| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606463 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2016 | 9 Pages |
•The release amount of catalysts could be easily controlled by removing the film.•High catalytic efficiency with extremely low Pd-loading down to 10−6 mol%.•High stability in the air and free phosphorus ligands.
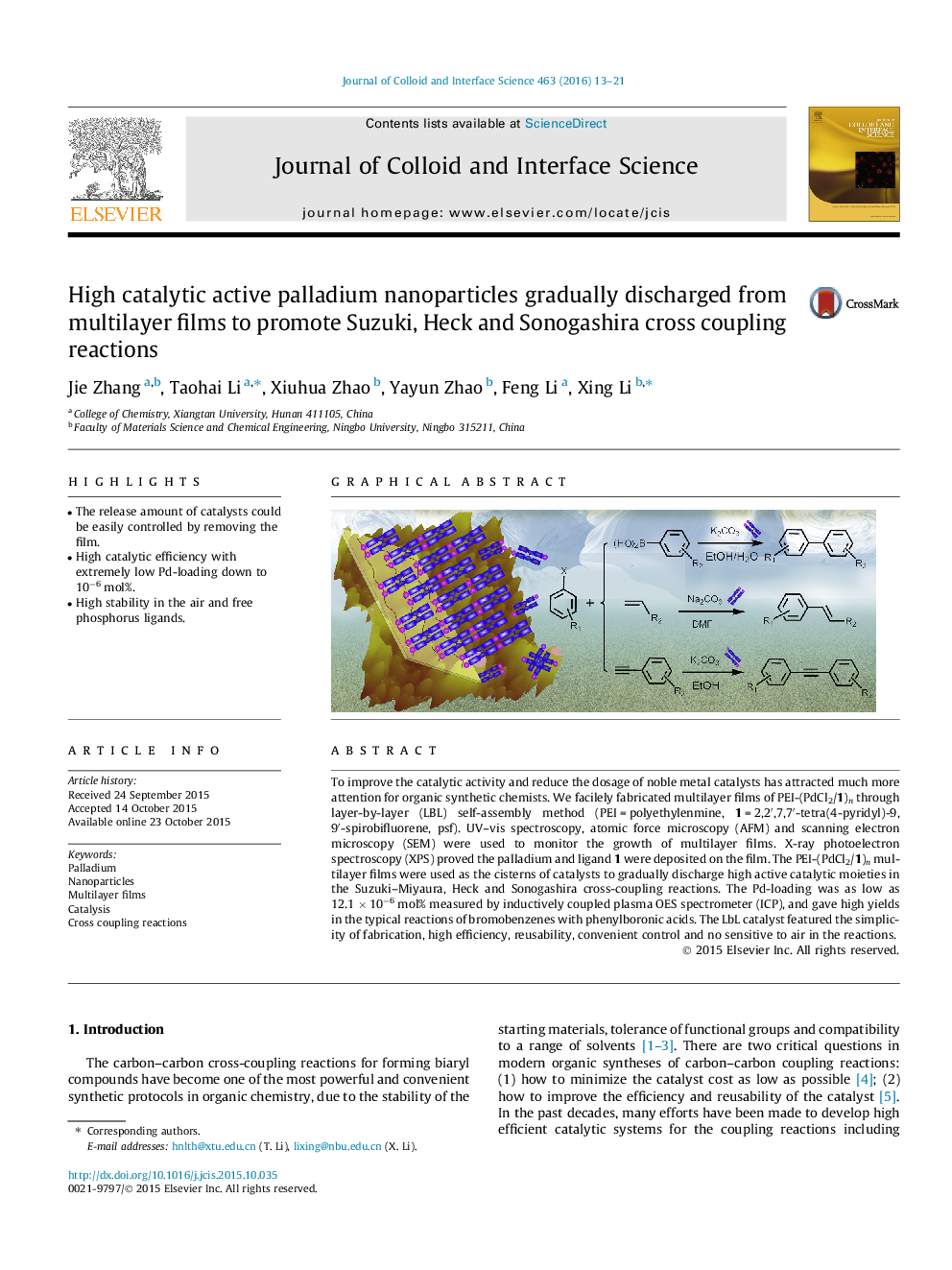
To improve the catalytic activity and reduce the dosage of noble metal catalysts has attracted much more attention for organic synthetic chemists. We facilely fabricated multilayer films of PEI-(PdCl2/1)n through layer-by-layer (LBL) self-assembly method (PEI = polyethylenmine, 1 = 2,2′,7,7′-tetra(4-pyridyl)-9,9′-spirobifluorene, psf). UV–vis spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) were used to monitor the growth of multilayer films. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) proved the palladium and ligand 1 were deposited on the film. The PEI-(PdCl2/1)n multilayer films were used as the cisterns of catalysts to gradually discharge high active catalytic moieties in the Suzuki–Miyaura, Heck and Sonogashira cross-coupling reactions. The Pd-loading was as low as 12.1 × 10−6 mol% measured by inductively coupled plasma OES spectrometer (ICP), and gave high yields in the typical reactions of bromobenzenes with phenylboronic acids. The LbL catalyst featured the simplicity of fabrication, high efficiency, reusability, convenient control and no sensitive to air in the reactions.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (401 K)Download as PowerPoint slide