| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592633 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2014 | 8 Pages |
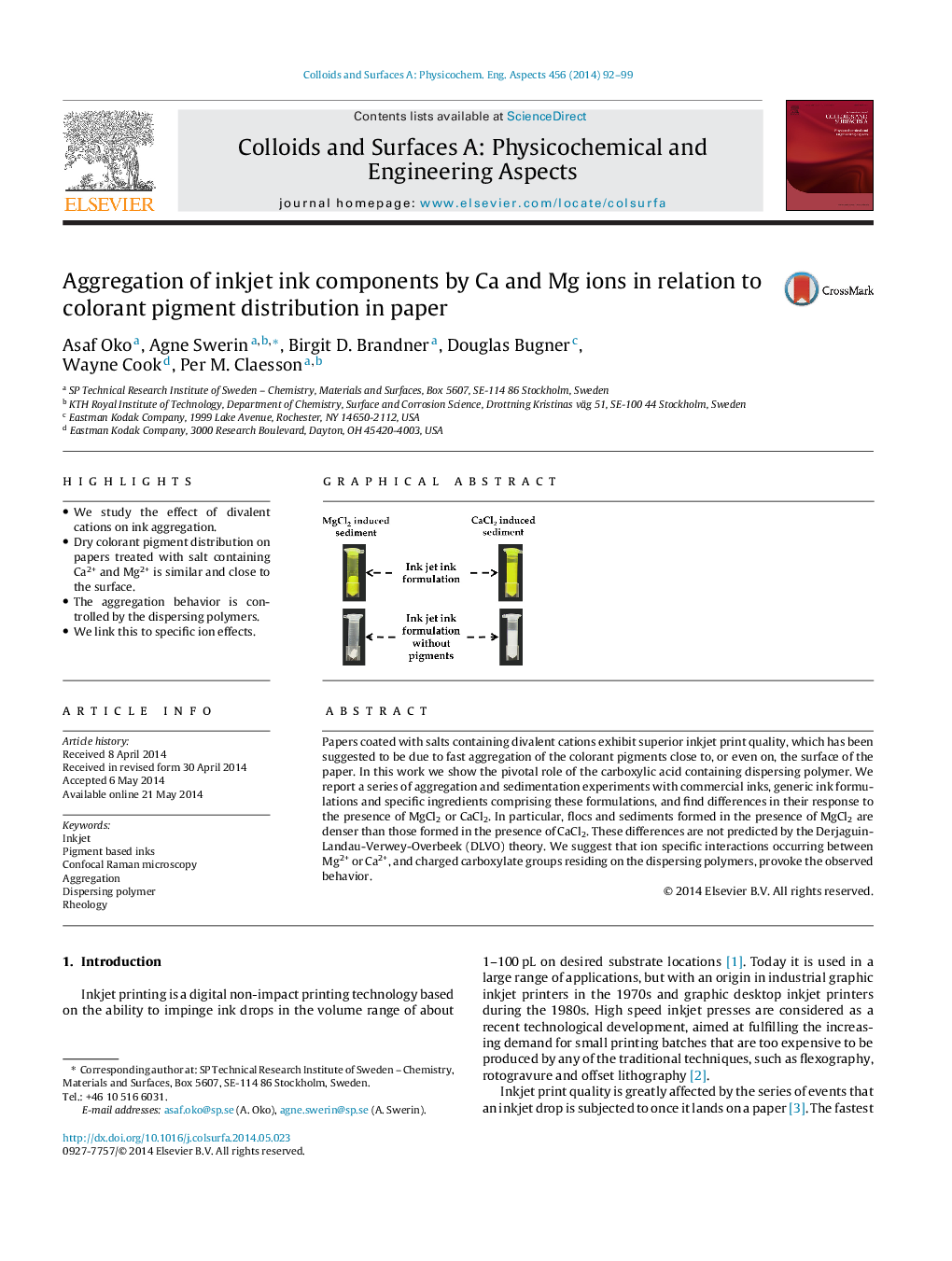
•We study the effect of divalent cations on ink aggregation.•Dry colorant pigment distribution on papers treated with salt containing Ca2+ and Mg2+ is similar and close to the surface.•The aggregation behavior is controlled by the dispersing polymers.•We link this to specific ion effects.
Papers coated with salts containing divalent cations exhibit superior inkjet print quality, which has been suggested to be due to fast aggregation of the colorant pigments close to, or even on, the surface of the paper. In this work we show the pivotal role of the carboxylic acid containing dispersing polymer. We report a series of aggregation and sedimentation experiments with commercial inks, generic ink formulations and specific ingredients comprising these formulations, and find differences in their response to the presence of MgCl2 or CaCl2. In particular, flocs and sediments formed in the presence of MgCl2 are denser than those formed in the presence of CaCl2. These differences are not predicted by the Derjaguin-Landau-Verwey-Overbeek (DLVO) theory. We suggest that ion specific interactions occurring between Mg2+ or Ca2+, and charged carboxylate groups residing on the dispersing polymers, provoke the observed behavior.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide