| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 645800 | Applied Thermal Engineering | 2014 | 6 Pages |
•Discontinuous graphite fiber/Cu composites for heat sink applications are developed.•The Cr element is pre-coated on graphite fiber to improve interfacial bonding.•The formed Cr3C2 layer helps to enhance thermal conductivity and reduce CTE.•The composites have high thermal conductivity, low CTE and good machinability.
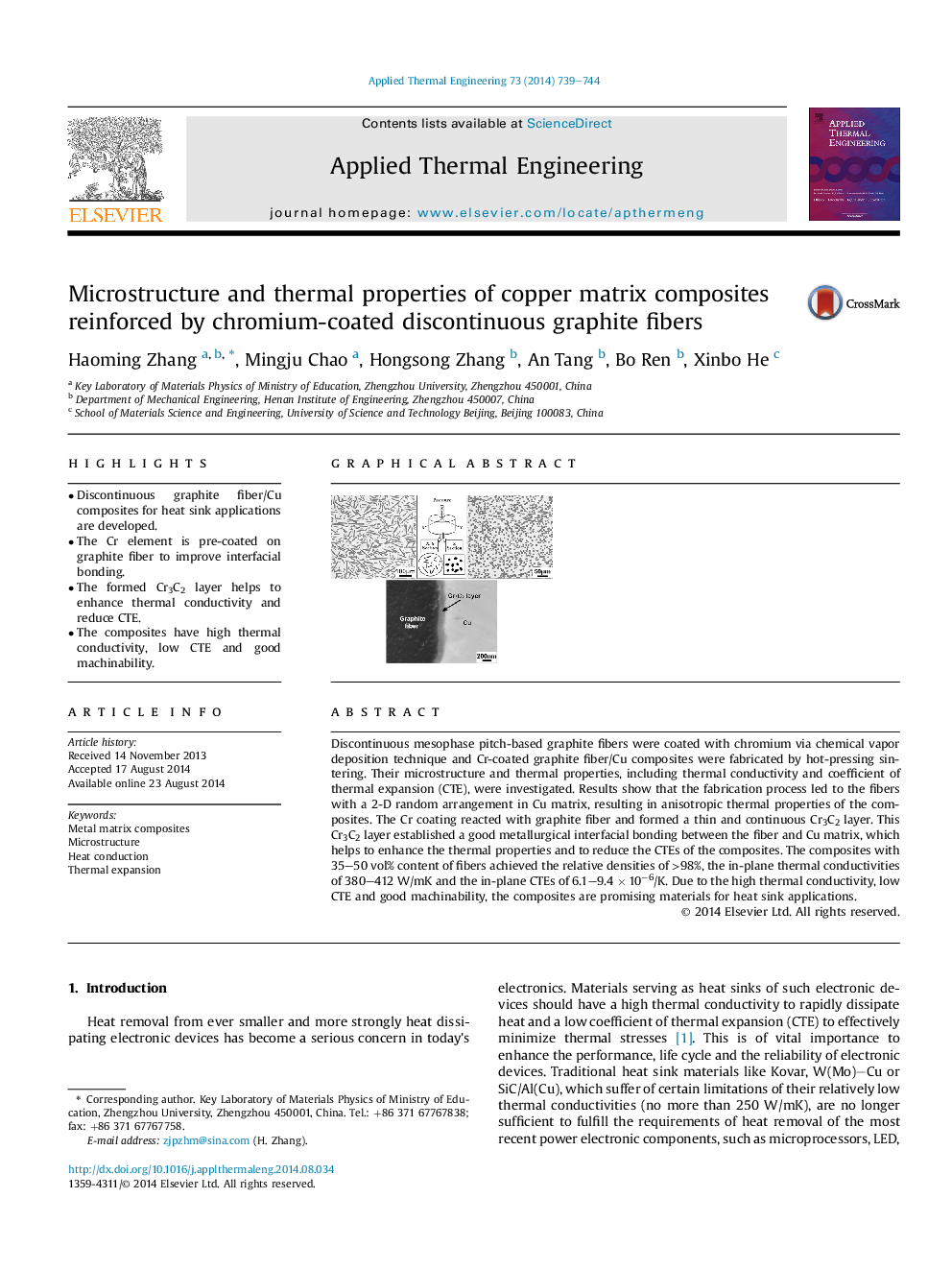
Discontinuous mesophase pitch-based graphite fibers were coated with chromium via chemical vapor deposition technique and Cr-coated graphite fiber/Cu composites were fabricated by hot-pressing sintering. Their microstructure and thermal properties, including thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), were investigated. Results show that the fabrication process led to the fibers with a 2-D random arrangement in Cu matrix, resulting in anisotropic thermal properties of the composites. The Cr coating reacted with graphite fiber and formed a thin and continuous Cr3C2 layer. This Cr3C2 layer established a good metallurgical interfacial bonding between the fiber and Cu matrix, which helps to enhance the thermal properties and to reduce the CTEs of the composites. The composites with 35–50 vol% content of fibers achieved the relative densities of >98%, the in-plane thermal conductivities of 380–412 W/mK and the in-plane CTEs of 6.1–9.4 × 10−6/K. Due to the high thermal conductivity, low CTE and good machinability, the composites are promising materials for heat sink applications.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide