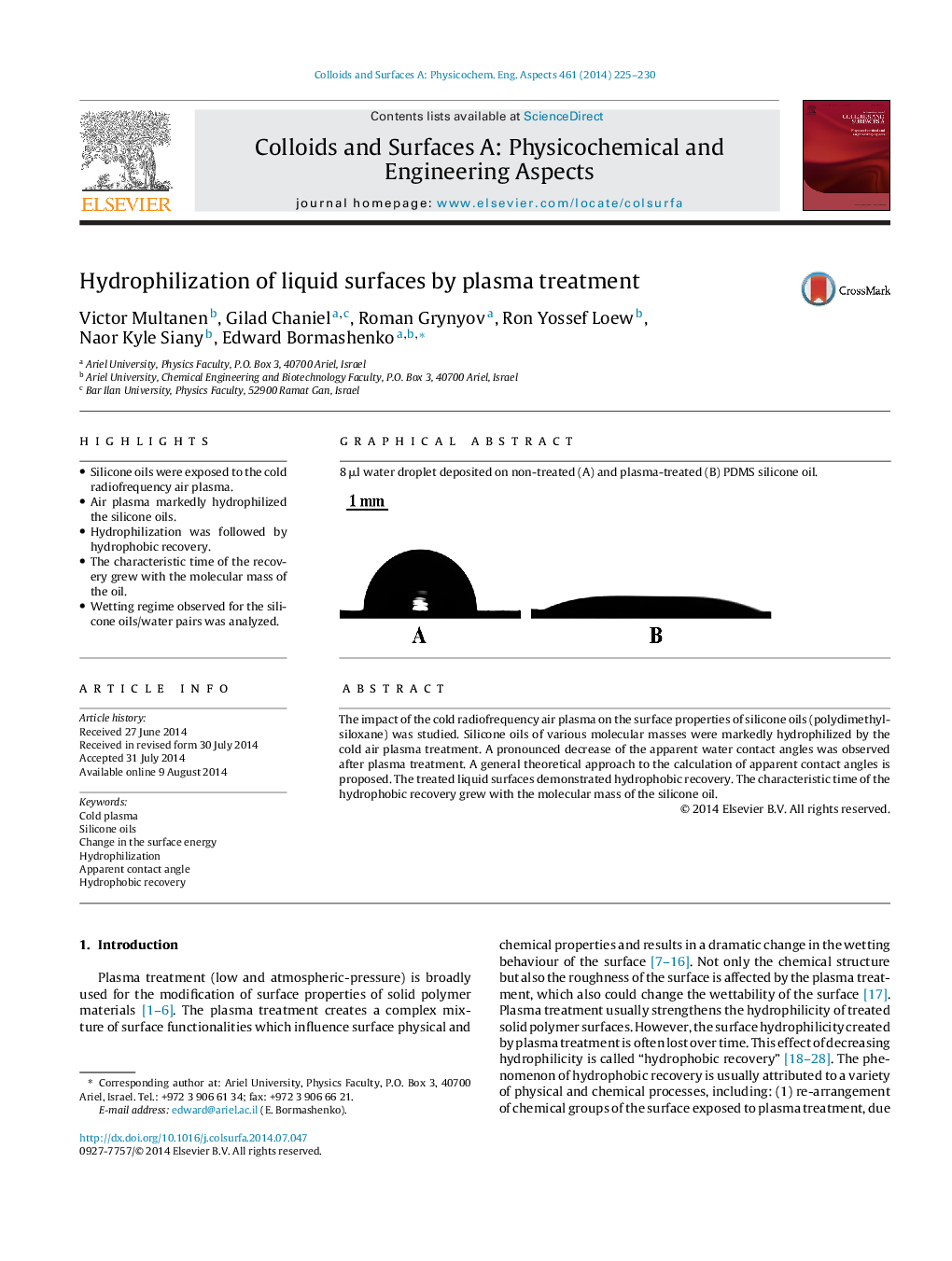
•Silicone oils were exposed to the cold radiofrequency air plasma.•Air plasma markedly hydrophilized the silicone oils.•Hydrophilization was followed by hydrophobic recovery.•The characteristic time of the recovery grew with the molecular mass of the oil.•Wetting regime observed for the silicone oils/water pairs was analyzed.
The impact of the cold radiofrequency air plasma on the surface properties of silicone oils (polydimethylsiloxane) was studied. Silicone oils of various molecular masses were markedly hydrophilized by the cold air plasma treatment. A pronounced decrease of the apparent water contact angles was observed after plasma treatment. A general theoretical approach to the calculation of apparent contact angles is proposed. The treated liquid surfaces demonstrated hydrophobic recovery. The characteristic time of the hydrophobic recovery grew with the molecular mass of the silicone oil.
Graphical abstract8 μl water droplet deposited on non-treated (A) and plasma-treated (B) PDMS silicone oil.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide