| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593761 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2013 | 6 Pages |
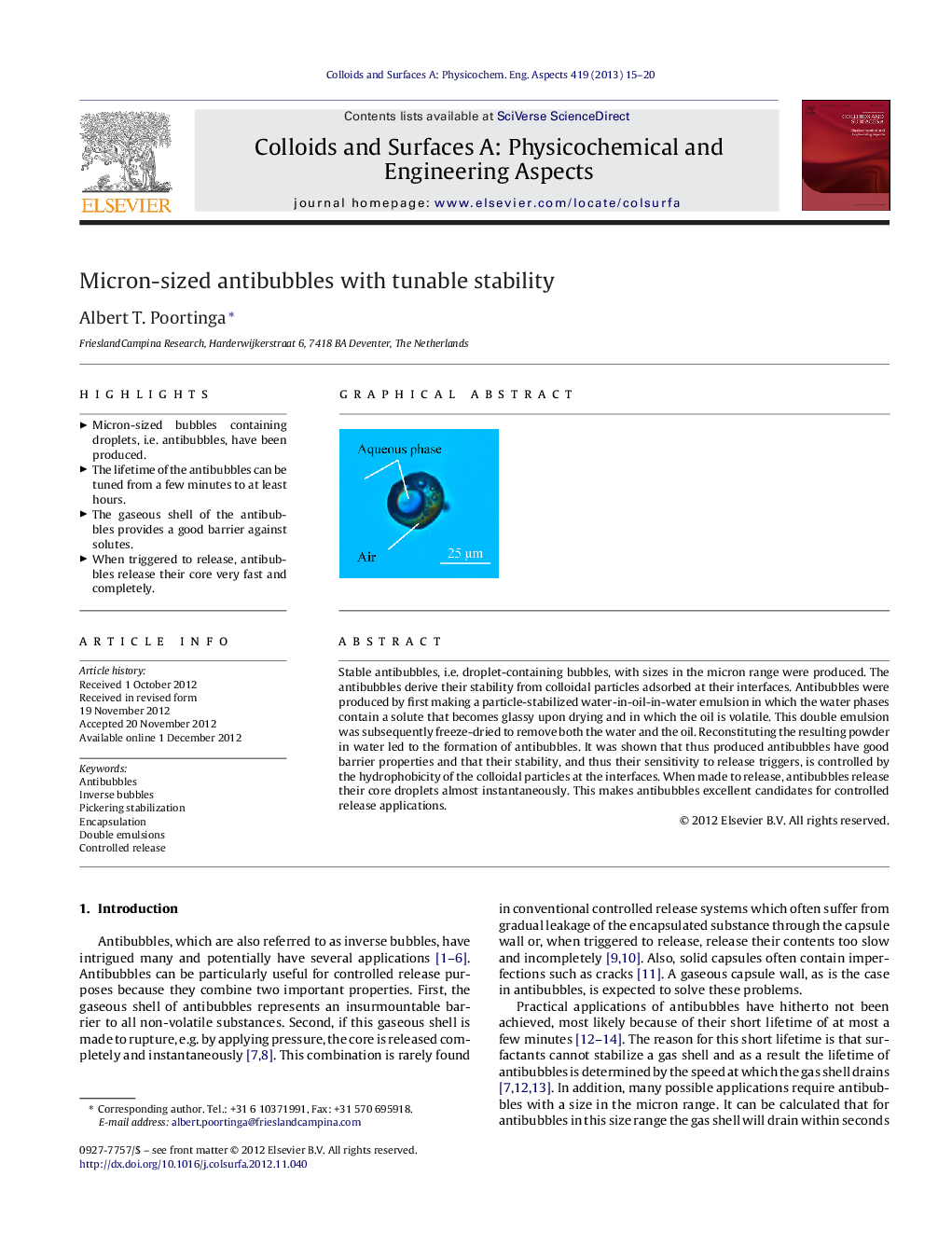
Stable antibubbles, i.e. droplet-containing bubbles, with sizes in the micron range were produced. The antibubbles derive their stability from colloidal particles adsorbed at their interfaces. Antibubbles were produced by first making a particle-stabilized water-in-oil-in-water emulsion in which the water phases contain a solute that becomes glassy upon drying and in which the oil is volatile. This double emulsion was subsequently freeze-dried to remove both the water and the oil. Reconstituting the resulting powder in water led to the formation of antibubbles. It was shown that thus produced antibubbles have good barrier properties and that their stability, and thus their sensitivity to release triggers, is controlled by the hydrophobicity of the colloidal particles at the interfaces. When made to release, antibubbles release their core droplets almost instantaneously. This makes antibubbles excellent candidates for controlled release applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Micron-sized bubbles containing droplets, i.e. antibubbles, have been produced. ► The lifetime of the antibubbles can be tuned from a few minutes to at least hours. ► The gaseous shell of the antibubbles provides a good barrier against solutes. ► When triggered to release, antibubbles release their core very fast and completely.