| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1286264 | Journal of Power Sources | 2016 | 6 Pages |
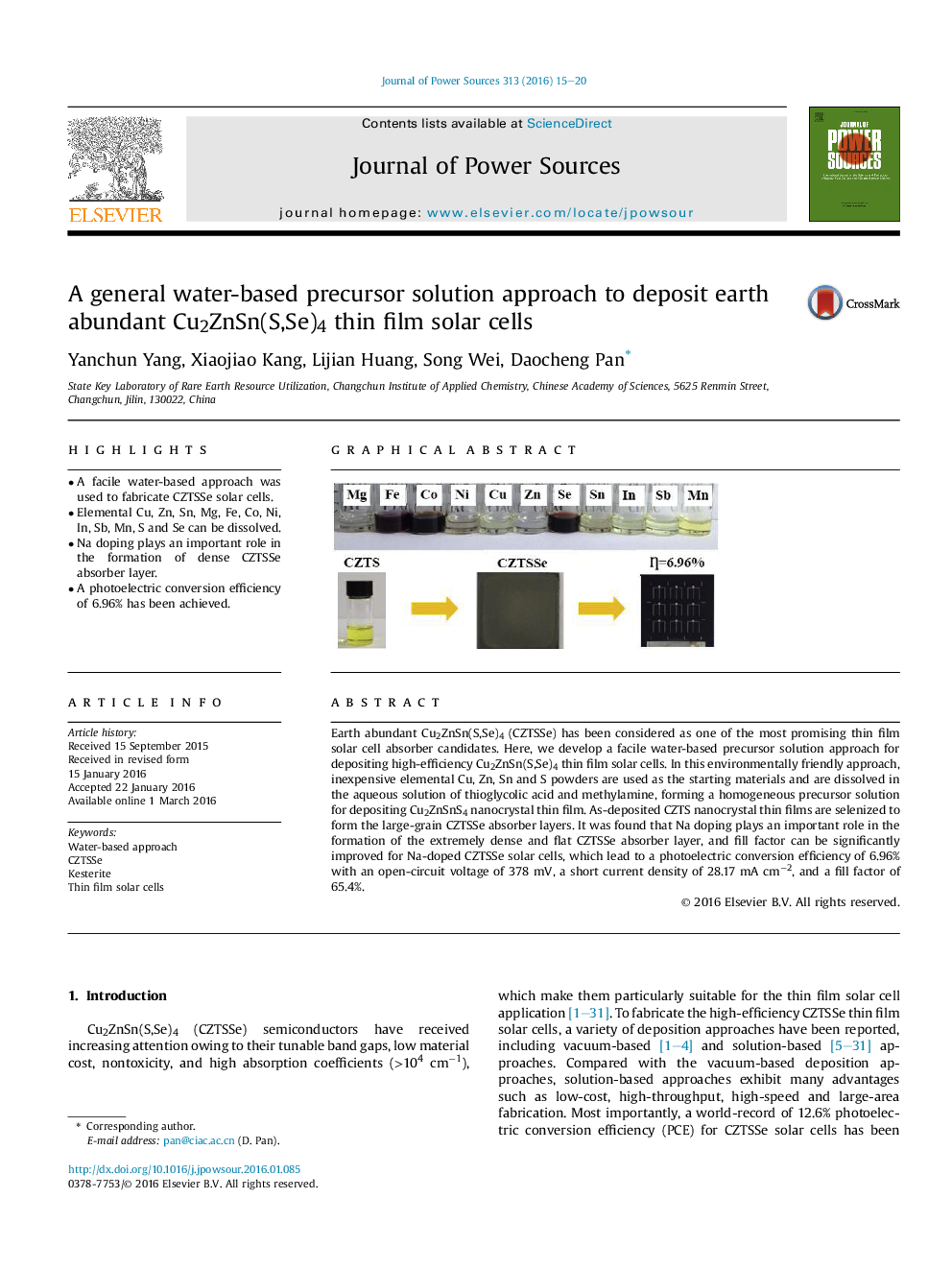
•A facile water-based approach was used to fabricate CZTSSe solar cells.•Elemental Cu, Zn, Sn, Mg, Fe, Co, Ni, In, Sb, Mn, S and Se can be dissolved.•Na doping plays an important role in the formation of dense CZTSSe absorber layer.•A photoelectric conversion efficiency of 6.96% has been achieved.
Earth abundant Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 (CZTSSe) has been considered as one of the most promising thin film solar cell absorber candidates. Here, we develop a facile water-based precursor solution approach for depositing high-efficiency Cu2ZnSn(S,Se)4 thin film solar cells. In this environmentally friendly approach, inexpensive elemental Cu, Zn, Sn and S powders are used as the starting materials and are dissolved in the aqueous solution of thioglycolic acid and methylamine, forming a homogeneous precursor solution for depositing Cu2ZnSnS4 nanocrystal thin film. As-deposited CZTS nanocrystal thin films are selenized to form the large-grain CZTSSe absorber layers. It was found that Na doping plays an important role in the formation of the extremely dense and flat CZTSSe absorber layer, and fill factor can be significantly improved for Na-doped CZTSSe solar cells, which lead to a photoelectric conversion efficiency of 6.96% with an open-circuit voltage of 378 mV, a short current density of 28.17 mA cm−2, and a fill factor of 65.4%.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide