| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593948 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2012 | 9 Pages |
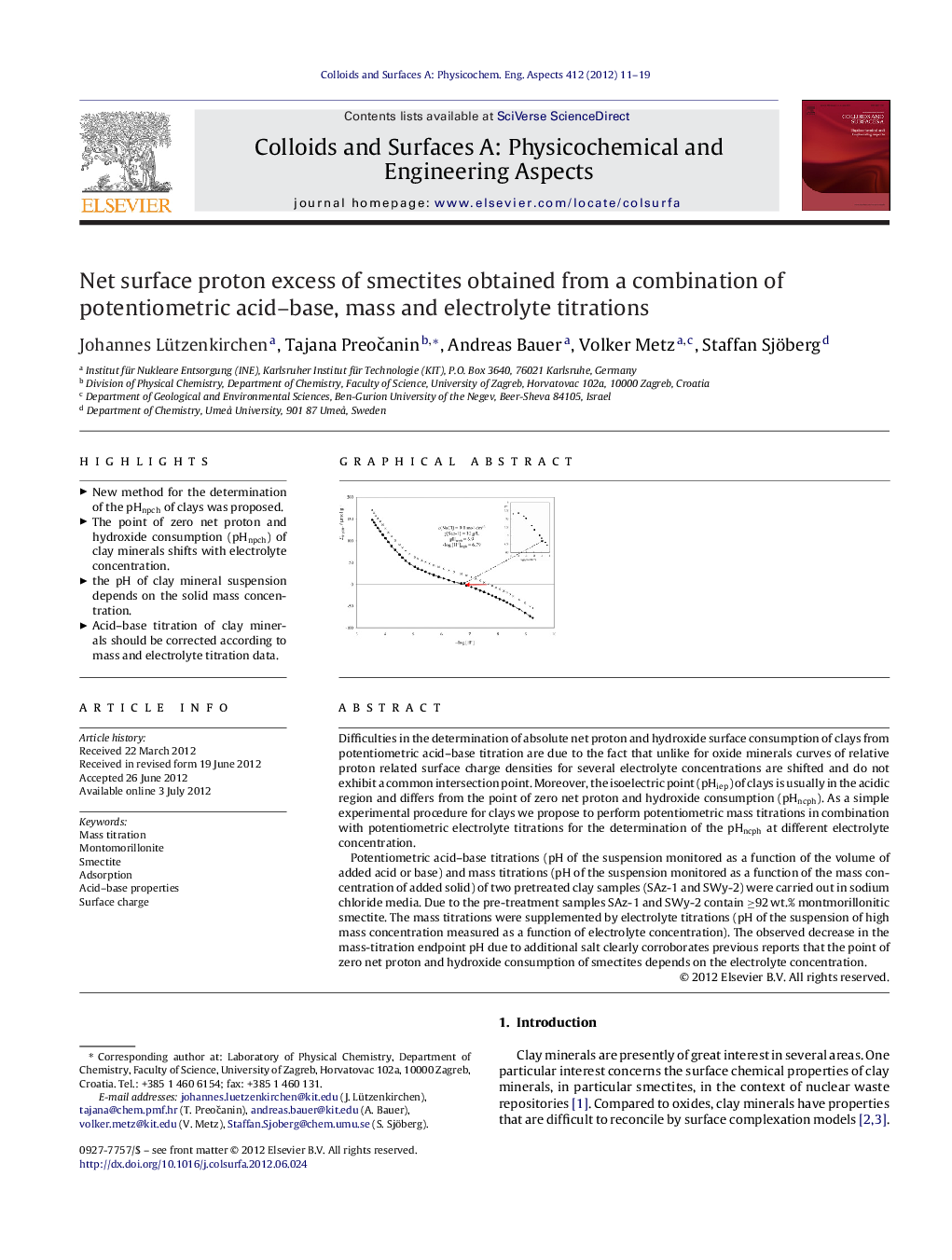
Difficulties in the determination of absolute net proton and hydroxide surface consumption of clays from potentiometric acid–base titration are due to the fact that unlike for oxide minerals curves of relative proton related surface charge densities for several electrolyte concentrations are shifted and do not exhibit a common intersection point. Moreover, the isoelectric point (pHiep) of clays is usually in the acidic region and differs from the point of zero net proton and hydroxide consumption (pHncph). As a simple experimental procedure for clays we propose to perform potentiometric mass titrations in combination with potentiometric electrolyte titrations for the determination of the pHncph at different electrolyte concentration.Potentiometric acid–base titrations (pH of the suspension monitored as a function of the volume of added acid or base) and mass titrations (pH of the suspension monitored as a function of the mass concentration of added solid) of two pretreated clay samples (SAz-1 and SWy-2) were carried out in sodium chloride media. Due to the pre-treatment samples SAz-1 and SWy-2 contain ≥92 wt.% montmorillonitic smectite. The mass titrations were supplemented by electrolyte titrations (pH of the suspension of high mass concentration measured as a function of electrolyte concentration). The observed decrease in the mass-titration endpoint pH due to additional salt clearly corroborates previous reports that the point of zero net proton and hydroxide consumption of smectites depends on the electrolyte concentration.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► New method for the determination of the pHnpch of clays was proposed. ► The point of zero net proton and hydroxide consumption (pHnpch) of clay minerals shifts with electrolyte concentration. ► the pH of clay mineral suspension depends on the solid mass concentration. ► Acid–base titration of clay minerals should be corrected according to mass and electrolyte titration data.