| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6995780 | Journal of Colloid and Interface Science | 2015 | 7 Pages |
Abstract
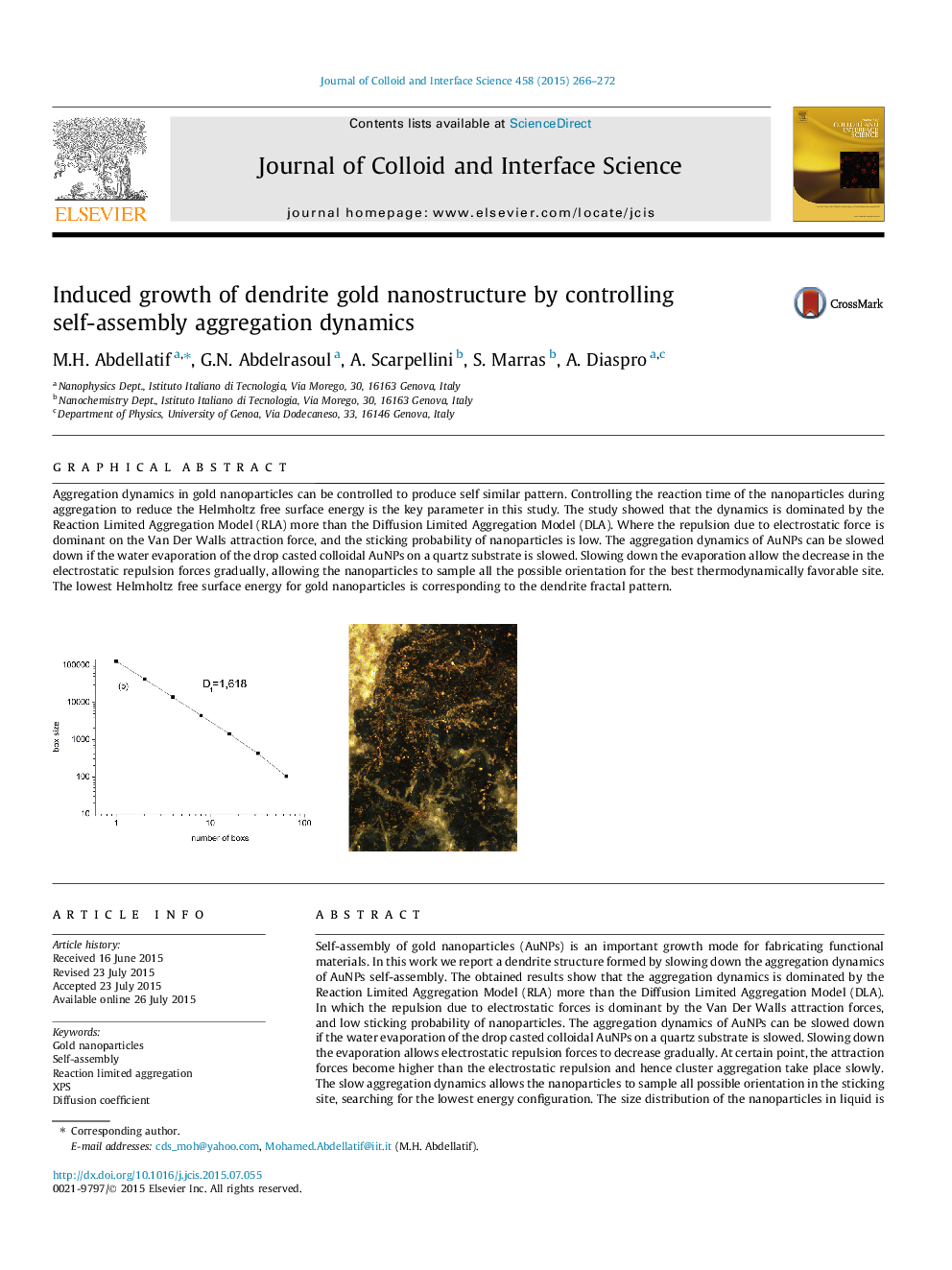
Aggregation dynamics in gold nanoparticles can be controlled to produce self similar pattern. Controlling the reaction time of the nanoparticles during aggregation to reduce the Helmholtz free surface energy is the key parameter in this study. The study showed that the dynamics is dominated by the Reaction Limited Aggregation Model (RLA) more than the Diffusion Limited Aggregation Model (DLA). Where the repulsion due to electrostatic force is dominant on the Van Der Walls attraction force, and the sticking probability of nanoparticles is low. The aggregation dynamics of AuNPs can be slowed down if the water evaporation of the drop casted colloidal AuNPs on a quartz substrate is slowed. Slowing down the evaporation allow the decrease in the electrostatic repulsion forces gradually, allowing the nanoparticles to sample all the possible orientation for the best thermodynamically favorable site. The lowest Helmholtz free surface energy for gold nanoparticles is corresponding to the dendrite fractal pattern.214
Related Topics
Physical Sciences and Engineering
Chemical Engineering
Colloid and Surface Chemistry
Authors
M.H. Abdellatif, G.N. Abdelrasoul, A. Scarpellini, S. Marras, A. Diaspro,