| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1286276 | Journal of Power Sources | 2015 | 8 Pages |
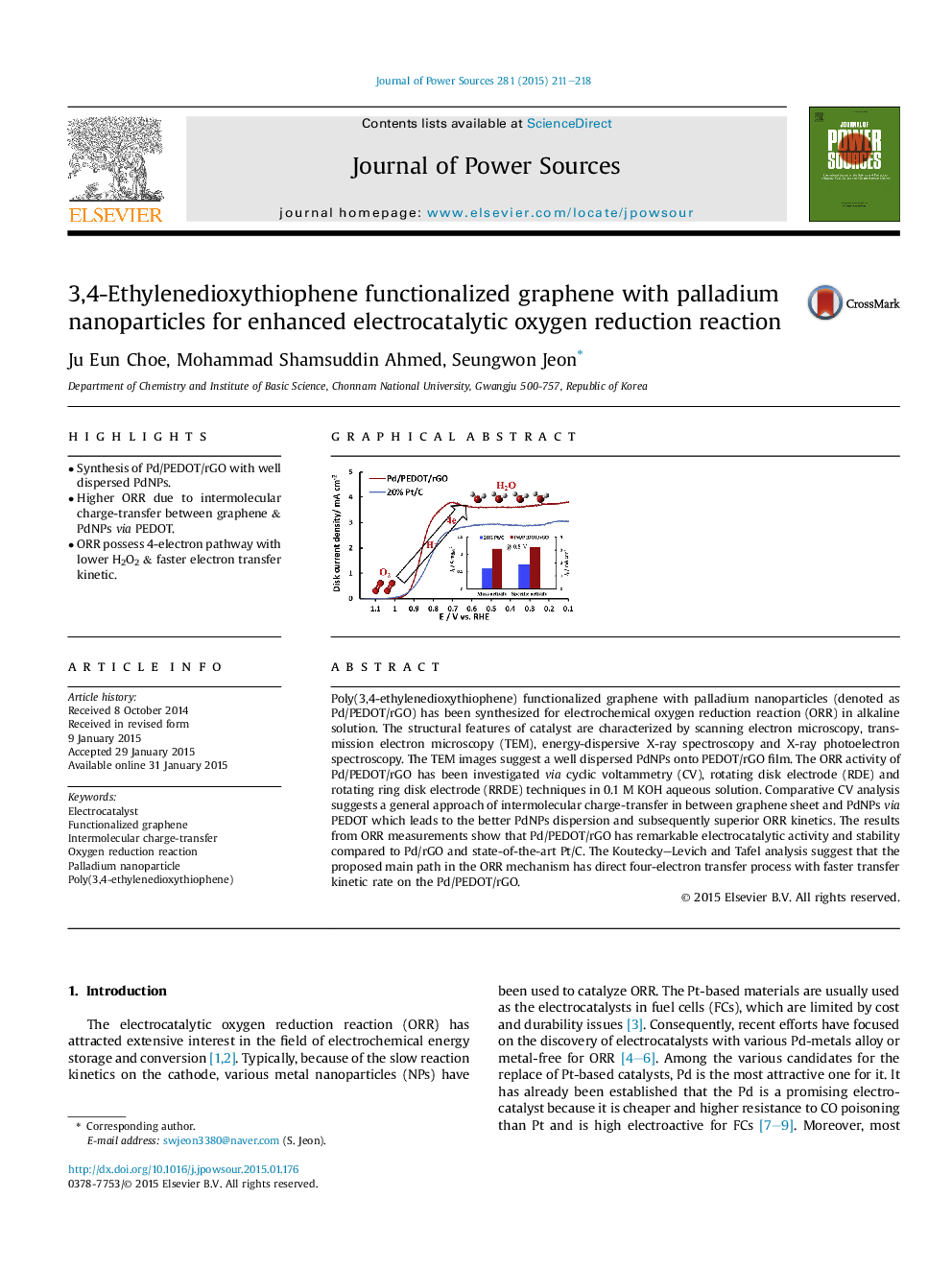
•Synthesis of Pd/PEDOT/rGO with well dispersed PdNPs.•Higher ORR due to intermolecular charge-transfer between graphene & PdNPs via PEDOT.•ORR possess 4-electron pathway with lower H2O2 & faster electron transfer kinetic.
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) functionalized graphene with palladium nanoparticles (denoted as Pd/PEDOT/rGO) has been synthesized for electrochemical oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in alkaline solution. The structural features of catalyst are characterized by scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The TEM images suggest a well dispersed PdNPs onto PEDOT/rGO film. The ORR activity of Pd/PEDOT/rGO has been investigated via cyclic voltammetry (CV), rotating disk electrode (RDE) and rotating ring disk electrode (RRDE) techniques in 0.1 M KOH aqueous solution. Comparative CV analysis suggests a general approach of intermolecular charge-transfer in between graphene sheet and PdNPs via PEDOT which leads to the better PdNPs dispersion and subsequently superior ORR kinetics. The results from ORR measurements show that Pd/PEDOT/rGO has remarkable electrocatalytic activity and stability compared to Pd/rGO and state-of-the-art Pt/C. The Koutecky–Levich and Tafel analysis suggest that the proposed main path in the ORR mechanism has direct four-electron transfer process with faster transfer kinetic rate on the Pd/PEDOT/rGO.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide