| Article ID | Journal | Published Year | Pages | File Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1288068 | Journal of Power Sources | 2013 | 5 Pages |
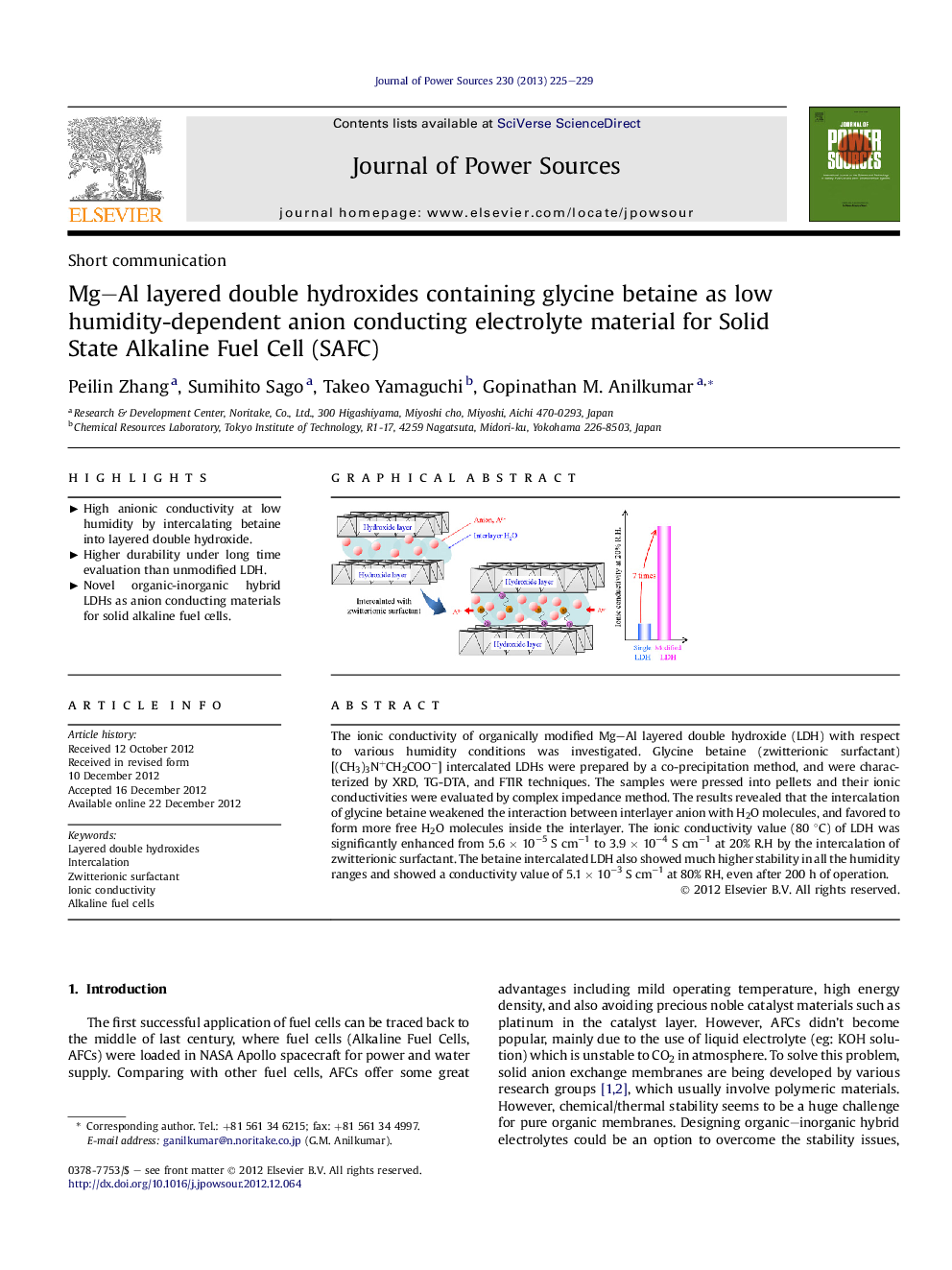
The ionic conductivity of organically modified Mg–Al layered double hydroxide (LDH) with respect to various humidity conditions was investigated. Glycine betaine (zwitterionic surfactant) [(CH3)3N+CH2COO−] intercalated LDHs were prepared by a co-precipitation method, and were characterized by XRD, TG-DTA, and FTIR techniques. The samples were pressed into pellets and their ionic conductivities were evaluated by complex impedance method. The results revealed that the intercalation of glycine betaine weakened the interaction between interlayer anion with H2O molecules, and favored to form more free H2O molecules inside the interlayer. The ionic conductivity value (80 °C) of LDH was significantly enhanced from 5.6 × 10−5 S cm−1 to 3.9 × 10−4 S cm−1 at 20% R.H by the intercalation of zwitterionic surfactant. The betaine intercalated LDH also showed much higher stability in all the humidity ranges and showed a conductivity value of 5.1 × 10−3 S cm−1 at 80% RH, even after 200 h of operation.
Graphical abstractFigure optionsDownload full-size imageDownload as PowerPoint slideHighlights► High anionic conductivity at low humidity by intercalating betaine into layered double hydroxide. ► Higher durability under long time evaluation than unmodified LDH. ► Novel organic-inorganic hybrid LDHs as anion conducting materials for solid alkaline fuel cells.