| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 593998 | Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects | 2012 | 7 Pages |
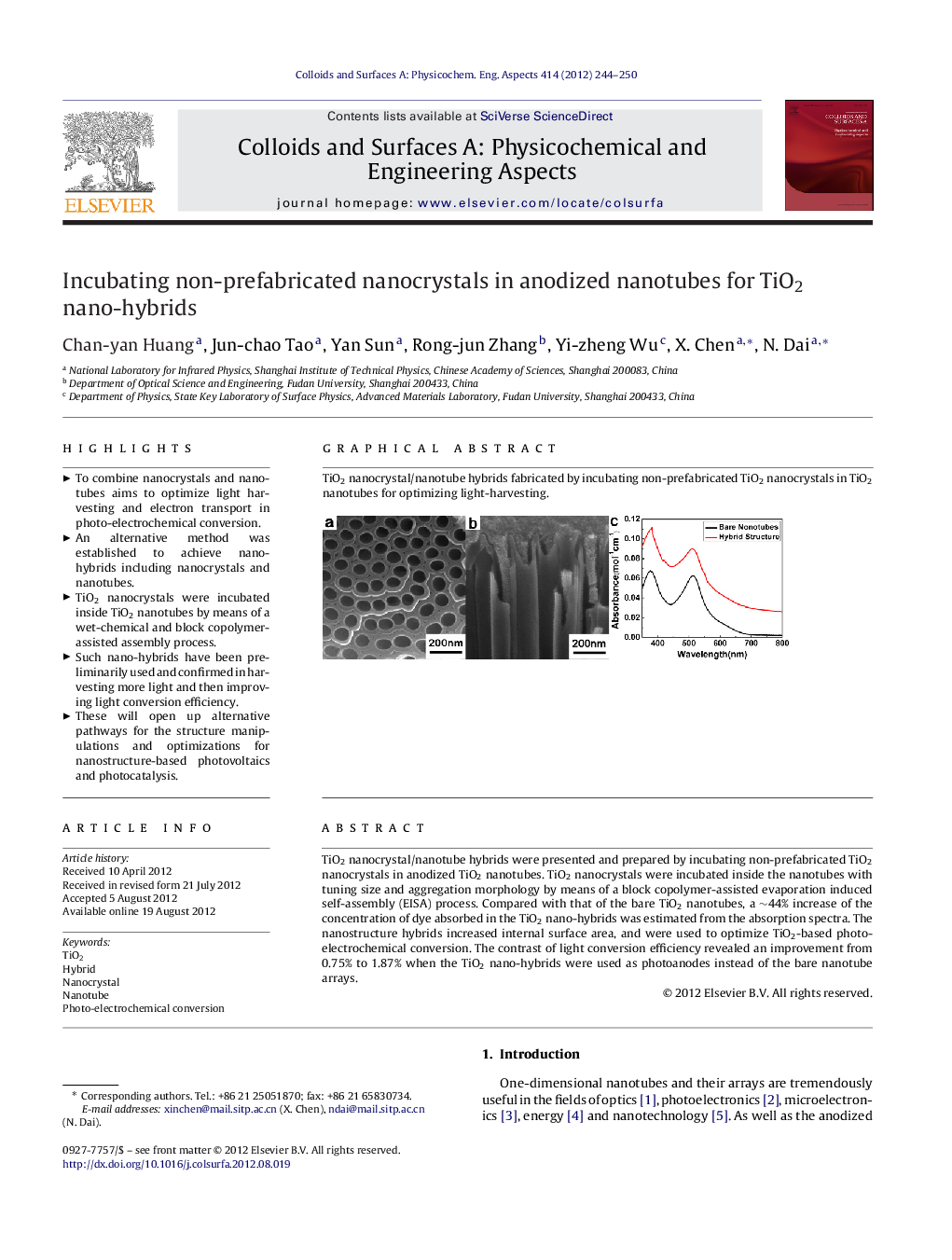
TiO2 nanocrystal/nanotube hybrids were presented and prepared by incubating non-prefabricated TiO2 nanocrystals in anodized TiO2 nanotubes. TiO2 nanocrystals were incubated inside the nanotubes with tuning size and aggregation morphology by means of a block copolymer-assisted evaporation induced self-assembly (EISA) process. Compared with that of the bare TiO2 nanotubes, a ∼44% increase of the concentration of dye absorbed in the TiO2 nano-hybrids was estimated from the absorption spectra. The nanostructure hybrids increased internal surface area, and were used to optimize TiO2-based photo-electrochemical conversion. The contrast of light conversion efficiency revealed an improvement from 0.75% to 1.87% when the TiO2 nano-hybrids were used as photoanodes instead of the bare nanotube arrays.
Graphical abstractTiO2 nanocrystal/nanotube hybrids fabricated by incubating non-prefabricated TiO2 nanocrystals in TiO2 nanotubes for optimizing light-harvesting.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► To combine nanocrystals and nanotubes aims to optimize light harvesting and electron transport in photo-electrochemical conversion. ► An alternative method was established to achieve nano-hybrids including nanocrystals and nanotubes. ► TiO2 nanocrystals were incubated inside TiO2 nanotubes by means of a wet-chemical and block copolymer-assisted assembly process. ► Such nano-hybrids have been preliminarily used and confirmed in harvesting more light and then improving light conversion efficiency. ► These will open up alternative pathways for the structure manipulations and optimizations for nanostructure-based photovoltaics and photocatalysis.