| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593574 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2013 | 8 Pages |
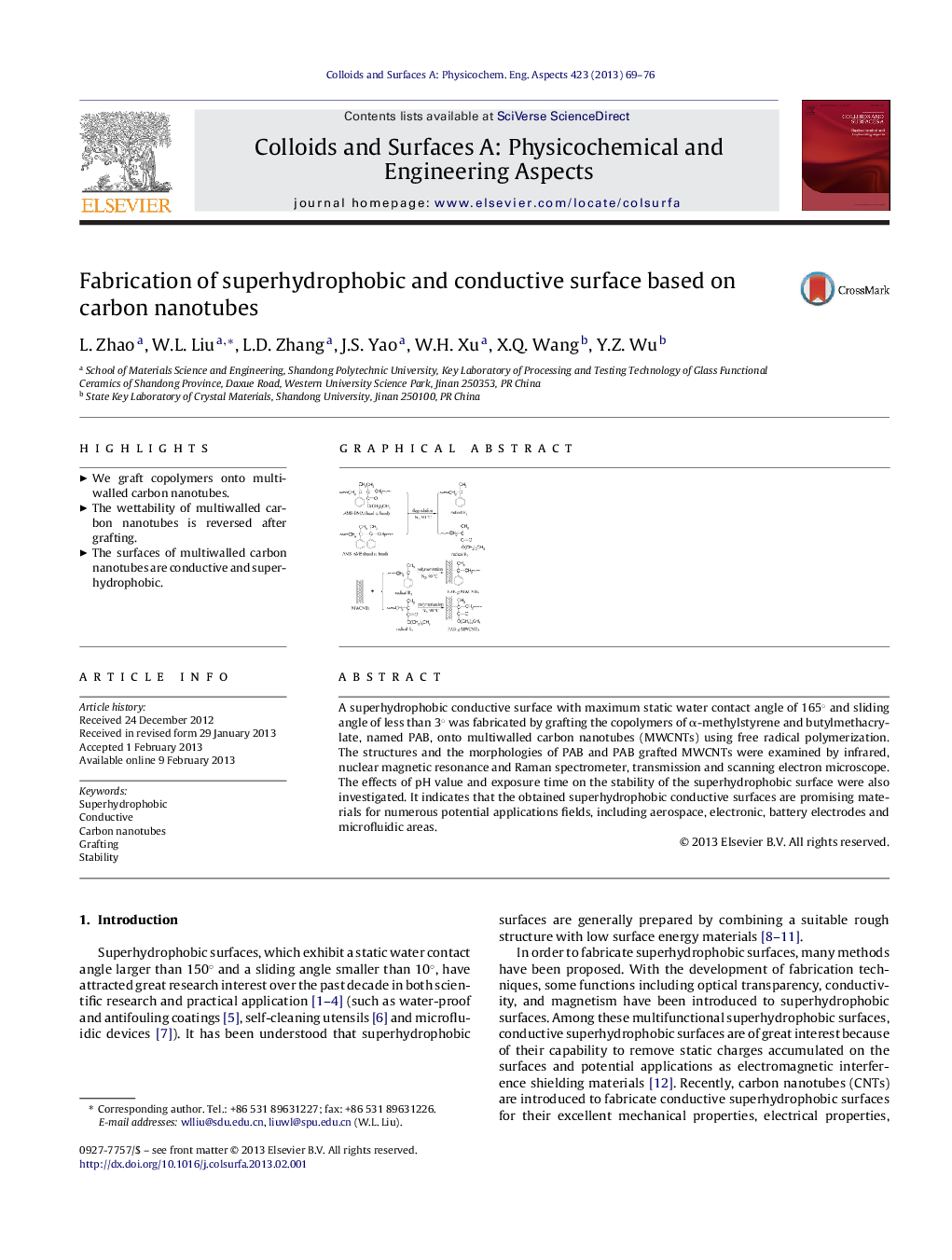
A superhydrophobic conductive surface with maximum static water contact angle of 165° and sliding angle of less than 3° was fabricated by grafting the copolymers of α-methylstyrene and butylmethacrylate, named PAB, onto multiwalled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) using free radical polymerization. The structures and the morphologies of PAB and PAB grafted MWCNTs were examined by infrared, nuclear magnetic resonance and Raman spectrometer, transmission and scanning electron microscope. The effects of pH value and exposure time on the stability of the superhydrophobic surface were also investigated. It indicates that the obtained superhydrophobic conductive surfaces are promising materials for numerous potential applications fields, including aerospace, electronic, battery electrodes and microfluidic areas.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► We graft copolymers onto multiwalled carbon nanotubes. ► The wettability of multiwalled carbon nanotubes is reversed after grafting. ► The surfaces of multiwalled carbon nanotubes are conductive and superhydrophobic.