| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592630 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2014 | 8 Pages |
•Carbon nanotube (CNT) surface was modified by admicellar polymerization with polyacrylonitrile (PAN) film coating.•Zeta potential, FT-IR, FT-Raman, TGA, DSC, TEM, and SEM were used for characterization.•The good dispersion of PAN-coated CNT in PAN matrix enhanced the mechanical strength of its composites.
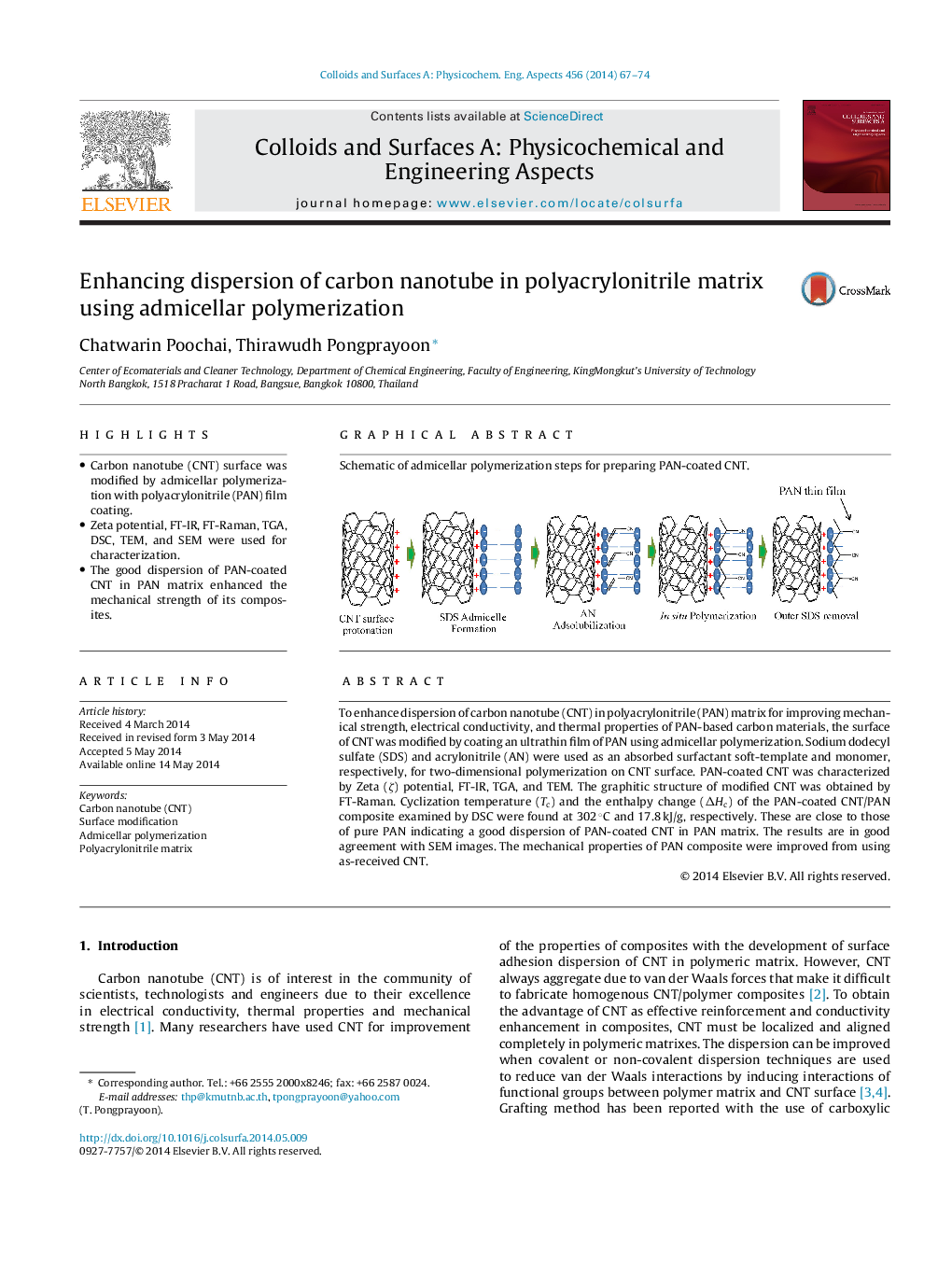
To enhance dispersion of carbon nanotube (CNT) in polyacrylonitrile (PAN) matrix for improving mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and thermal properties of PAN-based carbon materials, the surface of CNT was modified by coating an ultrathin film of PAN using admicellar polymerization. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and acrylonitrile (AN) were used as an absorbed surfactant soft-template and monomer, respectively, for two-dimensional polymerization on CNT surface. PAN-coated CNT was characterized by Zeta (ζ) potential, FT-IR, TGA, and TEM. The graphitic structure of modified CNT was obtained by FT-Raman. Cyclization temperature (Tc) and the enthalpy change (ΔHc) of the PAN-coated CNT/PAN composite examined by DSC were found at 302 °C and 17.8 kJ/g, respectively. These are close to those of pure PAN indicating a good dispersion of PAN-coated CNT in PAN matrix. The results are in good agreement with SEM images. The mechanical properties of PAN composite were improved from using as-received CNT.
Graphical abstractSchematic of admicellar polymerization steps for preparing PAN-coated CNT.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide