| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606428 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2016 | 7 Pages |
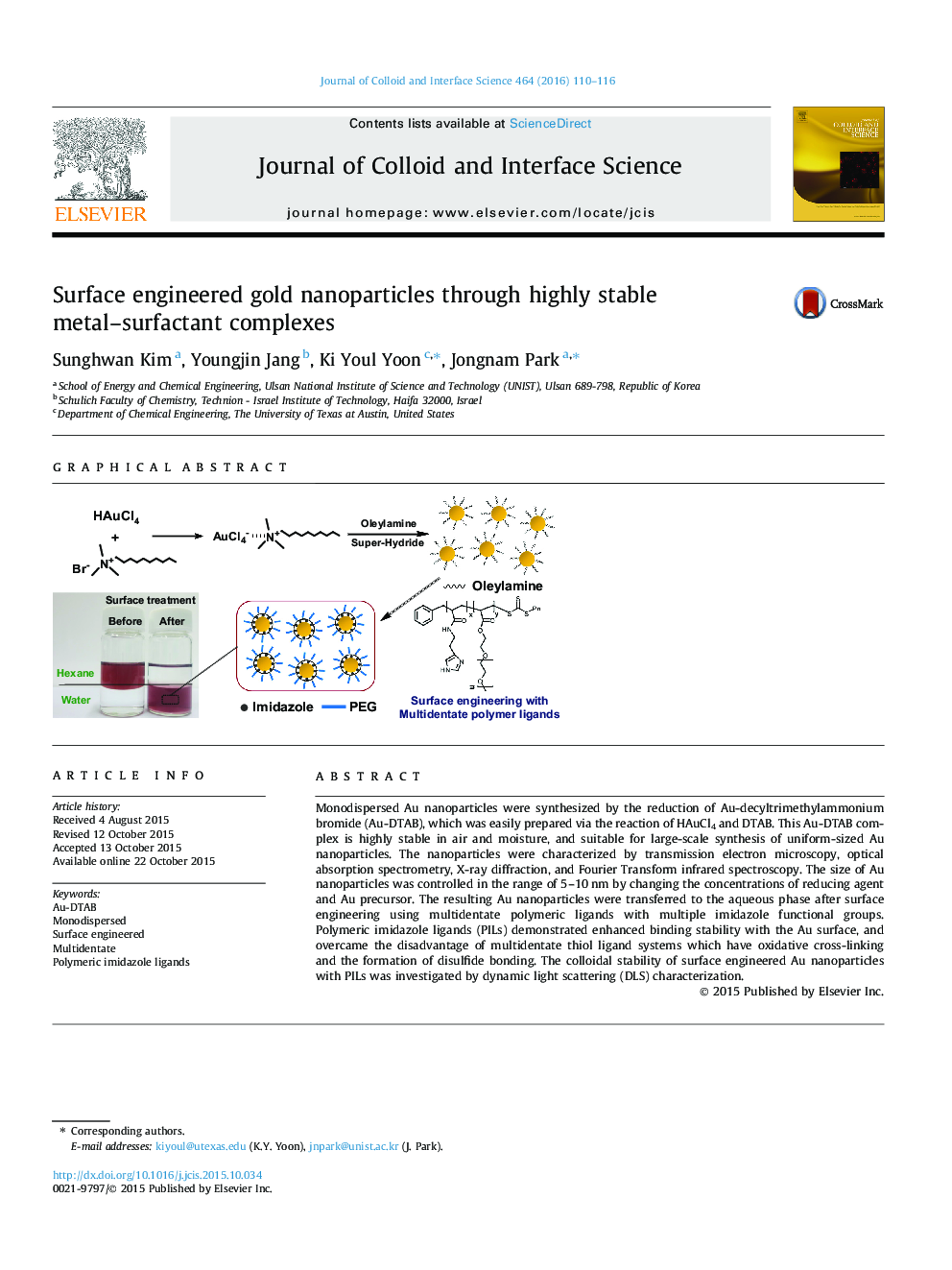
Monodispersed Au nanoparticles were synthesized by the reduction of Au-decyltrimethylammonium bromide (Au-DTAB), which was easily prepared via the reaction of HAuCl4 and DTAB. This Au-DTAB complex is highly stable in air and moisture, and suitable for large-scale synthesis of uniform-sized Au nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, optical absorption spectrometry, X-ray diffraction, and Fourier Transform infrared spectroscopy. The size of Au nanoparticles was controlled in the range of 5–10 nm by changing the concentrations of reducing agent and Au precursor. The resulting Au nanoparticles were transferred to the aqueous phase after surface engineering using multidentate polymeric ligands with multiple imidazole functional groups. Polymeric imidazole ligands (PILs) demonstrated enhanced binding stability with the Au surface, and overcame the disadvantage of multidentate thiol ligand systems which have oxidative cross-linking and the formation of disulfide bonding. The colloidal stability of surface engineered Au nanoparticles with PILs was investigated by dynamic light scattering (DLS) characterization.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (219 K)Download as PowerPoint slide