| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1286777 | Journal of Power Sources | 2014 | 9 Pages |
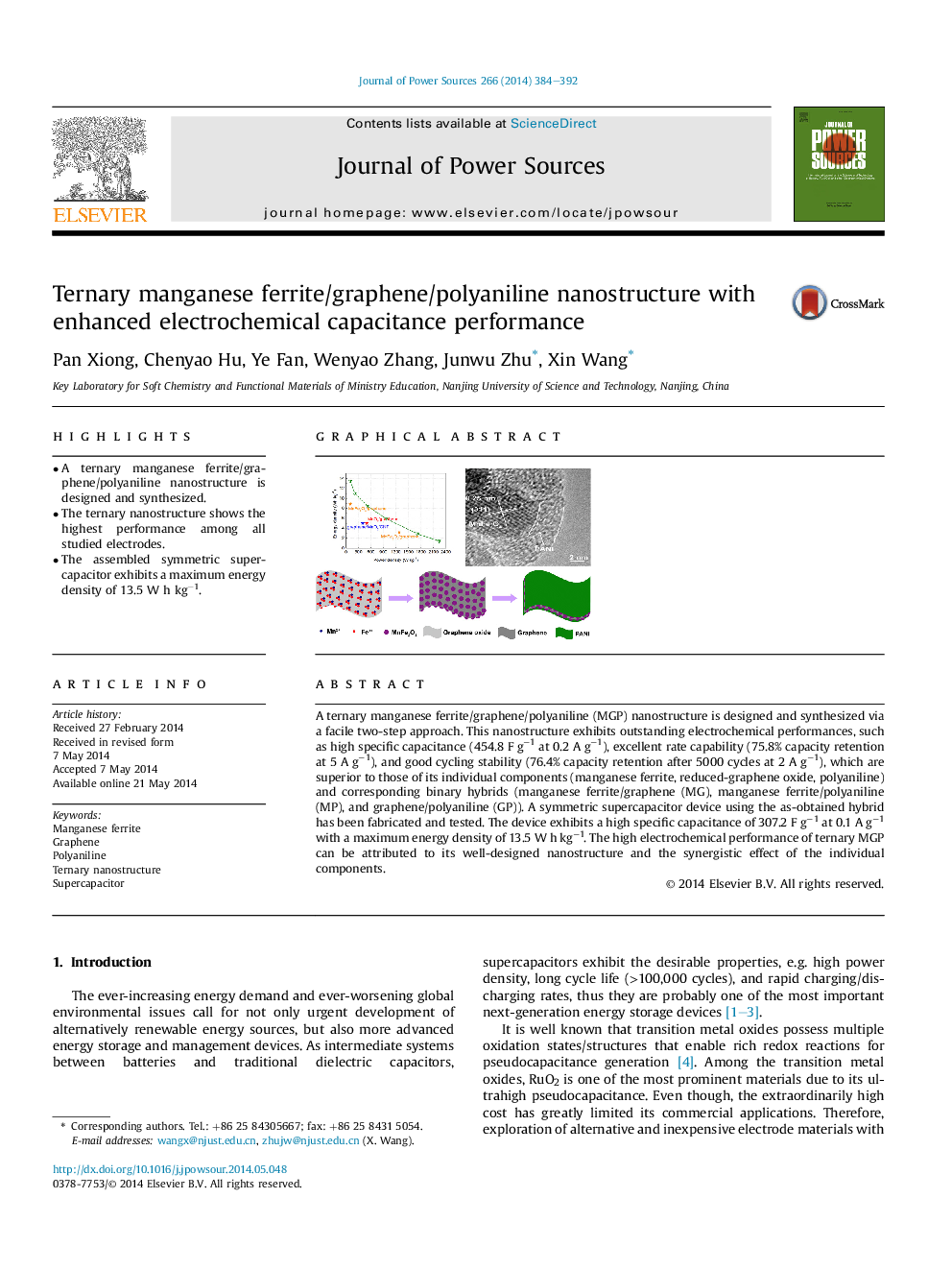
•A ternary manganese ferrite/graphene/polyaniline nanostructure is designed and synthesized.•The ternary nanostructure shows the highest performance among all studied electrodes.•The assembled symmetric supercapacitor exhibits a maximum energy density of 13.5 W h kg−1.
A ternary manganese ferrite/graphene/polyaniline (MGP) nanostructure is designed and synthesized via a facile two-step approach. This nanostructure exhibits outstanding electrochemical performances, such as high specific capacitance (454.8 F g−1 at 0.2 A g−1), excellent rate capability (75.8% capacity retention at 5 A g−1), and good cycling stability (76.4% capacity retention after 5000 cycles at 2 A g−1), which are superior to those of its individual components (manganese ferrite, reduced-graphene oxide, polyaniline) and corresponding binary hybrids (manganese ferrite/graphene (MG), manganese ferrite/polyaniline (MP), and graphene/polyaniline (GP)). A symmetric supercapacitor device using the as-obtained hybrid has been fabricated and tested. The device exhibits a high specific capacitance of 307.2 F g−1 at 0.1 A g−1 with a maximum energy density of 13.5 W h kg−1. The high electrochemical performance of ternary MGP can be attributed to its well-designed nanostructure and the synergistic effect of the individual components.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slide