| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606385 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2016 | 6 Pages |
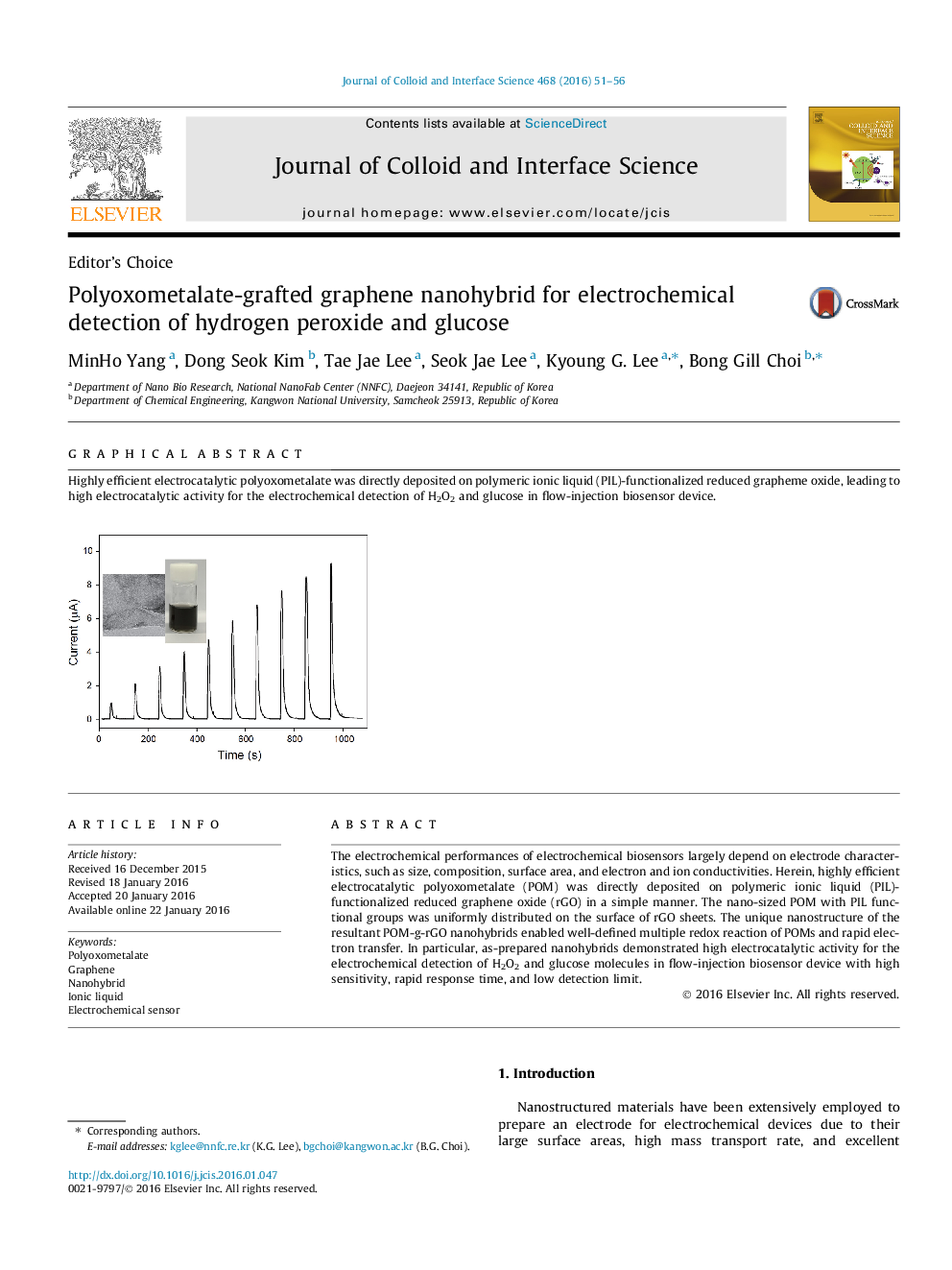
The electrochemical performances of electrochemical biosensors largely depend on electrode characteristics, such as size, composition, surface area, and electron and ion conductivities. Herein, highly efficient electrocatalytic polyoxometalate (POM) was directly deposited on polymeric ionic liquid (PIL)-functionalized reduced graphene oxide (rGO) in a simple manner. The nano-sized POM with PIL functional groups was uniformly distributed on the surface of rGO sheets. The unique nanostructure of the resultant POM-g-rGO nanohybrids enabled well-defined multiple redox reaction of POMs and rapid electron transfer. In particular, as-prepared nanohybrids demonstrated high electrocatalytic activity for the electrochemical detection of H2O2 and glucose molecules in flow-injection biosensor device with high sensitivity, rapid response time, and low detection limit.
Graphical abstractHighly efficient electrocatalytic polyoxometalate was directly deposited on polymeric ionic liquid (PIL)-functionalized reduced grapheme oxide, leading to high electrocatalytic activity for the electrochemical detection of H2O2 and glucose in flow-injection biosensor device.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (89 K)Download as PowerPoint slide