| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1287666 | Journal of Power Sources | 2013 | 7 Pages |
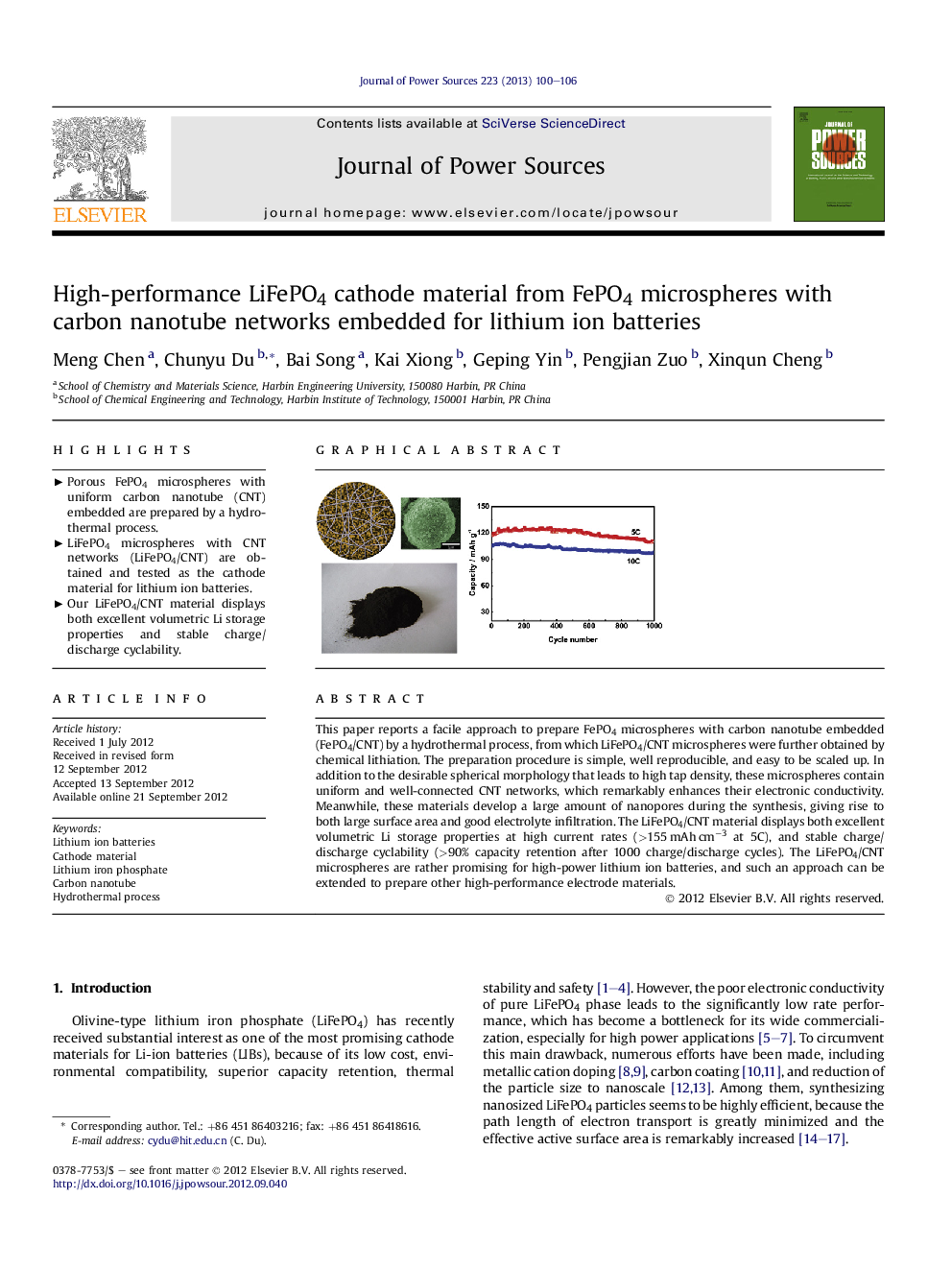
This paper reports a facile approach to prepare FePO4 microspheres with carbon nanotube embedded (FePO4/CNT) by a hydrothermal process, from which LiFePO4/CNT microspheres were further obtained by chemical lithiation. The preparation procedure is simple, well reproducible, and easy to be scaled up. In addition to the desirable spherical morphology that leads to high tap density, these microspheres contain uniform and well-connected CNT networks, which remarkably enhances their electronic conductivity. Meanwhile, these materials develop a large amount of nanopores during the synthesis, giving rise to both large surface area and good electrolyte infiltration. The LiFePO4/CNT material displays both excellent volumetric Li storage properties at high current rates (>155 mAh cm−3 at 5C), and stable charge/discharge cyclability (>90% capacity retention after 1000 charge/discharge cycles). The LiFePO4/CNT microspheres are rather promising for high-power lithium ion batteries, and such an approach can be extended to prepare other high-performance electrode materials.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► Porous FePO4 microspheres with uniform carbon nanotube (CNT) embedded are prepared by a hydrothermal process. ► LiFePO4 microspheres with CNT networks (LiFePO4/CNT) are obtained and tested as the cathode material for lithium ion batteries. ► Our LiFePO4/CNT material displays both excellent volumetric Li storage properties and stable charge/discharge cyclability.