| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1284290 | Journal of Power Sources | 2014 | 8 Pages |
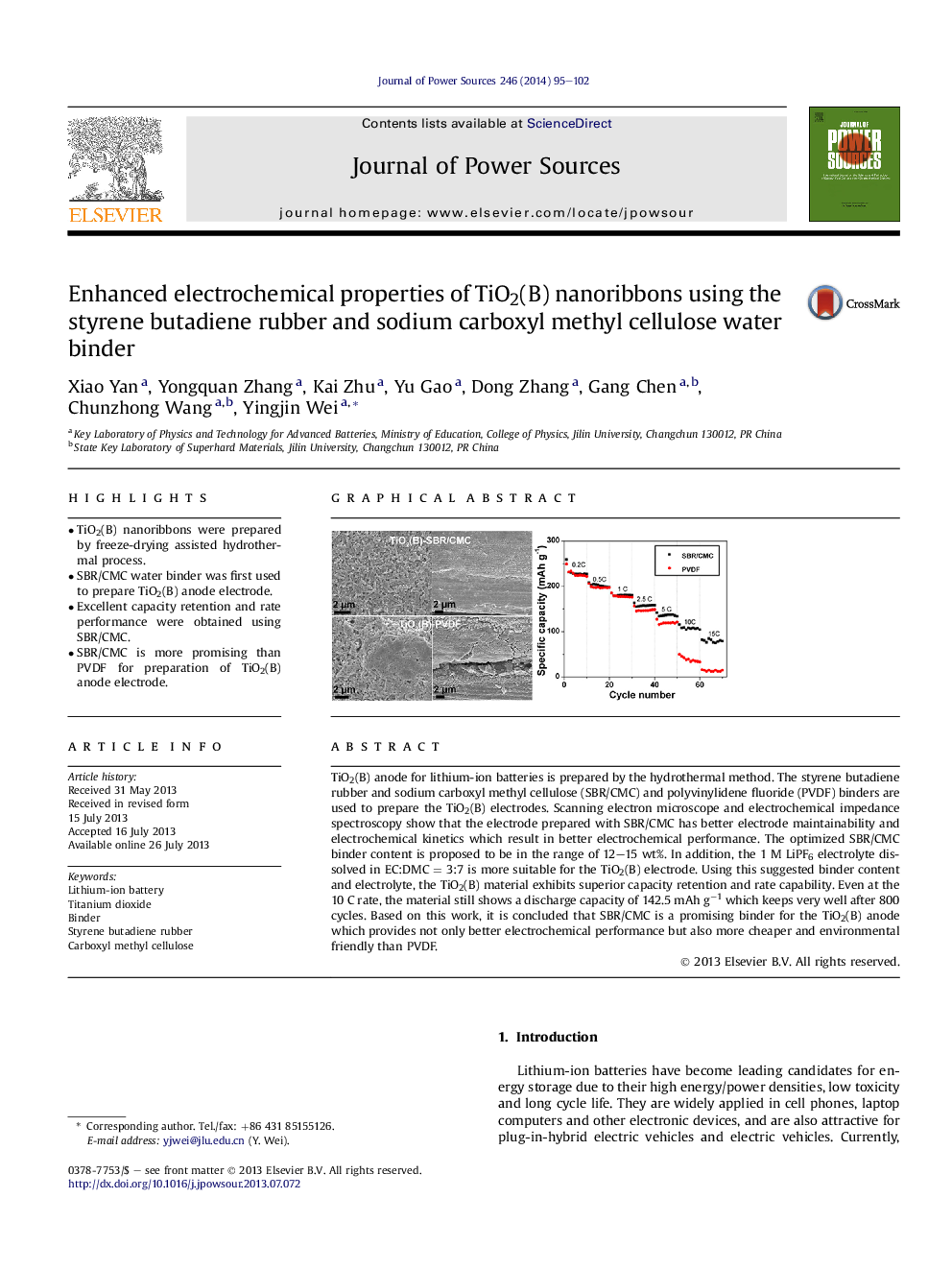
•TiO2(B) nanoribbons were prepared by freeze-drying assisted hydrothermal process.•SBR/CMC water binder was first used to prepare TiO2(B) anode electrode.•Excellent capacity retention and rate performance were obtained using SBR/CMC.•SBR/CMC is more promising than PVDF for preparation of TiO2(B) anode electrode.
TiO2(B) anode for lithium-ion batteries is prepared by the hydrothermal method. The styrene butadiene rubber and sodium carboxyl methyl cellulose (SBR/CMC) and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) binders are used to prepare the TiO2(B) electrodes. Scanning electron microscope and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy show that the electrode prepared with SBR/CMC has better electrode maintainability and electrochemical kinetics which result in better electrochemical performance. The optimized SBR/CMC binder content is proposed to be in the range of 12–15 wt%. In addition, the 1 M LiPF6 electrolyte dissolved in EC:DMC = 3:7 is more suitable for the TiO2(B) electrode. Using this suggested binder content and electrolyte, the TiO2(B) material exhibits superior capacity retention and rate capability. Even at the 10 C rate, the material still shows a discharge capacity of 142.5 mAh g−1 which keeps very well after 800 cycles. Based on this work, it is concluded that SBR/CMC is a promising binder for the TiO2(B) anode which provides not only better electrochemical performance but also more cheaper and environmental friendly than PVDF.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide