| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1286664 | Journal of Power Sources | 2014 | 9 Pages |
•The different performance of reported dyes was rationalized by DFT calculations.•Present a comprehensive strategy to design high-efficiency dye.•Designed dyes 6 and 7 are promising candidates to further improve efficiency.
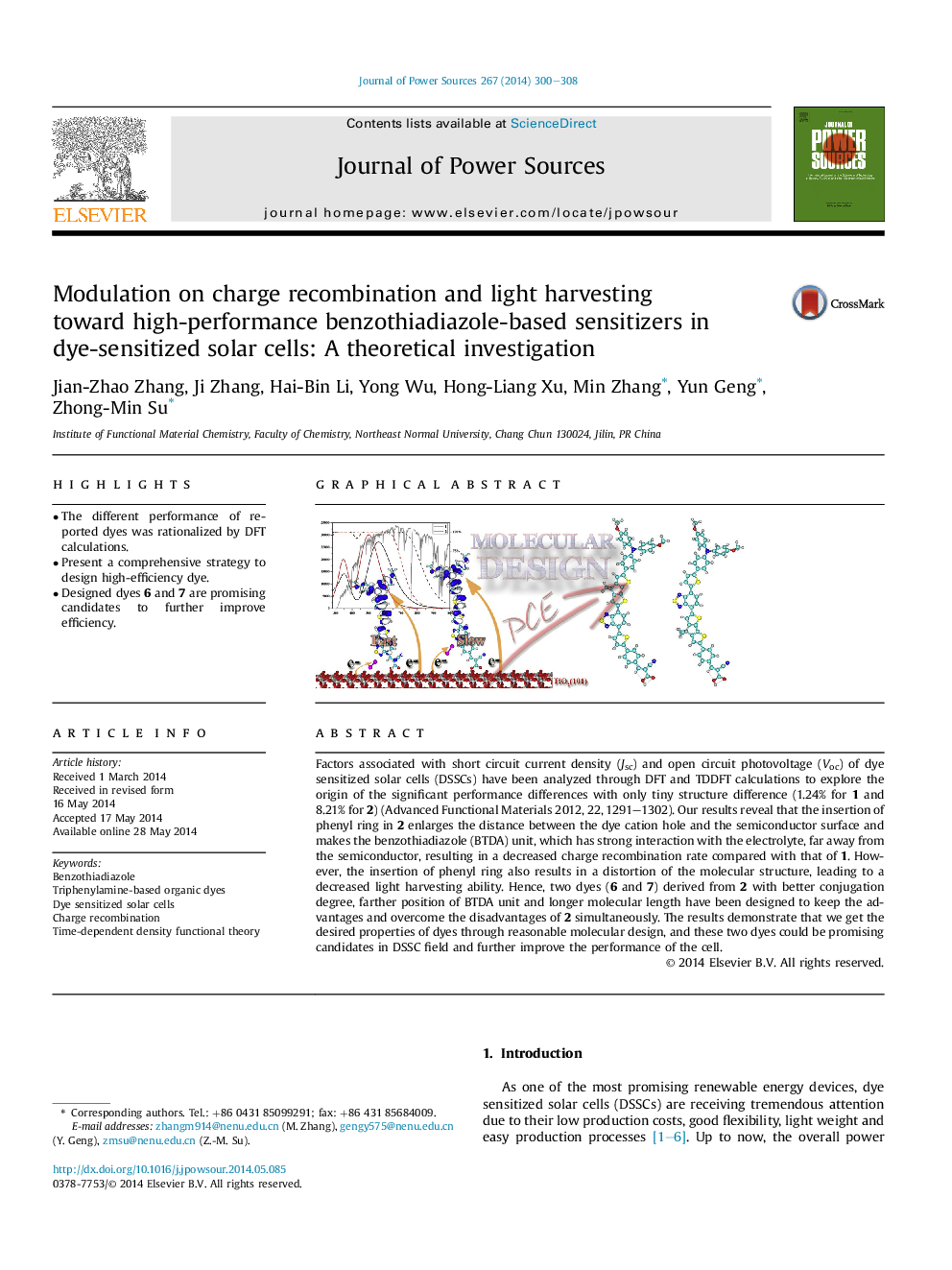
Factors associated with short circuit current density (Jsc) and open circuit photovoltage (Voc) of dye sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) have been analyzed through DFT and TDDFT calculations to explore the origin of the significant performance differences with only tiny structure difference (1.24% for 1 and 8.21% for 2) (Advanced Functional Materials 2012, 22, 1291–1302). Our results reveal that the insertion of phenyl ring in 2 enlarges the distance between the dye cation hole and the semiconductor surface and makes the benzothiadiazole (BTDA) unit, which has strong interaction with the electrolyte, far away from the semiconductor, resulting in a decreased charge recombination rate compared with that of 1. However, the insertion of phenyl ring also results in a distortion of the molecular structure, leading to a decreased light harvesting ability. Hence, two dyes (6 and 7) derived from 2 with better conjugation degree, farther position of BTDA unit and longer molecular length have been designed to keep the advantages and overcome the disadvantages of 2 simultaneously. The results demonstrate that we get the desired properties of dyes through reasonable molecular design, and these two dyes could be promising candidates in DSSC field and further improve the performance of the cell.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide