| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593604 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2013 | 7 Pages |
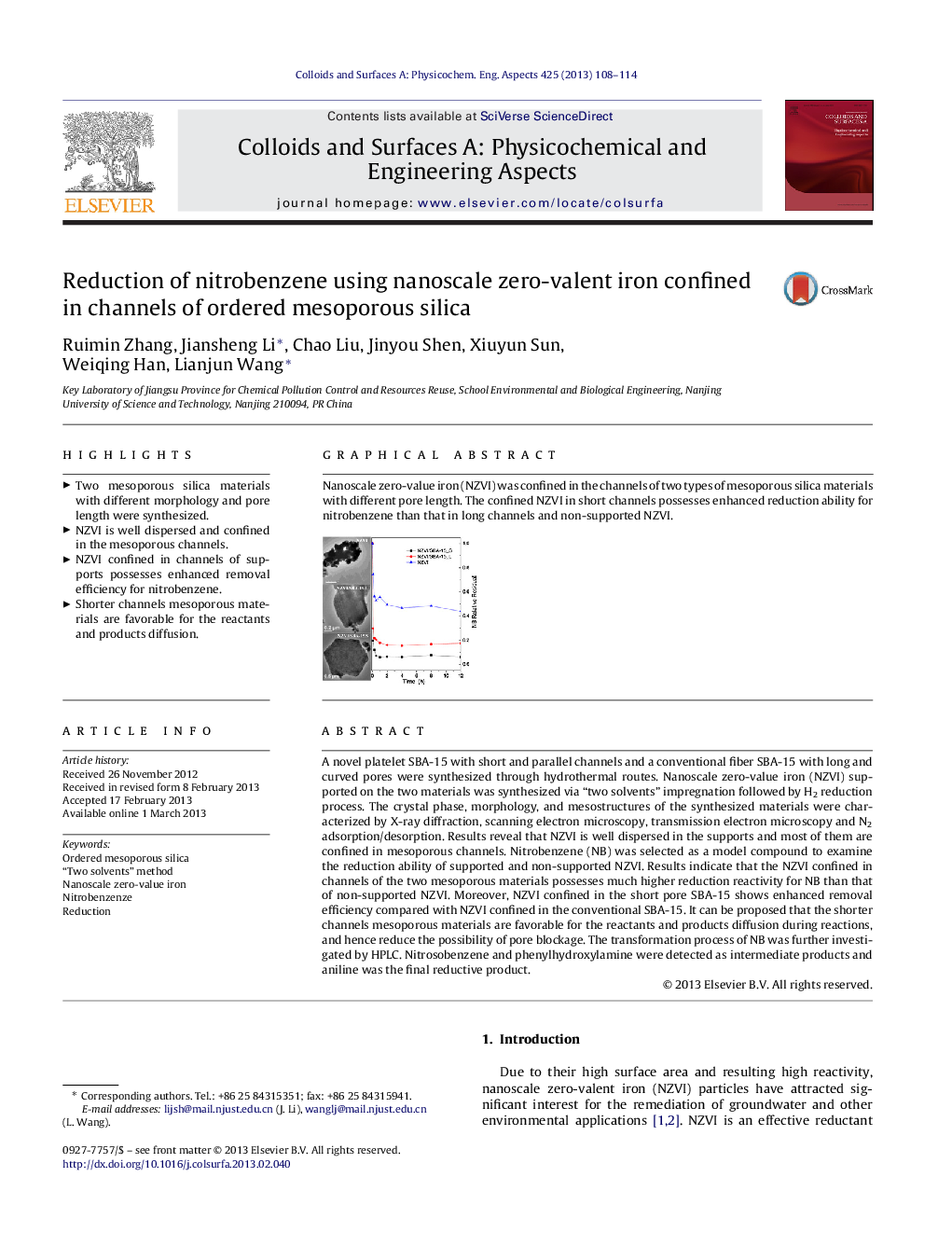
A novel platelet SBA-15 with short and parallel channels and a conventional fiber SBA-15 with long and curved pores were synthesized through hydrothermal routes. Nanoscale zero-value iron (NZVI) supported on the two materials was synthesized via “two solvents” impregnation followed by H2 reduction process. The crystal phase, morphology, and mesostructures of the synthesized materials were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and N2 adsorption/desorption. Results reveal that NZVI is well dispersed in the supports and most of them are confined in mesoporous channels. Nitrobenzene (NB) was selected as a model compound to examine the reduction ability of supported and non-supported NZVI. Results indicate that the NZVI confined in channels of the two mesoporous materials possesses much higher reduction reactivity for NB than that of non-supported NZVI. Moreover, NZVI confined in the short pore SBA-15 shows enhanced removal efficiency compared with NZVI confined in the conventional SBA-15. It can be proposed that the shorter channels mesoporous materials are favorable for the reactants and products diffusion during reactions, and hence reduce the possibility of pore blockage. The transformation process of NB was further investigated by HPLC. Nitrosobenzene and phenylhydroxylamine were detected as intermediate products and aniline was the final reductive product.
Graphical abstractNanoscale zero-value iron (NZVI) was confined in the channels of two types of mesoporous silica materials with different pore length. The confined NZVI in short channels possesses enhanced reduction ability for nitrobenzene than that in long channels and non-supported NZVI.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Two mesoporous silica materials with different morphology and pore length were synthesized. ► NZVI is well dispersed and confined in the mesoporous channels. ► NZVI confined in channels of supports possesses enhanced removal efficiency for nitrobenzene. ► Shorter channels mesoporous materials are favorable for the reactants and products diffusion.