| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606685 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2015 | 7 Pages |
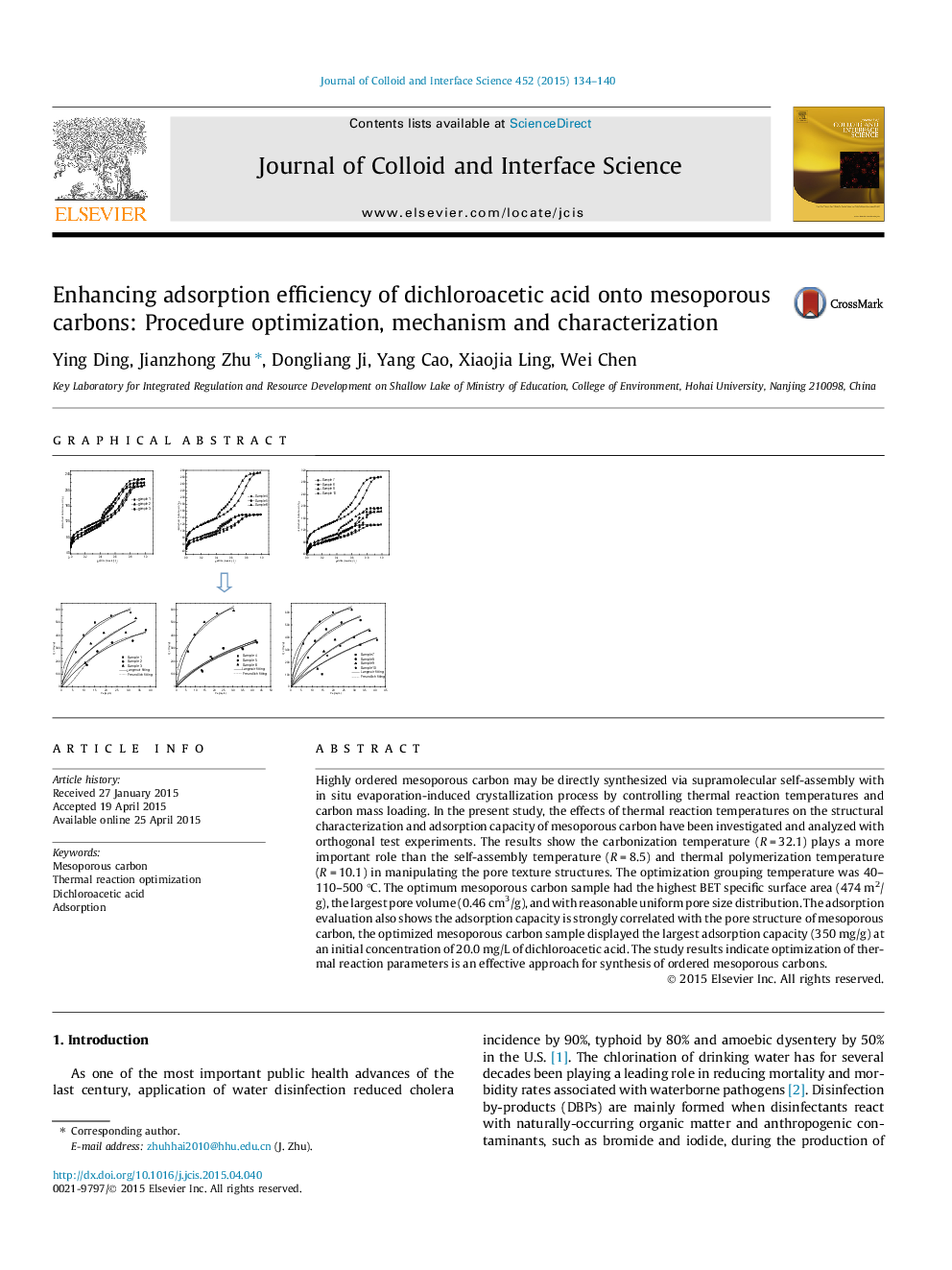
Highly ordered mesoporous carbon may be directly synthesized via supramolecular self-assembly with in situ evaporation-induced crystallization process by controlling thermal reaction temperatures and carbon mass loading. In the present study, the effects of thermal reaction temperatures on the structural characterization and adsorption capacity of mesoporous carbon have been investigated and analyzed with orthogonal test experiments. The results show the carbonization temperature (R = 32.1) plays a more important role than the self-assembly temperature (R = 8.5) and thermal polymerization temperature (R = 10.1) in manipulating the pore texture structures. The optimization grouping temperature was 40–110–500 °C. The optimum mesoporous carbon sample had the highest BET specific surface area (474 m2/g), the largest pore volume (0.46 cm3/g), and with reasonable uniform pore size distribution. The adsorption evaluation also shows the adsorption capacity is strongly correlated with the pore structure of mesoporous carbon, the optimized mesoporous carbon sample displayed the largest adsorption capacity (350 mg/g) at an initial concentration of 20.0 mg/L of dichloroacetic acid. The study results indicate optimization of thermal reaction parameters is an effective approach for synthesis of ordered mesoporous carbons.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (65 K)Download as PowerPoint slide