| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 606760 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2015 | 10 Pages |
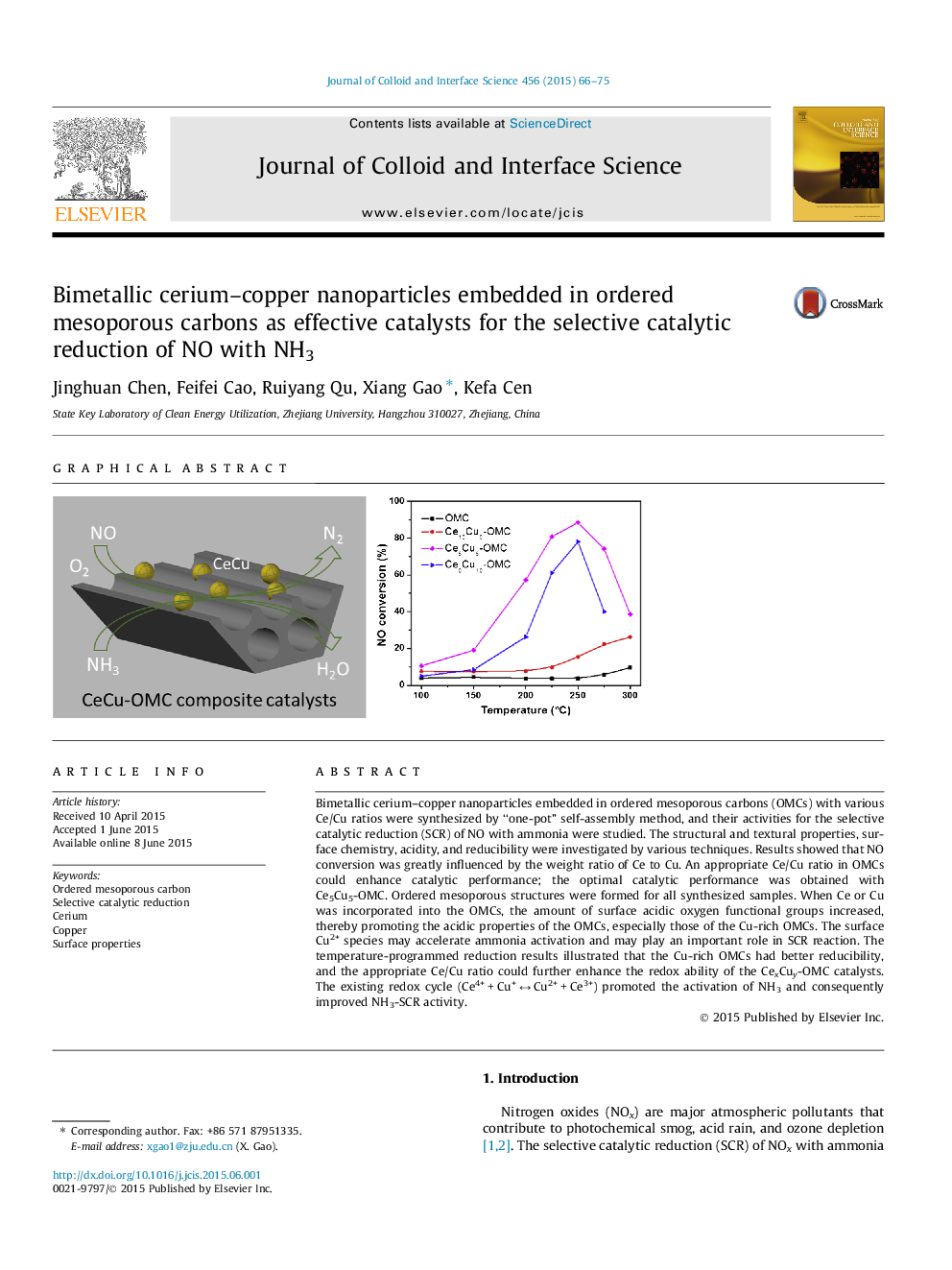
Bimetallic cerium–copper nanoparticles embedded in ordered mesoporous carbons (OMCs) with various Ce/Cu ratios were synthesized by “one-pot” self-assembly method, and their activities for the selective catalytic reduction (SCR) of NO with ammonia were studied. The structural and textural properties, surface chemistry, acidity, and reducibility were investigated by various techniques. Results showed that NO conversion was greatly influenced by the weight ratio of Ce to Cu. An appropriate Ce/Cu ratio in OMCs could enhance catalytic performance; the optimal catalytic performance was obtained with Ce5Cu5-OMC. Ordered mesoporous structures were formed for all synthesized samples. When Ce or Cu was incorporated into the OMCs, the amount of surface acidic oxygen functional groups increased, thereby promoting the acidic properties of the OMCs, especially those of the Cu-rich OMCs. The surface Cu2+ species may accelerate ammonia activation and may play an important role in SCR reaction. The temperature-programmed reduction results illustrated that the Cu-rich OMCs had better reducibility, and the appropriate Ce/Cu ratio could further enhance the redox ability of the CexCuy-OMC catalysts. The existing redox cycle (Ce4+ + Cu+ ↔ Cu2+ + Ce3+) promoted the activation of NH3 and consequently improved NH3-SCR activity.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload high-quality image (151 K)Download as PowerPoint slide