| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1285757 | Journal of Power Sources | 2016 | 7 Pages |
•3D macroporous nitrogen doped graphene is synthesised by ice-templating method.•Nitrogen is uniformly distributed on the 3D graphene surface.•Hierarchal porous structure is constructed in 3D graphene architecture.•3D porous nitrogen doped graphene achieves excellent supercapacitive performances.
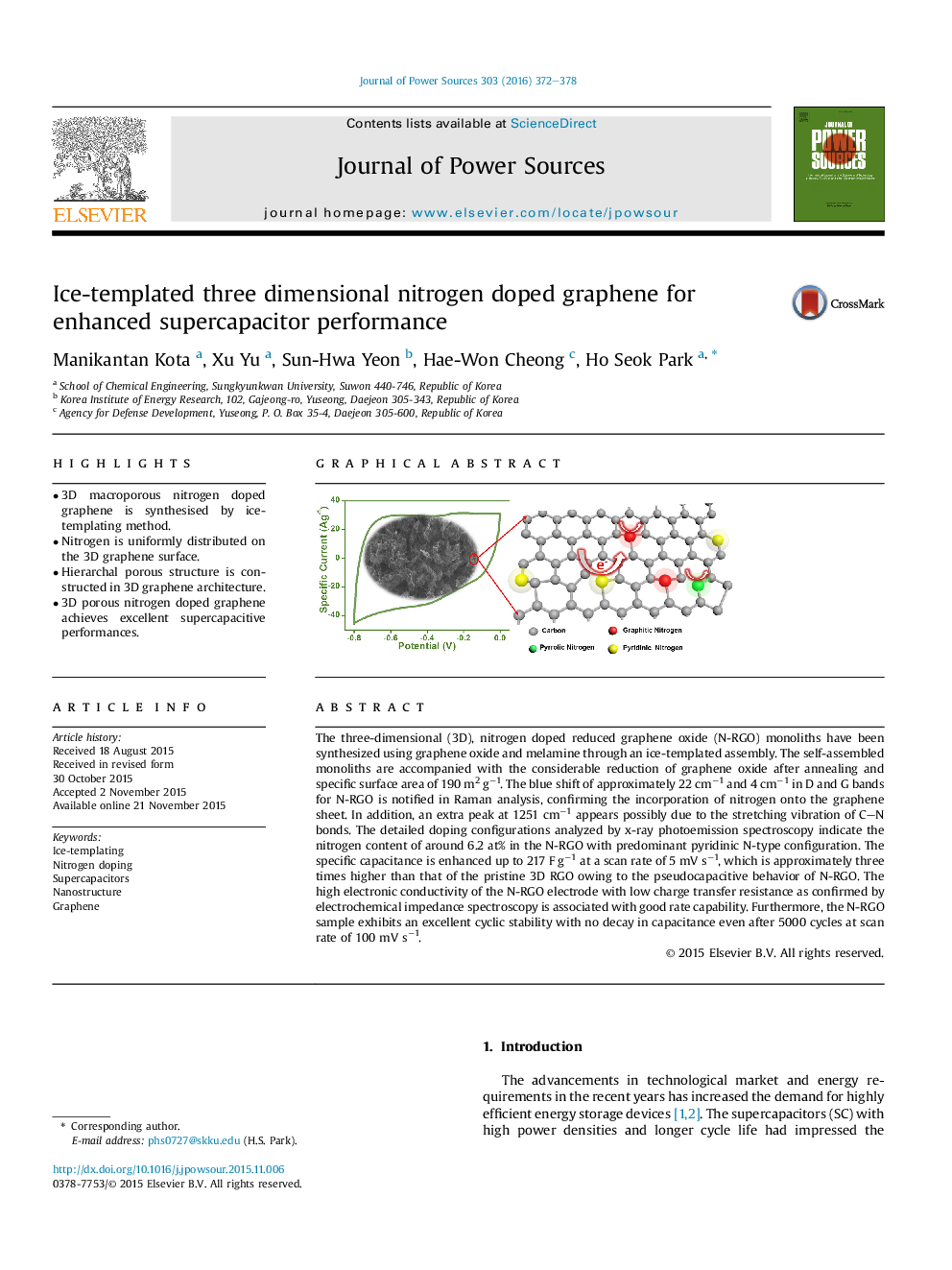
The three-dimensional (3D), nitrogen doped reduced graphene oxide (N-RGO) monoliths have been synthesized using graphene oxide and melamine through an ice-templated assembly. The self-assembled monoliths are accompanied with the considerable reduction of graphene oxide after annealing and specific surface area of 190 m2 g−1. The blue shift of approximately 22 cm−1 and 4 cm−1 in D and G bands for N-RGO is notified in Raman analysis, confirming the incorporation of nitrogen onto the graphene sheet. In addition, an extra peak at 1251 cm−1 appears possibly due to the stretching vibration of C–N bonds. The detailed doping configurations analyzed by x-ray photoemission spectroscopy indicate the nitrogen content of around 6.2 at% in the N-RGO with predominant pyridinic N-type configuration. The specific capacitance is enhanced up to 217 F g−1 at a scan rate of 5 mV s−1, which is approximately three times higher than that of the pristine 3D RGO owing to the pseudocapacitive behavior of N-RGO. The high electronic conductivity of the N-RGO electrode with low charge transfer resistance as confirmed by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy is associated with good rate capability. Furthermore, the N-RGO sample exhibits an excellent cyclic stability with no decay in capacitance even after 5000 cycles at scan rate of 100 mV s−1.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide