| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 592956 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2014 | 9 Pages |
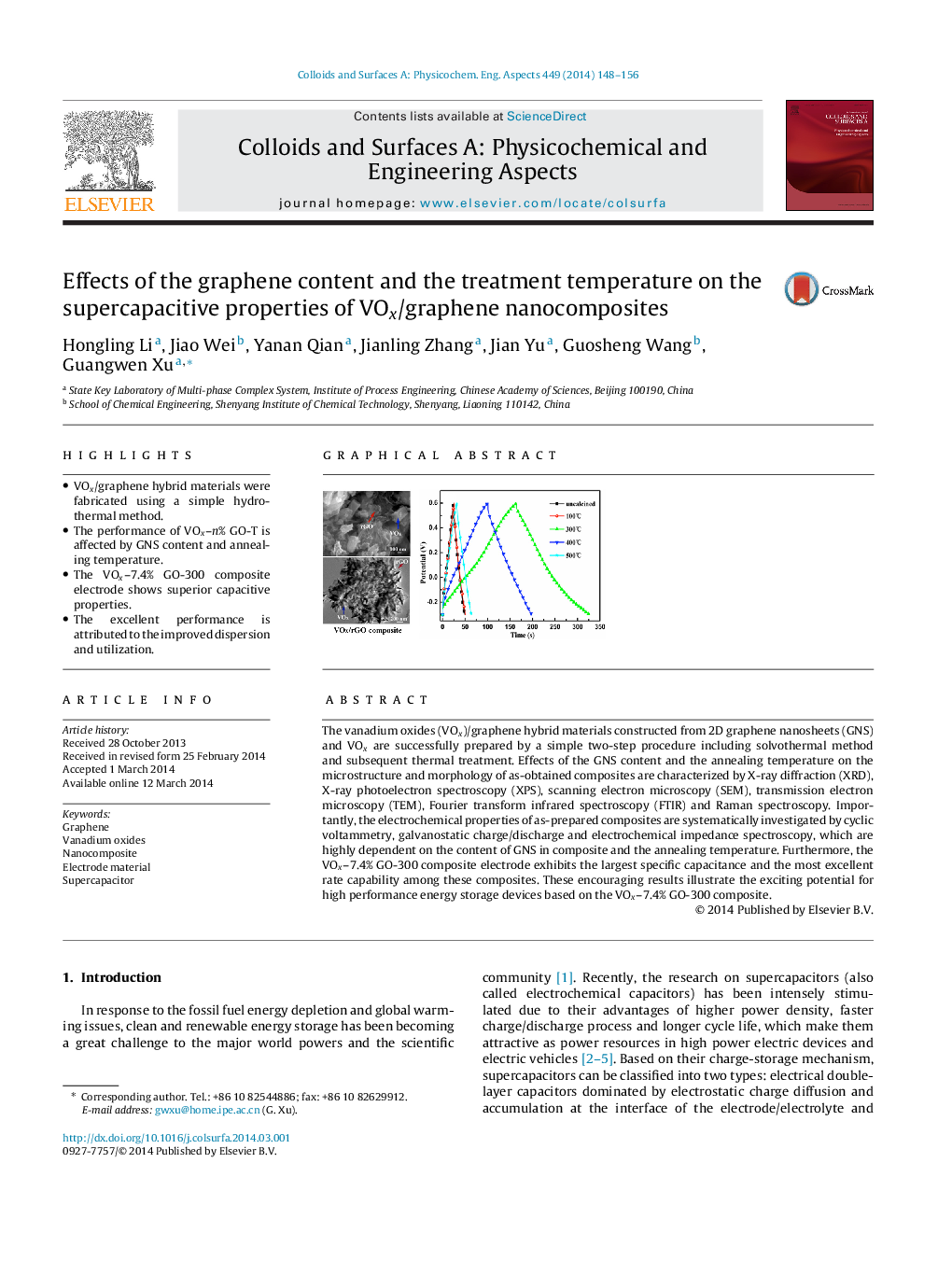
•VOx/graphene hybrid materials were fabricated using a simple hydrothermal method.•The performance of VOx–n% GO-T is affected by GNS content and annealing temperature.•The VOx–7.4% GO-300 composite electrode shows superior capacitive properties.•The excellent performance is attributed to the improved dispersion and utilization.
The vanadium oxides (VOx)/graphene hybrid materials constructed from 2D graphene nanosheets (GNS) and VOx are successfully prepared by a simple two-step procedure including solvothermal method and subsequent thermal treatment. Effects of the GNS content and the annealing temperature on the microstructure and morphology of as-obtained composites are characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) and Raman spectroscopy. Importantly, the electrochemical properties of as-prepared composites are systematically investigated by cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge/discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, which are highly dependent on the content of GNS in composite and the annealing temperature. Furthermore, the VOx–7.4% GO-300 composite electrode exhibits the largest specific capacitance and the most excellent rate capability among these composites. These encouraging results illustrate the exciting potential for high performance energy storage devices based on the VOx–7.4% GO-300 composite.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide