| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593911 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2012 | 9 Pages |
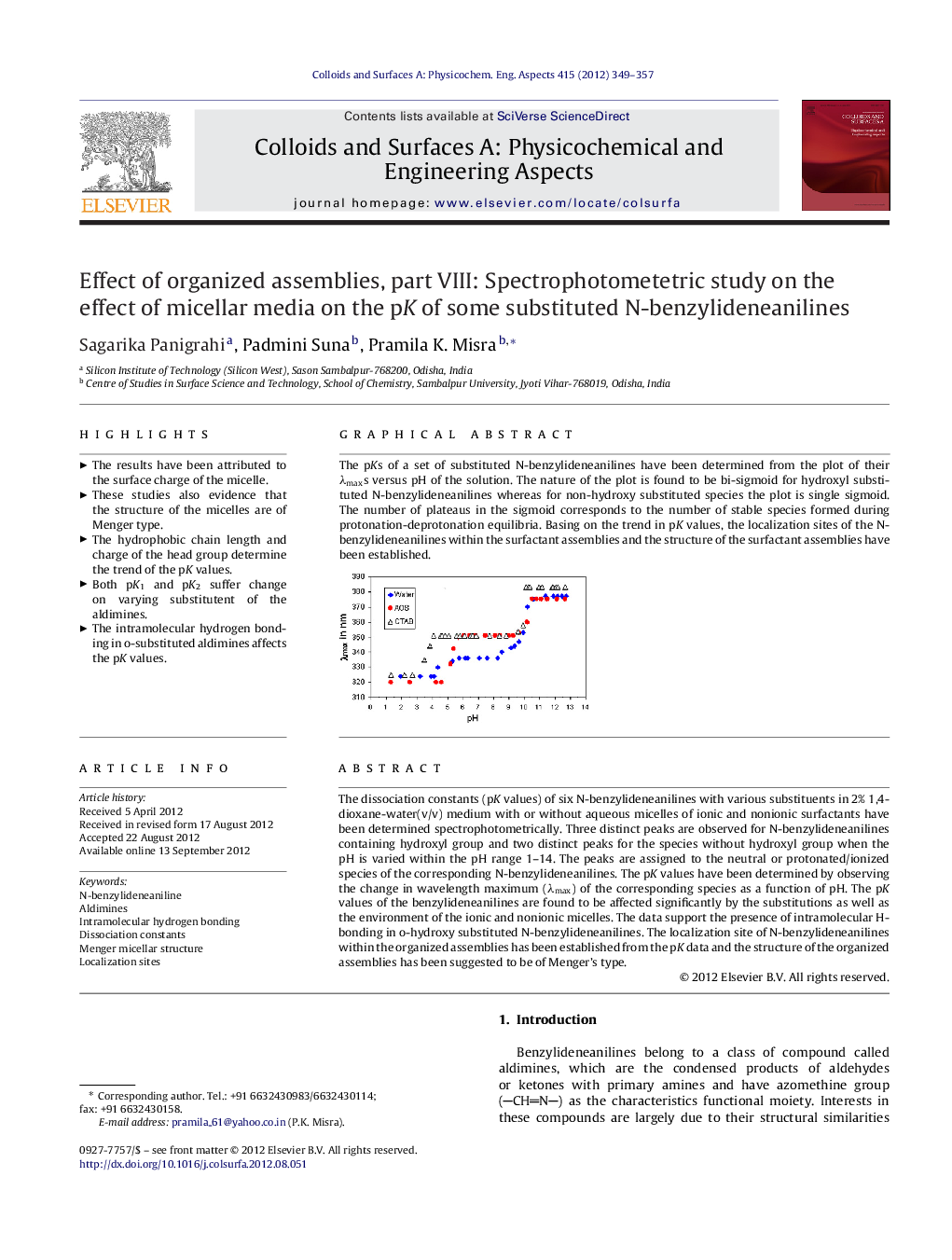
The dissociation constants (pK values) of six N-benzylideneanilines with various substituents in 2% 1,4-dioxane-water(v/v) medium with or without aqueous micelles of ionic and nonionic surfactants have been determined spectrophotometrically. Three distinct peaks are observed for N-benzylideneanilines containing hydroxyl group and two distinct peaks for the species without hydroxyl group when the pH is varied within the pH range 1–14. The peaks are assigned to the neutral or protonated/ionized species of the corresponding N-benzylideneanilines. The pK values have been determined by observing the change in wavelength maximum (λmax) of the corresponding species as a function of pH. The pK values of the benzylideneanilines are found to be affected significantly by the substitutions as well as the environment of the ionic and nonionic micelles. The data support the presence of intramolecular H-bonding in o-hydroxy substituted N-benzylideneanilines. The localization site of N-benzylideneanilines within the organized assemblies has been established from the pK data and the structure of the organized assemblies has been suggested to be of Menger's type.
Graphical abstractThe pKs of a set of substituted N-benzylideneanilines have been determined from the plot of their λmaxs versus pH of the solution. The nature of the plot is found to be bi-sigmoid for hydroxyl substituted N-benzylideneanilines whereas for non-hydroxy substituted species the plot is single sigmoid. The number of plateaus in the sigmoid corresponds to the number of stable species formed during protonation-deprotonation equilibria. Basing on the trend in pK values, the localization sites of the N-benzylideneanilines within the surfactant assemblies and the structure of the surfactant assemblies have been established.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The results have been attributed to the surface charge of the micelle. ► These studies also evidence that the structure of the micelles are of Menger type. ► The hydrophobic chain length and charge of the head group determine the trend of the pK values. ► Both pK1 and pK2 suffer change on varying substitutent of the aldimines. ► The intramolecular hydrogen bonding in o-substituted aldimines affects the pK values.