| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 646115 | Applied Thermal Engineering | 2014 | 7 Pages |
•Different internal structures and thickness of heat exchangers were proposed.•Power output testing system of the two heat exchangers was characterized.•Chaos-shaped heat exchanger (5 mm thickness) shows better performance.
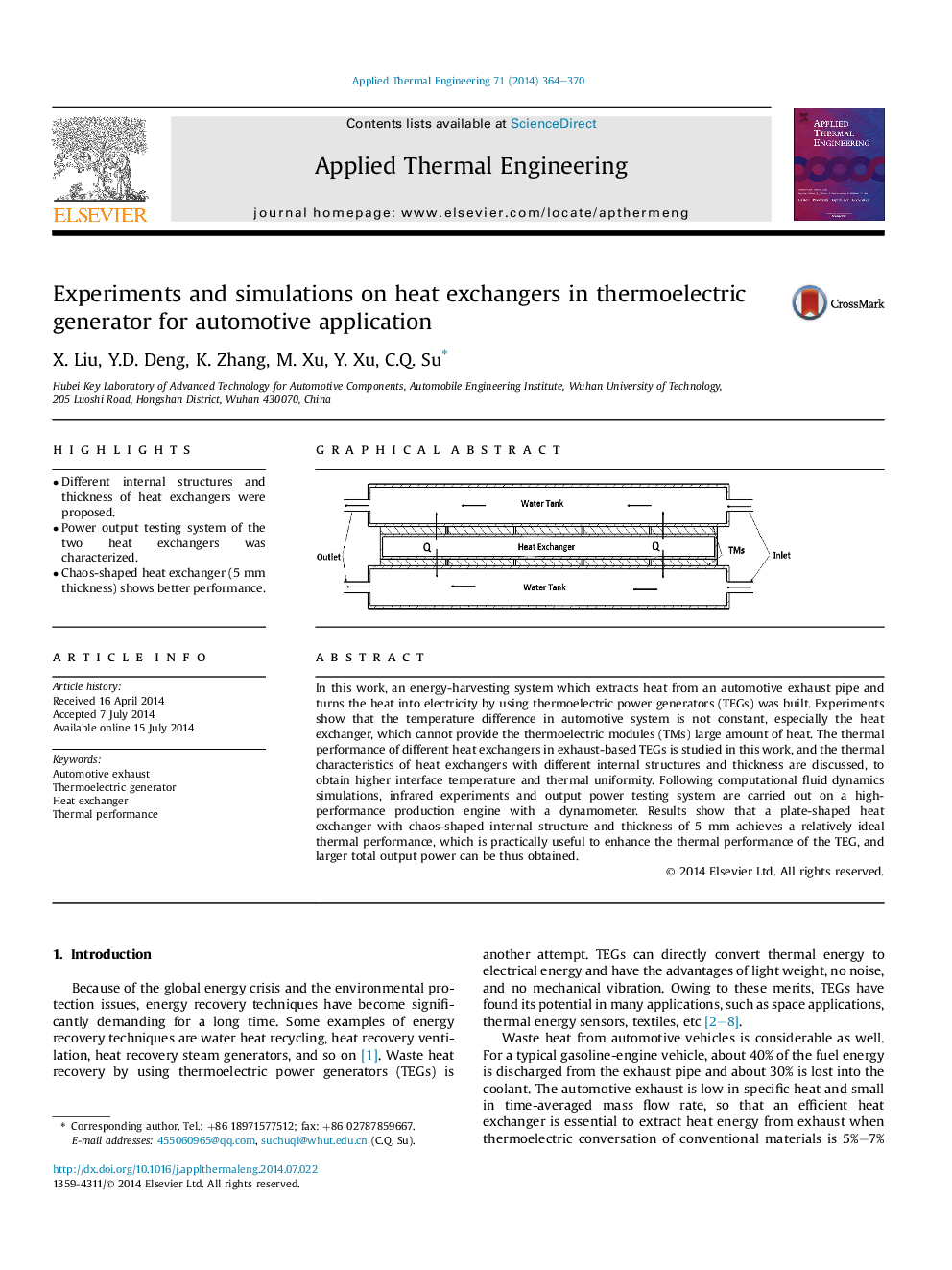
In this work, an energy-harvesting system which extracts heat from an automotive exhaust pipe and turns the heat into electricity by using thermoelectric power generators (TEGs) was built. Experiments show that the temperature difference in automotive system is not constant, especially the heat exchanger, which cannot provide the thermoelectric modules (TMs) large amount of heat. The thermal performance of different heat exchangers in exhaust-based TEGs is studied in this work, and the thermal characteristics of heat exchangers with different internal structures and thickness are discussed, to obtain higher interface temperature and thermal uniformity. Following computational fluid dynamics simulations, infrared experiments and output power testing system are carried out on a high-performance production engine with a dynamometer. Results show that a plate-shaped heat exchanger with chaos-shaped internal structure and thickness of 5 mm achieves a relatively ideal thermal performance, which is practically useful to enhance the thermal performance of the TEG, and larger total output power can be thus obtained.
Graphical abstractThe thermal and electrical characteristics of different heat exchangers of automotive exhaust-based thermoelectric generator are discussed, to obtain higher interface temperature and thermal uniformity.Figure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide