| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1287974 | Journal of Power Sources | 2013 | 8 Pages |
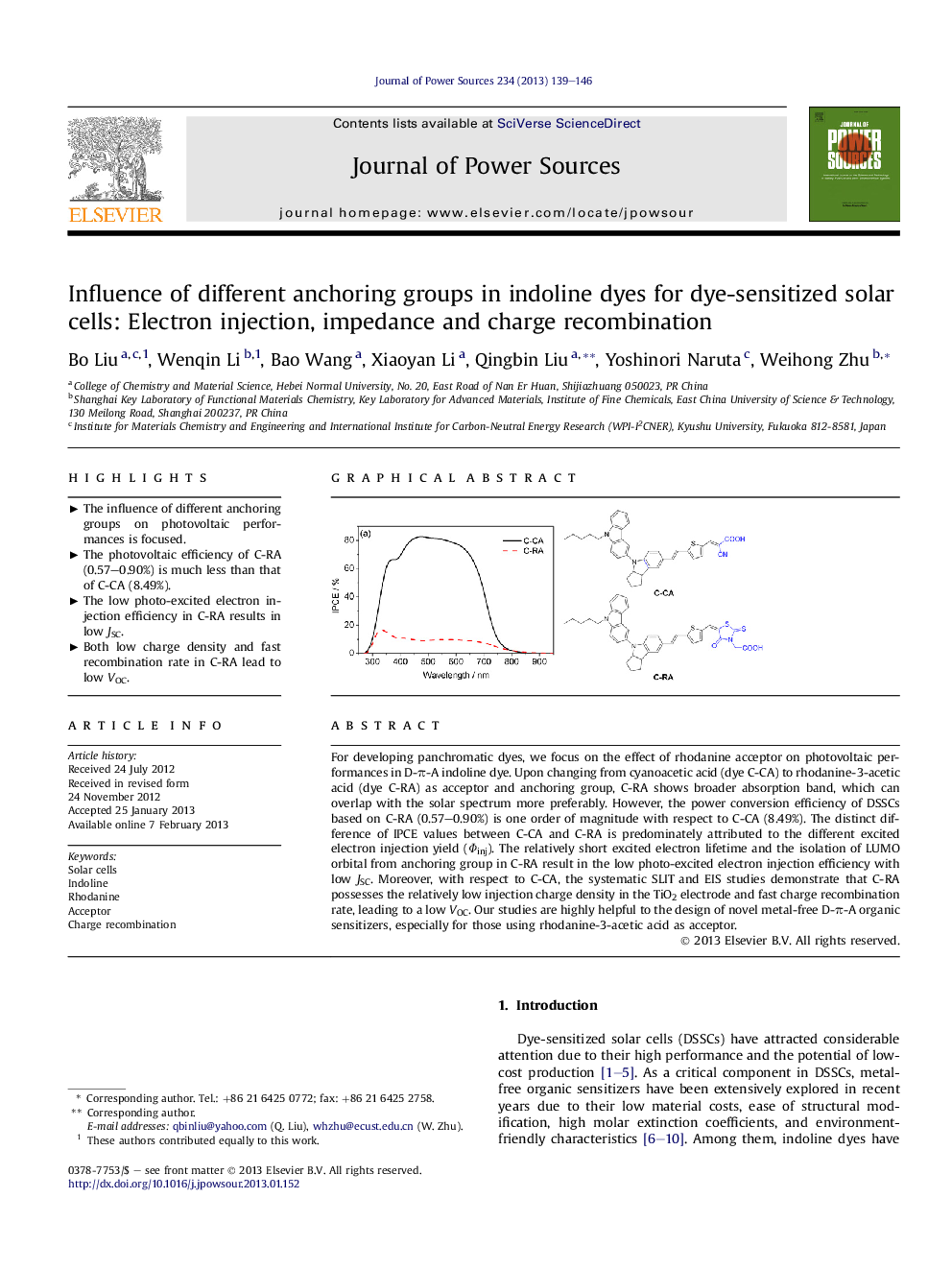
For developing panchromatic dyes, we focus on the effect of rhodanine acceptor on photovoltaic performances in D-π-A indoline dye. Upon changing from cyanoacetic acid (dye C-CA) to rhodanine-3-acetic acid (dye C-RA) as acceptor and anchoring group, C-RA shows broader absorption band, which can overlap with the solar spectrum more preferably. However, the power conversion efficiency of DSSCs based on C-RA (0.57–0.90%) is one order of magnitude with respect to C-CA (8.49%). The distinct difference of IPCE values between C-CA and C-RA is predominately attributed to the different excited electron injection yield (Φinj). The relatively short excited electron lifetime and the isolation of LUMO orbital from anchoring group in C-RA result in the low photo-excited electron injection efficiency with low JSC. Moreover, with respect to C-CA, the systematic SLIT and EIS studies demonstrate that C-RA possesses the relatively low injection charge density in the TiO2 electrode and fast charge recombination rate, leading to a low VOC. Our studies are highly helpful to the design of novel metal-free D-π-A organic sensitizers, especially for those using rhodanine-3-acetic acid as acceptor.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► The influence of different anchoring groups on photovoltaic performances is focused. ► The photovoltaic efficiency of C-RA (0.57–0.90%) is much less than that of C-CA (8.49%). ► The low photo-excited electron injection efficiency in C-RA results in low JSC. ► Both low charge density and fast recombination rate in C-RA lead to low VOC.