| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606491 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2016 | 9 Pages |
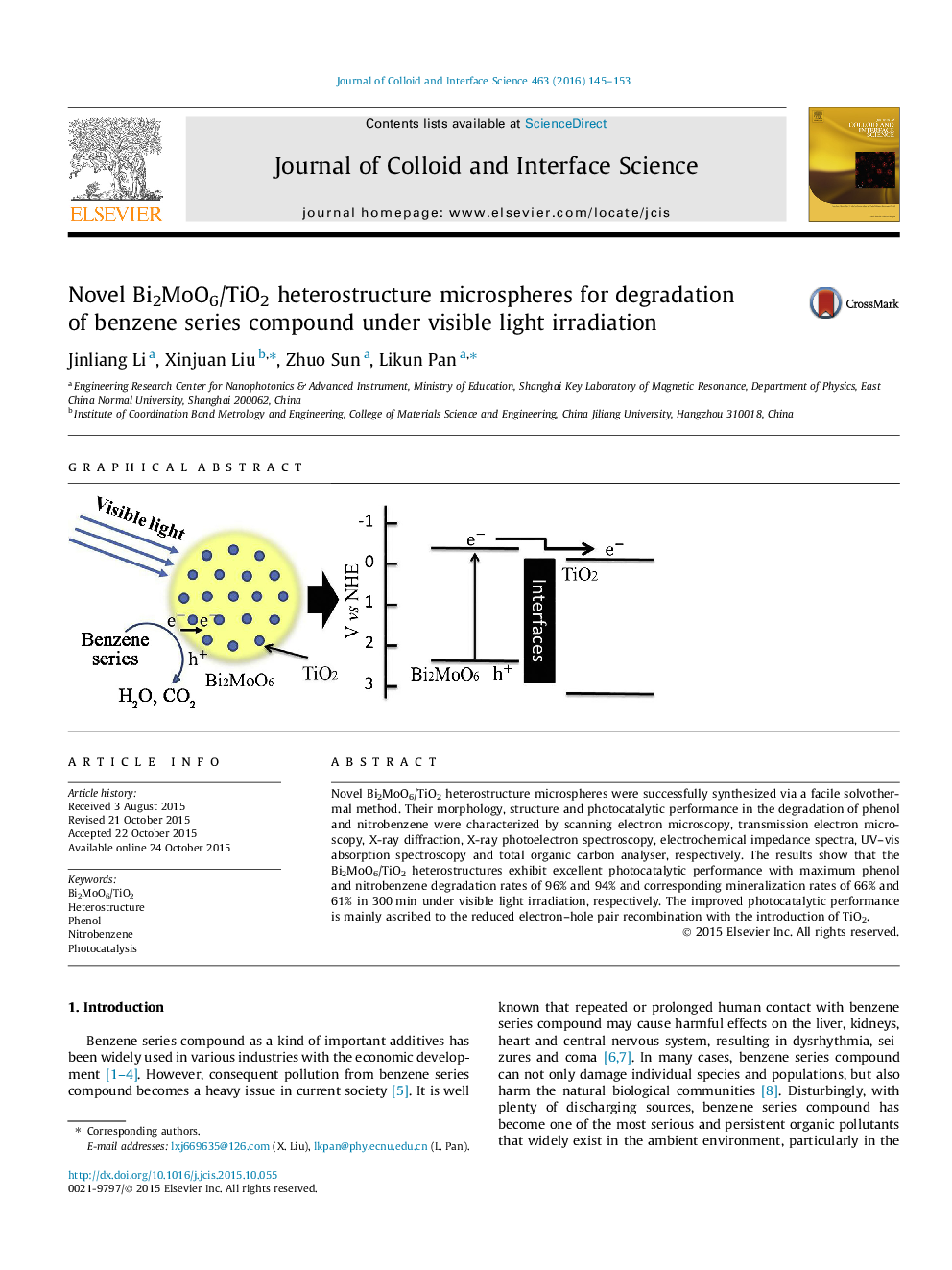
Novel Bi2MoO6/TiO2 heterostructure microspheres were successfully synthesized via a facile solvothermal method. Their morphology, structure and photocatalytic performance in the degradation of phenol and nitrobenzene were characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, X-ray diffraction, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, electrochemical impedance spectra, UV–vis absorption spectroscopy and total organic carbon analyser, respectively. The results show that the Bi2MoO6/TiO2 heterostructures exhibit excellent photocatalytic performance with maximum phenol and nitrobenzene degradation rates of 96% and 94% and corresponding mineralization rates of 66% and 61% in 300 min under visible light irradiation, respectively. The improved photocatalytic performance is mainly ascribed to the reduced electron–hole pair recombination with the introduction of TiO2.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (148 K)Download as PowerPoint slide