| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6478661 | Applied Energy | 2017 | 9 Pages |
â¢A case study of a geothermal heat pump in an office building.â¢A numerical model in EnergyPlus is validated by experimental results.â¢An energy, economic and environmental analysis is presented.â¢A comparison with other technologies demonstrates the potential of the system.
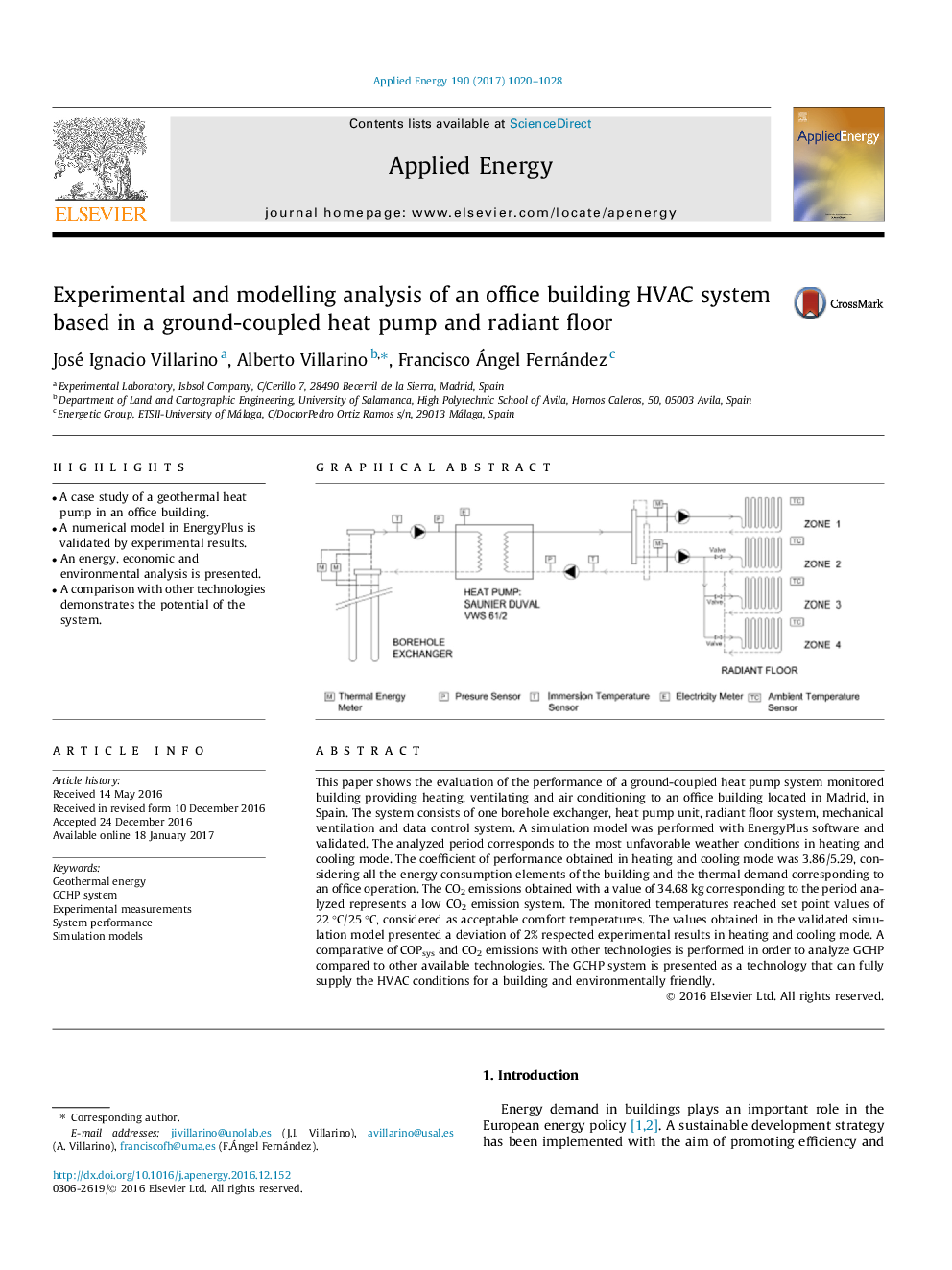
This paper shows the evaluation of the performance of a ground-coupled heat pump system monitored building providing heating, ventilating and air conditioning to an office building located in Madrid, in Spain. The system consists of one borehole exchanger, heat pump unit, radiant floor system, mechanical ventilation and data control system. A simulation model was performed with EnergyPlus software and validated. The analyzed period corresponds to the most unfavorable weather conditions in heating and cooling mode. The coefficient of performance obtained in heating and cooling mode was 3.86/5.29, considering all the energy consumption elements of the building and the thermal demand corresponding to an office operation. The CO2 emissions obtained with a value of 34.68 kg corresponding to the period analyzed represents a low CO2 emission system. The monitored temperatures reached set point values of 22 °C/25 °C, considered as acceptable comfort temperatures. The values obtained in the validated simulation model presented a deviation of 2% respected experimental results in heating and cooling mode. A comparative of COPsys and CO2 emissions with other technologies is performed in order to analyze GCHP compared to other available technologies. The GCHP system is presented as a technology that can fully supply the HVAC conditions for a building and environmentally friendly.
Graphical abstractDownload high-res image (59KB)Download full-size image