| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 612980 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2006 | 6 Pages |
The natural bentonite used in this study contained montmorillonite in addition to low cristobalite. The uptake of aqueous Co2+ ions was investigated as a function of time, concentration, and temperature. In addition, the change in the interlayer space of montmorillonite was analyzed using XRPD, and the distribution of fixed Co2+ ions on the heterogeneous clay surface was recorded using EDS mapping. The sorbed amount of Co2+ appeared to closely follow Freundlich isotherm, with the sorption process showing apparent endothermic behavior. The relevance of the apparent ΔHoΔHo values is briefly discussed. Analysis of the Co-sorbed bentonite samples using SEM/EDS showed that the montmorillonite fraction in the mineral was more effective in Co2+ fixation than the cristobalite fraction. XRPD analysis demonstrated that the interlayer space of montmorillonite was slightly modified at the end of sorption.
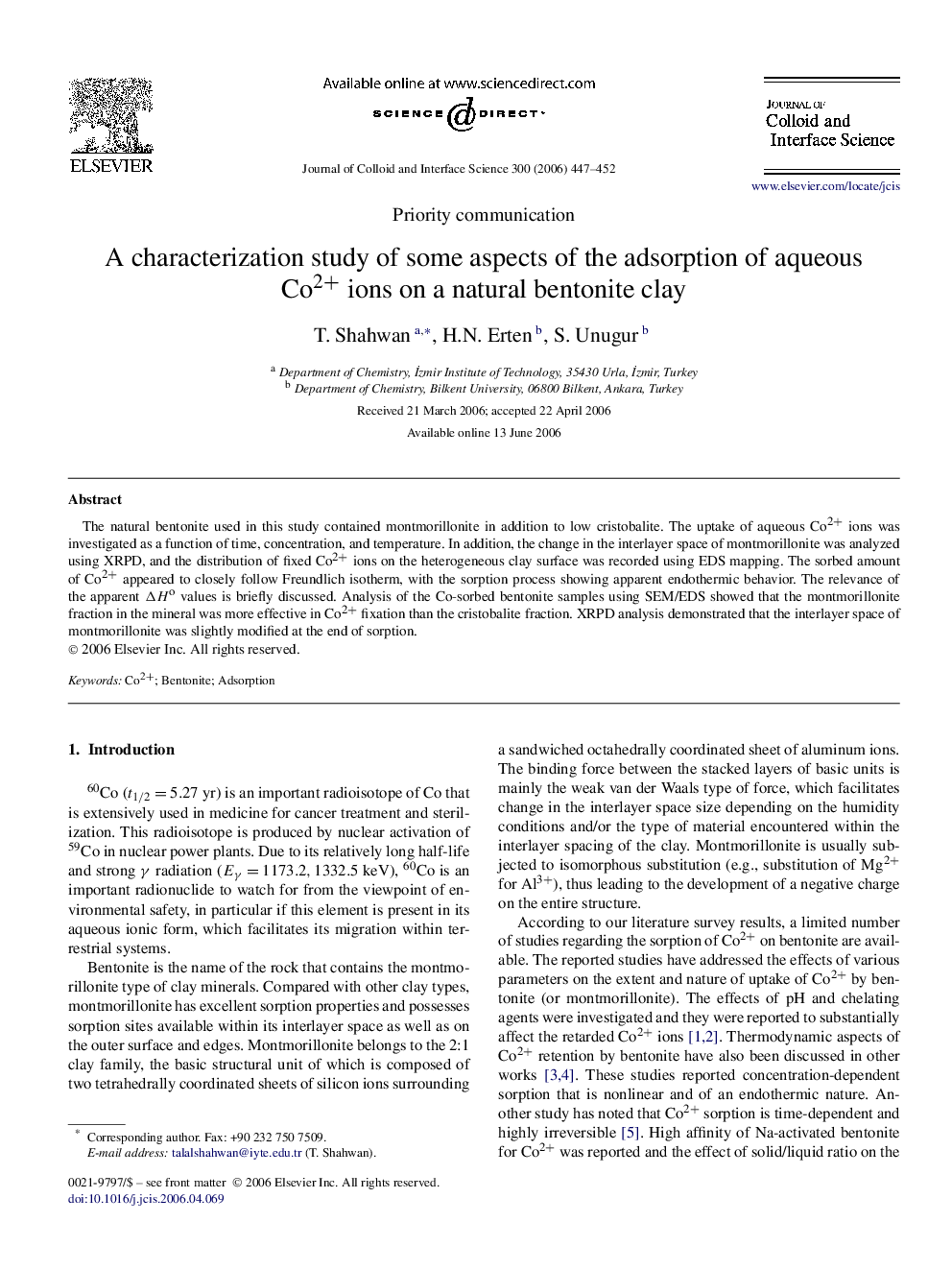
Graphical abstractX-ray diffraction patterns of montmorillonite before (i) and after Co2+ sorption (ii, iii, iv). The figures show slight changes in the d001d001 features of montmorillonite following sorption.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide