| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593771 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2013 | 6 Pages |
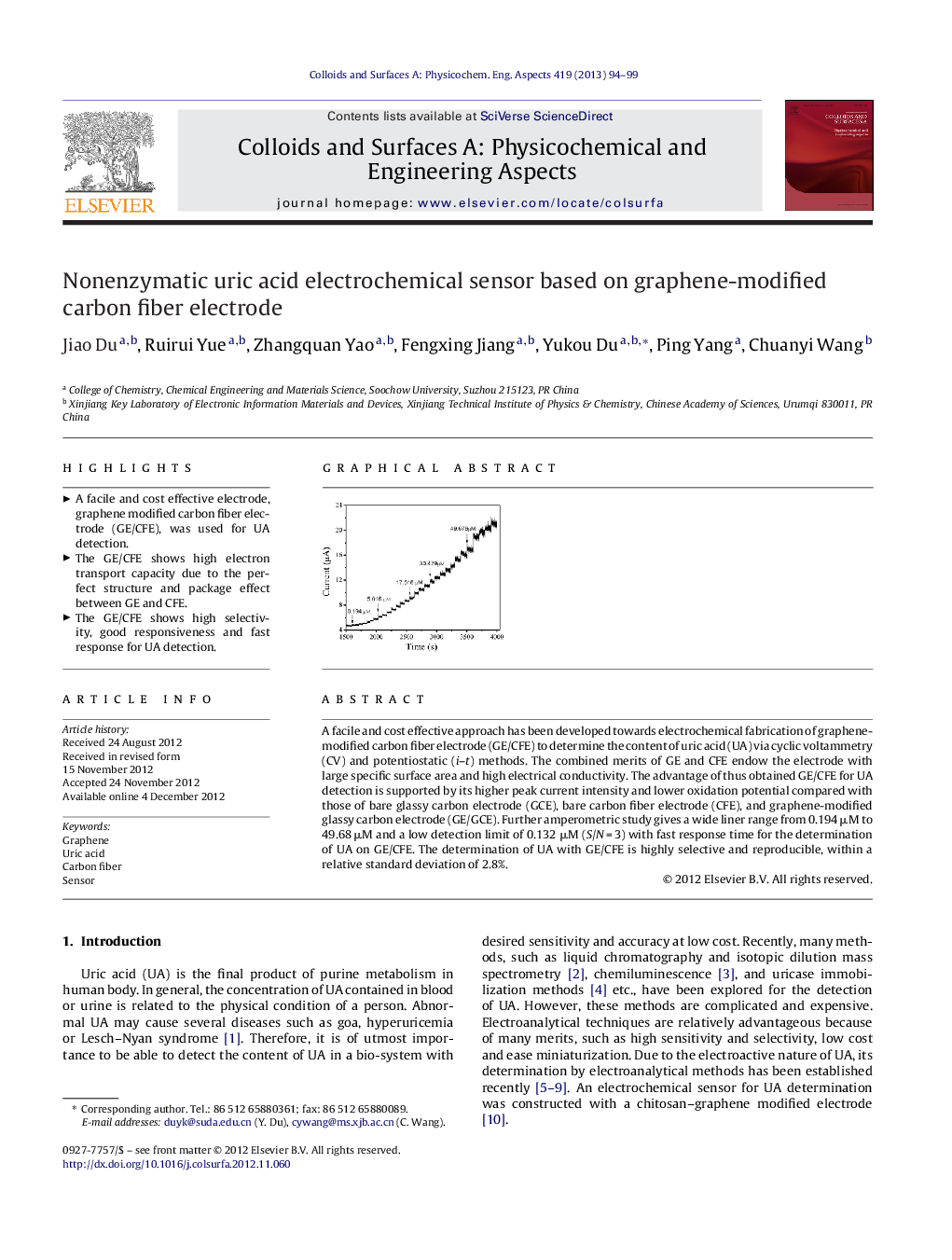
A facile and cost effective approach has been developed towards electrochemical fabrication of graphene-modified carbon fiber electrode (GE/CFE) to determine the content of uric acid (UA) via cyclic voltammetry (CV) and potentiostatic (i–t) methods. The combined merits of GE and CFE endow the electrode with large specific surface area and high electrical conductivity. The advantage of thus obtained GE/CFE for UA detection is supported by its higher peak current intensity and lower oxidation potential compared with those of bare glassy carbon electrode (GCE), bare carbon fiber electrode (CFE), and graphene-modified glassy carbon electrode (GE/GCE). Further amperometric study gives a wide liner range from 0.194 μM to 49.68 μM and a low detection limit of 0.132 μM (S/N = 3) with fast response time for the determination of UA on GE/CFE. The determination of UA with GE/CFE is highly selective and reproducible, within a relative standard deviation of 2.8%.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► A facile and cost effective electrode, graphene modified carbon fiber electrode (GE/CFE), was used for UA detection. ► The GE/CFE shows high electron transport capacity due to the perfect structure and package effect between GE and CFE. ► The GE/CFE shows high selectivity, good responsiveness and fast response for UA detection.