| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606521 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2016 | 6 Pages |
The facile and low cost simple chemical bath deposition (CBD) method is employed to synthesize red colored selenium thin films. These selenium films are characterized for structural, morphological, topographical and wettability studies. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern showed the crystalline nature of selenium thin film with hexagonal crystal structure. The scanning electron microscopy (SEM) study displays selenium nanoparticles ranging from 20 to 475 nm. A specific surface area of 30.5 m2 g−1 is observed for selenium nanoparticles. The selenium nanoparticles hold mesopores in the range of 1.39 nm, taking benefits of the good physicochemical stability and excellent porosity. Subsequently, the electrochemical properties of selenium thin films are deliberated by cyclic voltammetry (CV), galvanostatic charge–discharge and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) techniques. The selenium thin film shows specific capacitance (Cs) of 21.98 F g−1 with 91% electrochemical stability.
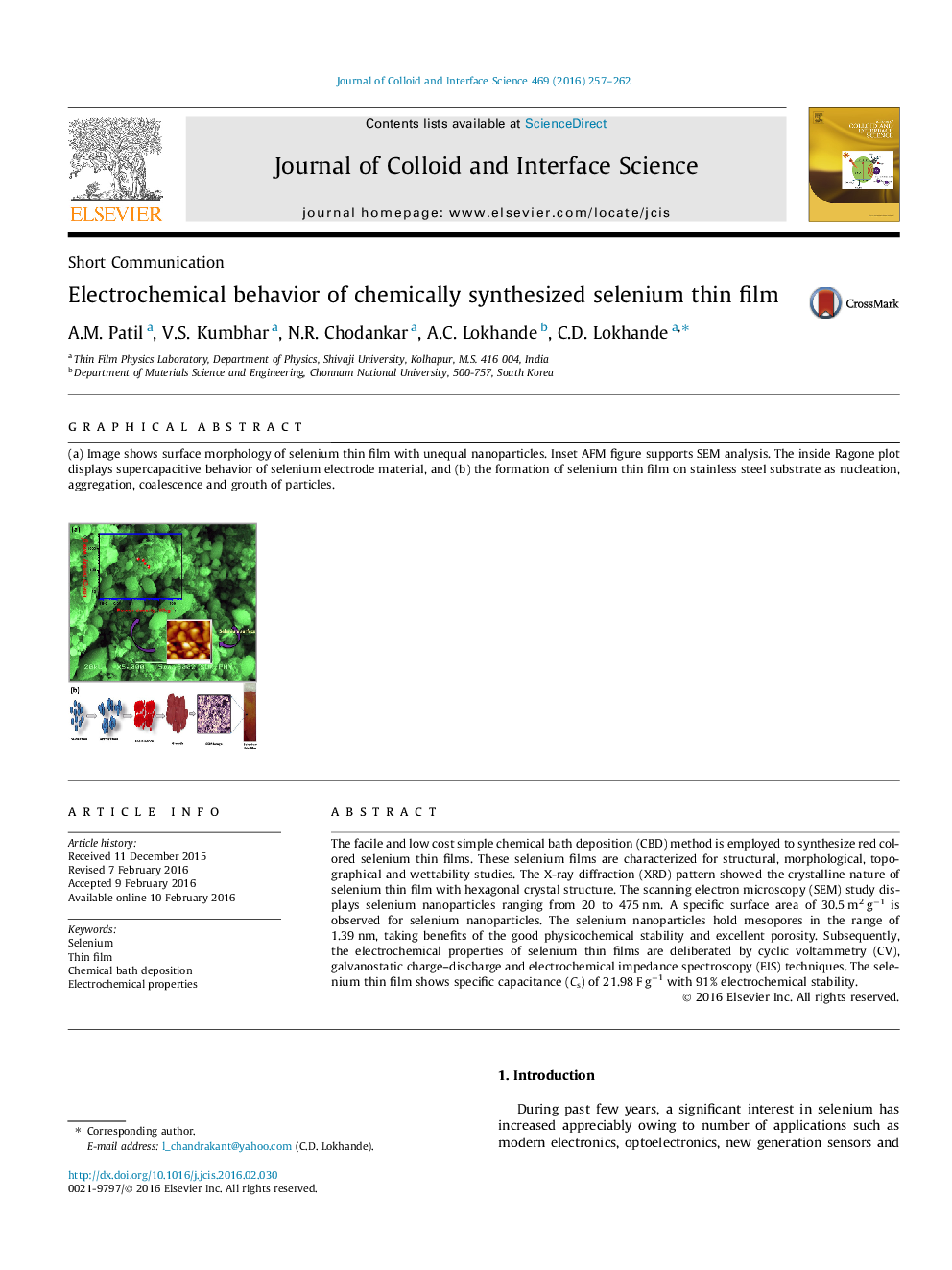
Graphical abstract(a) Image shows surface morphology of selenium thin film with unequal nanoparticles. Inset AFM figure supports SEM analysis. The inside Ragone plot displays supercapacitive behavior of selenium electrode material, and (b) the formation of selenium thin film on stainless steel substrate as nucleation, aggregation, coalescence and grouth of particles.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (169 K)Download as PowerPoint slide