| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593796 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2013 | 8 Pages |
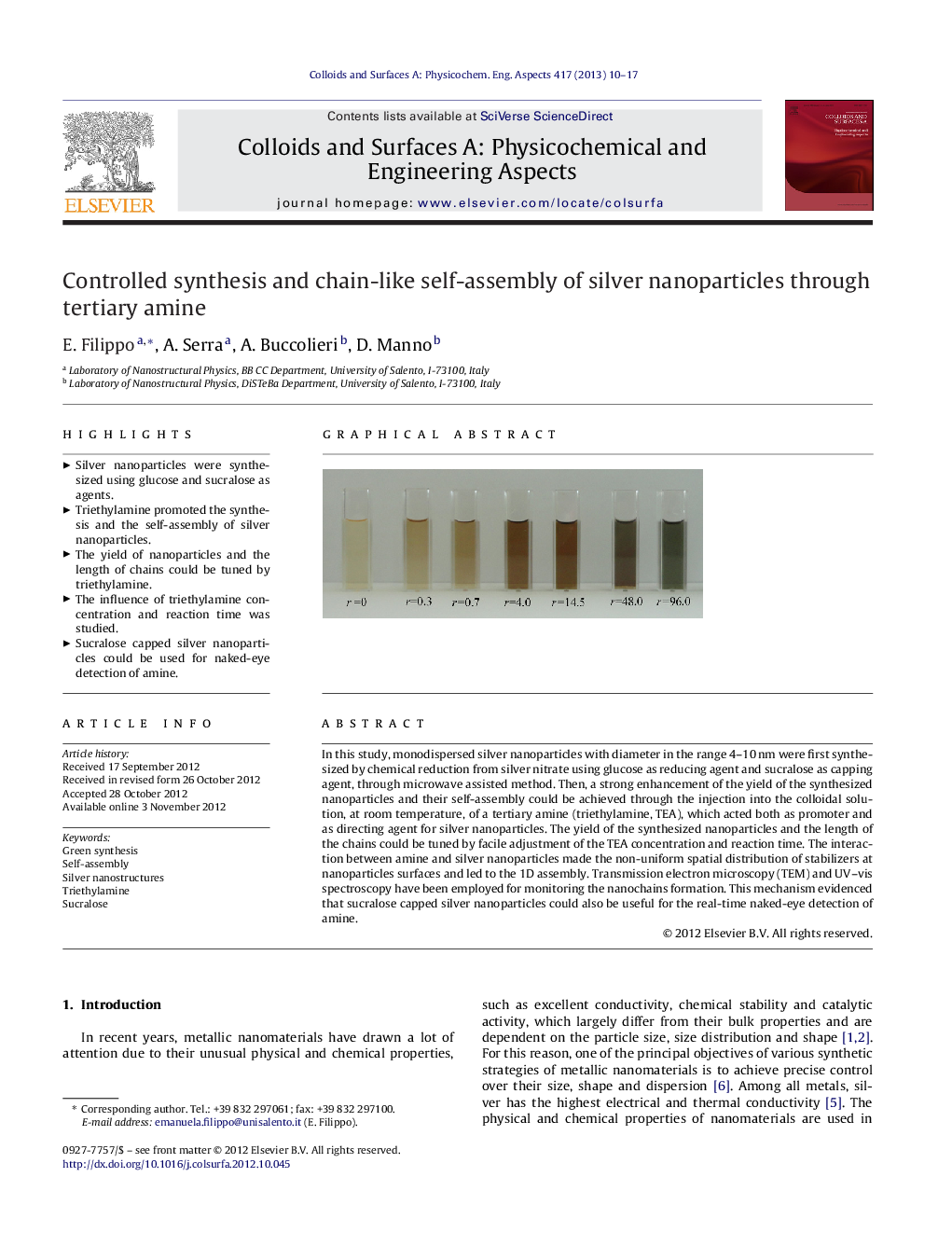
In this study, monodispersed silver nanoparticles with diameter in the range 4–10 nm were first synthesized by chemical reduction from silver nitrate using glucose as reducing agent and sucralose as capping agent, through microwave assisted method. Then, a strong enhancement of the yield of the synthesized nanoparticles and their self-assembly could be achieved through the injection into the colloidal solution, at room temperature, of a tertiary amine (triethylamine, TEA), which acted both as promoter and as directing agent for silver nanoparticles. The yield of the synthesized nanoparticles and the length of the chains could be tuned by facile adjustment of the TEA concentration and reaction time. The interaction between amine and silver nanoparticles made the non-uniform spatial distribution of stabilizers at nanoparticles surfaces and led to the 1D assembly. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and UV–vis spectroscopy have been employed for monitoring the nanochains formation. This mechanism evidenced that sucralose capped silver nanoparticles could also be useful for the real-time naked-eye detection of amine.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Silver nanoparticles were synthesized using glucose and sucralose as agents. ► Triethylamine promoted the synthesis and the self-assembly of silver nanoparticles. ► The yield of nanoparticles and the length of chains could be tuned by triethylamine. ► The influence of triethylamine concentration and reaction time was studied. ► Sucralose capped silver nanoparticles could be used for naked-eye detection of amine.